Abstract
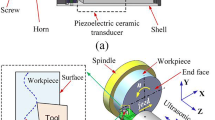
In this study, micro-dimples were prepared on a polyimide composite surface to obtain the dual benefits of polymer materials and surface texture. Micro-ultrasonic machining is employed for the first time for micro-dimple fabrication on polyimide composite surfaces. Surface textures of simple patterns were fabricated successfully with dimple depths of 150 μm, side lengths of 225-425 μm, and area ratios of 10-30%. The friction coefficient of the micro-dimple surfaces with side lengths of 325 or 425 μm could be increased by up to 100% of that of non-textured surfaces, alongside a significant enhancement of wear resistance. The results show that surface texturing of polyimide composite can be applied successfully to increase the friction coefficient and reduce wear, thereby contributing to a large output torque.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.S. Zhao, Ultrasonic Motor: Technologies and Applications, Science Press, Beijing, 2010, p 1–149
W. Qiu, Y. Mizuno, M. Tabaru, and K. Nakamura, Can Lubricant Enhance the Torque of Ultrasonic Motors? An Experimental Investigation, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 105, p 224102
T. Mashimo, Micro Ultrasonic Motor Using a Cube with a Side Length of 0.5 mm, IEEE ASME Trans. Mech., 2016, 21, p 1189–1192
Y.Y. Qu, Y.H. Zhang, and J.J. Qu, Micro-Driving Behavior of Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Resin for Standing-Wave Ultrasonic Motor, Polym. Compos., 2016, 37, p 2152–2159
Q.J. Ding, G. Zhao, H.M. Peng, Y.D. Zhang, and H.F. Li, Properties of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride)-Based Friction Materials of Ultrasonic Motors, Polym. Compos., 2016, 37, p 547–552
R.M. Tieck, G.P. Carman, and A. Novel Approach, A Novel Approach to Improving the Available Power Output of Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Motors, 2004 IMECE, Nov 13–20 (California), Am. Soc. Mech. Eng., 2004, 2004, p 941–948
P.G. Grutzmacher, A. Rosenkranz, and C. Gachot, How to Guide Lubricants: Tailored Laser Surface Patterns on Stainless Steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 370, p 59–66
M. Kang, Y.M. Park, B.H. Kim, and Y.H. Seo, Micro- and Nanoscale Surface Texturing Effects on Surface Friction, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 345, p 344–348
C. Lorenzo-Martin and O.O. Ajayi, Effect of Sic Particle Impact Nano-Texturing on Tribological Performance of 304L Stainless Steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 315, p 287–291
H.W. Yu, W. Huang, and X.L. Wang, Dimple Patterns Design for Different Circumstances, Lubr. Sci., 2013, 25, p 67–78
Z. Wang, Q. Zhao, C. Wang, and Y. Zhang, Modulation of Dry Tribological Property of Stainless Steel by Femtosecond Laser Surface Texturing, Appl. Phys. A, 2015, 119, p 1155–1163
S. Hammouti, B. Beaugiraud, M. Salvia, C. Mauclair, A. Pascale-Hamri, S. Benayoun, and S. Valette, Elaboration of Submicron Structures on PEEK Polymer by Femtosecond Laser, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 327, p 277–287
X.L. Chen, N.S. Qu, H.S. Li, and Z.Y. Xu, Pulsed Electrochemical Micromachining for Generating Micro-Dimple Arrays on a Cylindrical Surface with a Flexible Mask, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 343, p 141–147
R.V. Rao and V.D. Kalyankar, Optimization of Modern Machining Process Using Advanced Optimization Techniques: A Review, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2014, 73, p 1159–1188
Z.Y. Yu, K.P. Rajurkar, and A. Tandon, Study of 3D Micro-Ultrasonic Machining, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME, 2004, 126, p 727–732
H. Zarepour, S.H. Yeo, P.C. Tan, and E. Aligiri, A New Approach for Force Measurement and Workpiece Clamping in Micro-Ultrasonic Machining, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2011, 53, p 517–522
J.J. Boy, E. Andrey, A. Boulouize, and C. Khan-Malek, Developments in Microultrasonic Machining (MUSM) at FEMTO-ST, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2010, 47, p 37–45
W.L. Zhu, Y.Q. Xing, K.F. Ehmann, and B.F. Ju, Ultrasonic Elliptical Vibration Texturing of the Rake Face of Carbide Cutting Tools for Adhesion Reduction, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2016, 85, p 2669–2679
H.Y. Zhang, Y. Yan, Z.B. Gu, Y. Wang, and T. Sun, Friction Enhancement Between Microscopically Patterned Polydimethylsiloxane and Rabbit Small Intestinal Tract Based on Different Lubrication Mechanisms, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng., 2016, 2, p 900–907
Q.F. Wang, Y.X. Wang, H.L. Wang, N. Fan, and F.Y. Yan, Experimental Investigation on Tribological Behavior of Several Polymer Materials Under Reciprocating Sliding and Fretting Wear Conditions, Tribol. Int., 2016, 104, p 73–82
Acknowledgments
The work described in this study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, Grant 2015CB057502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, N.S., Zhang, T. & Chen, X.L. Surface Texturing of Polyimide Composite by Micro-Ultrasonic Machining. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 1369–1377 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3224-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3224-y