Abstract
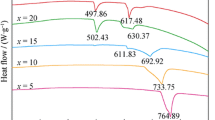
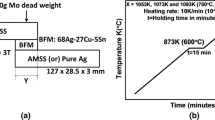
Mechanical alloying was used to prepare an Ag-Cu-Sn brazing alloy with the low amounts of intermetallic compounds. X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry were carried out to investigate the phase transformation of the as-milled samples. It seemed that the intermetallic compounds experienced the stage of synthesis-decomposition-resynthesis in the ball milling process. By controlling the ball milling time and tin contents, the solid solution phases of Ag (Cu, Sn) and Ag (Cu) were achieved in the 60Ag30Cu10Sn sample after milling for 40 h. Although the intermetallic compound will be generated during the brazing process, the improvement of their distributed morphology is beneficial for the good bonding interface of the joint with stainless steel substrate.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.L. Ma, S.B. Xue, and B. Wang, Study on Novel Ag-Cu-Zn-Sn Brazing Filler Metal Bearing Ga, J. Alloys compd., 2016, 688, p p854–862
J. Cao, L.X. Zhang, H.Q. Wang, L.Z. Wu, and J.C. Feng, Effect of Silver Content on Microstructure and Properties of Brass/Steel Induction Brazing Joint Using Ag-Cu-Zn-Sn Filler Metal, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2011, 27(4), p 377–381
Y. Liu., J. F. Xu, Q. Y. Zhai, and H. L. Liu, 低蒸汽压中温钎料研究进展 (Research Progress on Medium Temperature Brazing Alloys with Low Vapour Pressure), Foundry Technology. 2011, 32(10), 1435–1438 (in Chinese)
X. Ma, L.F. Li, Z. Zhang, H. Wang, E. Wang, and T. Qiu, Effects of Rare Earth La on Microstructure and Properties of Ag–21Cu–25Sn Alloy Ribbon Prepared by Melt Spinning, Mater. Des., 2015, 83, p 1–5
L.F. Li, T. Qiu, J. Yang, and Y.B. Feng, Effects of Rare Earth La on the Microstructure and Melting Property of (Ag-Cu28)-30Sn Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying, Rare Met., 2011, 30(1), p 49–52
M. Salehisaki, and M. Aryana, Effect of Microstructure on Corrosion Behavior of Ag-30Cu-27Sn Alloy Invitro Media, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 297, p 205–212
C.C. Koch, The Synthesis and Structure of Nanocrystalline Materials Produced by Mechanical Attrition: A Review, Nanostruct. Mater., 1993, 2, p p109–129
S. Sheibani, S. Heshmati-Manesh, and A. Ataie, Structural Investigation on Nano-crystalline Cu-Cr Supersaturated Solid Solution Prepared by Mechanical Alloying, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 495(1), p 59–62
F. Fang and M. He, Mechanical Alloying of Ag-Cu Immiscible Alloy System, J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Sci), 2006, E-11(1), p 84–87
O. Gingu, C. Nicolicescu, and G. Sima, Research of the Milling Time Influence On Ag-Cu Powder Particles Size Processed By Mechanical Alloying Route, Solid State Phenom., 2012, 188, p 382–387
L.F. Li, T. Qiu, J. Yang, and Y.B. Feng, Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Ag-Cu Supersaturated Solid Solution by Mechanical Alloying, Adv. Mater. Res., 2010, 92, p 271–276
L.F. Li, T. Qiu, J. Yang, and Y.B. Feng, Synthesis of Ag-Cu-Sn Nanocrystalline Alloys as Intermediate Temperature Solder by High Energy Ball Milling, Adv. Mater. Res., 2009, 79–82, p 449–452
D.K. Basri, L. Sisamouth, Y. Farazila, Y. Miyazawa, and T. Ariga, Brazeability and Mechanical Properties of Ag-Cu-Sn Brazing Filler Metals on Copper-Brazed Joint, Mater. Res. Innov., 2014, 18(S6), p p429–432
D.M. Jafarlou, E. Zalnezhad, M.A. Ezazi, N.A. Mardi, and M.A. Hassan, The Application of Equal Channel Angular Pressing to Join Dissimilar Metals, Aluminium Alloy and Steel, using an Ag-Cu-Sn Interlayer, Mater. Des., 2015, 87, p p553–566
J.P. Hammond, S.A. David, and J.J. Woodhouse, Process for Forming Unusually Strong Joints Between Metals and Ceramics by Brazing at Temperatures that do no Exceed 750 degree C., US 4621761 A
E. Ma and M. Atzmon, Calorimetric Evidence for Polymorphous Constraints on Metastable Zr-Al Phase Formation by Mechanical Alloying, J. Phys. Rev. Lett., 1991, 67(9), p 1126–1129
M. Oehringand and R. Bormann, NanocrystallineAlloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying and Ball Milling, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1991, 134, p 1330–1333
R.S. Maurya and T. Laha, Effect of Rare Earth and Transition Metal Elements on the Glass Forming Ability of Mechanical Alloyed Al-TM-RE Based Amorphous Alloys, J. Mater. Sci. Tech., 2015, 31(11), p 1118–1124
Q.Y. Zhang and H.S. Zhuang, Manual of the Ternary alloy phase diagrams, China Machine Press, Beijing, 2011
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Huaguang Advanced Welding Materials Co., LTD under Grant No. H131064.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Zheng, M., Wang, X. et al. Processing and Characterization of Ag-Cu-Sn Brazing Alloy Prepared by a Mechanical Alloying Method. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 1148–1153 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2930-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2930-1