Abstract
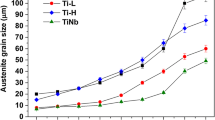
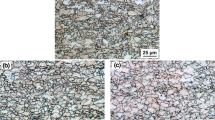
Four microalloyed samples were designed to study the effects of Ti and B additions on microstructures and mechanical properties. Experimental results show that the samples without B addition mainly contain well-developed pearlite and polygonal ferrite, whereas the B-containing samples consist of degenerated pearlite, polygonal ferrite, and Widmanstätten ferrite (WF). The B addition promotes the precipitation of the complex (Ti,Al,Nb)N and (Ti,Al,Nb)2CS phases during the hot-rolling process. Grain sizes are significantly refined by the combinations of undissolved (Ti,Al)N, (Ti,Al,Nb)N complex, (Ti,Al,Nb)2CS, and fine inclusions, which act as the nucleation sites of intragranular ferrite. The core of complex (Ti,Al,Nb)N precipitate is undissolved Ti-N-rich (Ti,Al)N phase, and the cap is Nb-N-rich (Nb,Ti)N phase. The property measurements show that the B addition enhances comprehensive properties of tensile strength and elongation, but decreases fracture toughness due to higher contents of the WF and subgrains.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.Y. Shin, K. Oh, S. Lee, and N.J. Kim, Correlation Study of Microstructure, Hardness, and Charpy Impact Properties in Heat Affected Zones of Three API, X80 Linepipe Steels Containing Complex Oxides, Met. Mater. Int., 2011, 17, p 29–40
R. Mendoza, J. Huante, M. Alanis, C. Gonzale-Rivera, and J.A. Juare-Islas, Processing of Ultra Low Carbon Steels with Mechanical Properties Adequate for Automotive Applications in the as-Annealed Condition, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2000, 276, p 203–209
J. Guo, C. Shang, S. Yang, H. Guo, X. Wang, and X. He, Weather Resistance of Low Carbon High Performance Bridge Steel, Mater. Des., 2009, 30, p 129–134
A. Avci, N. Lruya, M. Simsir, and A. Akdemir, Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Low-Carbon Steel-Plate-Reinforced Gray Cast Iron, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209, p 1410–1416
P.C.M. Rodrigues, E.V. Pereloma, and D.B. Santos, Mechanical Properties of a HSLA Bainitic Steel Subjected to Controlled Rolling with Accelerated Cooling, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2000, 283, p 136–143
R.D.K. Misra, H. Nathani, J.E. Hartmann, and F. Siciliano, Microstructural Evolution in a New 770 MPa Hot Rolled Nb-Ti Microalloyed Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, 394, p 339–352
H. Najafi, J. Rassizadehghani, and S. Norouzi, Mechanical Properties of As-Cast Microalloyed Steels Produced Investment Casting, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 656–663
S.R. Kulkarni, V.R. Selva, N.A. Phatak, S.K. Sexena, C.S. Zha, and T.E.I. Raghy, Study of Ti2SC Under Compression up to 47GPa, J. Alloys. Compd., 2008, 448, p L1–L4
G.K. Tirumalasetty, C.M. Fang, Q. Xu, J. Jansen, J. Sietsma, M.A. van Huis, and H.W. Zandbergen, Novel Ultrafine Fe(C) Precipitates Strengthen Transformation -Induced-Plasticity Steel, Acta Mater., 2012, 60, p 7160–7168
J.H. Shim, Y.W. Cho, S.H. Chung, J.D. Shim, and D.N. Lee, Nucleation of Intragranular Ferrite at Ti2O3 Particle in Low Carbon Steel, Acta Mater., 1999, 47, p 2751–2760
J.M. Gregg and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Solid-State Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite on Minerals Added to Molten Steel, Acta Mater., 1997, 45, p 739–748
K.E. Thelning, Steel and its Heat Treatment, Butterworths, New York, 1984, p 409–419
W.C. Leslic, The Physical Metallurgy of steels, McGraw-Hill International Book Company, New York, 1981, p 269–281
W. Stumpf and K. Banks, The Hot Working Characteristics of a Boron Bearing and a Conventional Low Carbon Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 418, p 86–94
B.M. Kapada, Hardenability Concepts with Application to Steel AIME, Warrendale, USA, 1978, p 448
J.E. Morral and J.B.B. Cameron, Hardenability Mechanisms, in B in Steel, Metall. Soc. AIME, 1980, 28, p 955
E. López-Chipres, I. Mejía, C. Maldonado, A. Bedoola-Jacuinde, and J.M. Cabrera, How Ductility Behavior of Boron Microalloyed Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2007, 460–461, p 464–470
D.A. Mortimer and M.G. Nicholas, Surface and Grain-Boundary Energies of AISI, 316 Stainless Steel in the Presence of Boron, Met. Sci., 1976, 10, p 326–332
J.E. Morral and J.B. Cameron, Model For Ferrite Nucleation Application to Boron Hardenability, Met. Trans. A., 1977, 8, p 1817–1819
W.D. Wang, S.H. Zhang, and X.L. He, Diffusion of Boron in Alloys, Acta Metall., 1995, 43, p 1693–1699
B. Hwang, D.W. Suh, and S.J. Kim, Austenitizing Temperature and Hardenability of Low-Carbon Steels, Scripta Mater., 2011, 64, p 1118–1120
L. Karlsson and H. Norden, Overview no. 63 Non-Equilibrium Grain Boundary Segregation of Boron in Austenitic Stainless Steel-II. Fine Scale Segregation Behavior, Acta Mater., 1988, 36, p 35–46
G. Xu, X. Gan, G. Ma, F. Luo, and H. Zou, The Development of Ti-Alloyed High Strength Microalloy Steel, Mater. Des., 2010, 31, p 2891–2896
H.L. Yi, L.X. Du, G.D. Wang, and X.H. Liu, Development of a As-Hot-Rolled Low Carbon Steel with High Yield Strength, ISIJ Int., 2006, 46, p 754–758
J. Hu, L.X. Du, J.J. Wang, and Q.Y. Sun, Cooling Process and Mechanical Properties Design of As-Hot-Rolled Low Carbon High Strength Microalloyed Steel for Automotive Wheel Usage, Mater. Des., 2014, 53, p 332–337
Y. Han, J. Shi, L. Xu, W.Q. Cao, and H. Dong, Effects of Ti Addition and Reheating Quenching on Grain Refinement and Mechanical Properties in Low Carbon Medium Manganese Martensitic Steel, Mater. Des., 2012, 34, p 427–434
A. Deva, B.K. Jha, and N.S. Mishra, Influence of Boron on Strain Hardening Behavior and Ductility of Low Carbon Hot Rolled Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2011, 528, p 7375–7380
J.R. Yang and L.C. Chang, The Effect of Stress on the Widmanstätten Ferrite Transformation, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1997, 223, p 158–167
J.W. Zhao, J.H. Lee, Y.W. Kim, Z.Y. Jiang, and C.S. Lee, Enhancing Mechanical Properties of a Low-Carbon Microalloyed Cast Steel by Controlled Heat Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, 559, p 427–435
G. Krauss, Steel: Processing, Structure, and Performance, Ohio, ASM International, 2005, p 109–111
H.R. Shercliff and M.F. Ashby, A Process Model for Age Hardening of Aluminium Alloys—II. Applications of the Model, Acta Mater., 1990, 38, p 1803–1812
R. Soto, W. Saikaly, X. Bano, C. Issartel, G. Rigaut, and A. Chara, Statistical and Theoretical Analysis of Precipitates in Dual-Phase Steels Microalloyed with Titanium and their Effect on Mechanical Properties, Acta Mater., 1990, 47, p 3475–3481
G.L. Dunlop, C.J. Carlsson, and G. Frimodig, Precipitation of VC in Ferrite and Pearlite During Direct Transformation of a Medium Carbon Microalloyed Steel, Met. Trans. A., 1978, 9, p 261–266
W. Saikaly, X. Bano, C. Issartel, G. Rigaut, L. Charria, and A. Chara, The Effects of Thermomechanical Processing on the Precipitation in an Industrial Dual-Phase Steel Microalloyed with Titanium, Met. Mater. Trans. A., 2001, 32, p 1939–1948
J. Hu, L.X. Du, and J.J. Wang, Effect of V on Intragranular Ferrite Nucleation of High Ti Bearing Steel, Scr. Mater., 2013, 68, p 953–956
R.Z. Valiev, A.V. Korznikov, and R.R. Mulyukov, Structure and Properties of Ultrafine-Grained Materials Produced by Severe Plastic Deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1993, 168, p 141–148
Y. Iwahashi, M. Furukawa, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, and T.G. Langdon, Microstructural Characteristics of Ultrafine-Grained Aluminum Produced Using Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, 29, p 2245–2252
P.B. Berbon, N.K. Tsenev, R.Z. Valiev, M. Furukawa, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, and T.G. Langdon, Fabrication of Bulk Ultrafine-Grained Materials Through Intense Plastic Straining, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, 29, p 2237–2243
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the key research project of Anhui Education Adminstration office (KJ2015A039) and the Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1608085QE102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Li, C. & Chen, W. Effects of Ti and B Addition on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Hot-Rolled High-Strength Nb-Containing Steels. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 3472–3481 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2181-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2181-6