Abstract
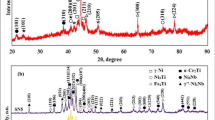
A Ni/Ti composite coating enhanced by an in situ synthesized TiN phase was fabricated on FV520B steel by plasma cladding technology. The in situ formation of the TiN phase was confirmed by XRD, SEM, and TEM. The cladding layer consisted of three regions on going from the top to the bottom, namely, columnar grain regions, columnar dendritic regions, and fine grain regions. The cladding layer was composed of Ni3Ti, TiN, (Fe, Ni), and Ti phases. The dendritic and columnar regions were mainly composed of the Ni3Ti and (Fe, Ni) phases. The Ti phase was observed at the branches of dendrite crystals and columnar grains. The volume fraction of the TiN phase in the cladding layer was about 3.2%. The maximum micro-hardness value of the in situ formed coating (760 HV0.2) was higher than that of the pure coating (537 HV0.2). The cladding layer had a small amount of scratch and wear debris when a load of 20 N was used. As the test load increased, the wear debris in the cladding layer also increased and the massive furrows were not observed.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q.Q. Zhou and Z.Y. Chun, Aging Process Optimization for a High Strength and Toughness of FV520B Martensitic Steel, Acta Metall. Sin., 2009, 45, p 1249–1254
F. Weng, C.Z. Chen, and H.J. Yu, Research Status of Laser Cladding on Titanium and its Alloy, Mater. Des., 2014, 58, p 412–425
X.D. Du, Y.F. Wang, K. Wang, and D.R. Xu, Microstructure and Wear Behaviour of WC-steel Composite Cladding, Mater. Technol., 2011, 26, p 90–95
J. Li, X. Luo, and G.J. Li, Effect of Y2O3 on the Sliding Wear Resistance of TiB/TiC-Reinforced Composite Coatings Fabricated by Laser Cladding, Wear, 2014, 310, p 72–82
G.J. Xu, M. Kutsuna, Z.J. Liu, and H. Zhang, Characteristics of Ni-based Coating Layer Formed by Laser and Plasma Cladding Processes, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, 417, p 1–2
P. Liu, W. Guo, H. Luo, Y. Zhang, and Y. Li, Surface Properties of In Situ Formed Ceramics and RE Reinforced Composite Coating, Mater. Technol., 2014, 29, p 36–39
P. Liu, B.Z. Zhao, Y.B. Zhang, and Y. Li, Research on Microstructures and Performance of Ni60–TiC–Mo Composite Coating on TA15 Titanium Alloy, Mater. Technol. Adv. Perform. Mater., 2012, 27, p 393–396
M. Das, K. Bhattacharya, S.A. Dittrick, C. Mandal, V.K. Balla, T.S.S. Kumar, A. Bandyopadhyay, and I. Manna, In Situ Synthesized TiB-TiN Reinforced Ti6Al4 V Alloy Composite Coatings: Microstructure, Tribological and In Vitro Biocompatibility, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed., 2014, 29, p 259–271
D.W. Zeng, C.S. Xie, and M.Q. Wang, In Situ Synthesis and Characterization of Fep/Cu Composite Coating on SAE 1045 Carbon Steel by Laser Cladding, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 344, p 357–364
J. Yang, D.D. Guo, L. Yu, L.M. Pan, T. Qiu, and J.X. Zhang, In Situ Synthesis Microstructure Mechanical Properties and Thermal Shock Resistance of (ZrB2 +SiC)/Zr2 [Al(Si)]4C5 Composites, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2014, 46, p 101–108
J.F. Nie, D.K. Li, E.Z. Wang, and X.F. Liu, In-Situ Synthesis of SiC Particles by the Structural Evolution of TiCx in Al–Simelt, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 613, p 407–412
X.X. Chu, R.J. Huang, H.H. Yang, Z.X. Wu, J.F. Lu, Y. Zhou, and L.F. Li, The Cryogenic Thermal Expansion and Mechanical Properties of Plasma Modified ZrW2O8 Reinforced Epoxy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 3367–3374
W.M. Sun, S.R. Jin, and X.L. Dong, Mechanism and Thermodynamic Calculation in Formation of Composite Ultrafine Ni-TiN Particles by “Active Plasma-Metal Reaction”, Acta Mater. Compos. Sin., 1999, 16, p 116–120 (in Chinese)
L.M. Zhang, D.B. Sun, H.Y. Yu, and H.Q. Li, Characteristics of Fe-Based Alloy Coating Produced by Plasma Cladding Process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 457, p 1–2
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2011CB013404), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51275105, 51375106), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M571391), Hei Long Jiang Postdoctoral Foundation (LBH-Z14050), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. HEUCF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, G., Li, Y., Cui, H. et al. Microstructure and Tribological Properties of In Situ Synthesized TiN Reinforced Ni/Ti Alloy Clad Layer Prepared by Plasma Cladding Technique. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 2412–2419 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2058-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2058-8