Abstract
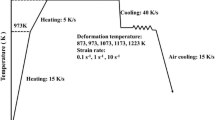
Hot deformation behavior of Nickel-based corrosion-resistant alloy (N08028) was studied in compression tests conducted in the temperature range of 1050-1200 °C and the strain rate range of 0.001-1 s−1. The flow stress behavior and microstructural evolution were observed during the hot deformation process. The results show that the flow stress increases with deformation temperature decreasing and strain rate increasing, and that the deformation activation energy (Q) is not a constant but increases with strain rate increasing at a given strain, which is closely related with dislocation movement. On this basis, a revised strain-dependent hyperbolic sine constitutive model was established, which considered that the “material constants” in the original model vary as functions of the strain and strain rate. The flow curves of N08028 alloy predicted by the proposed model are in good agreement with the experimental results, which indicates that the revised constitutive model can estimate precisely the flow curves of N08028 alloy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.Y. Sun, G. Liu, Q.D. Zhang, R. Li, and L.L. Wang, Determination of Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps of IN 028 Alloy Using Isothermal Hot Compression Test, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 595, p 92–98
A. Mirzaei, A. Zariei-Hanzaki, N. Haghdadi, and A. Marandi, Constitutive Description of High Temperature Flow Behavior of Sanicro-28 Super-Anstenitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 589, p 76–82
L. Wang, F. Liu, Q. Zuo, and C.F. Chen, Prediction of Flow Stress for N08028 Alloy Under Hot Working Conditions, Mater. Des., 2013, 47, p 737–745
L. Wang, F. Liu, J.J. Chen, Q. Zuo, and C.F. Chen, Hot Deformation Characteristics and Processing Map Analysis for Nickel-Based Corrosion Resistant Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 623, p 69–78
S.I. Kim and Y.C. Yoo, Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior of AISI, 304 Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 311, p 108–113
R. Ebrahimi, S.H. Zahiri, and A. Najafizadeh, Mathematical Modelling of the Stress-Strain Curves of Ti-IF Steel at High Temperature, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, 171, p 301–305
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, and J. Zhong, Effect of Temperature and Strain Rate on the Compressive Deformation Behavior of 42CrMo Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 205, p 308–315
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, and J. Zhong, Prediction of 42CrMo Steel Flow Stress at High Temperature and Strain Rate, Mech. Res. Commun., 2008, 35, p 142–150
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, and J. Zhong, Numerical Simulation for Stress/Strain Distribution and Microstructural Evolution in 42CrMo Steel During Hot Upsetting Process, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2008, 43, p 1117–1122
J.M. Cabrera, A.A.L. Omar, J.J. Jonas, and J.M. Prado, Modeling the Flow Behavior of a Medium Carbon Microalloyed Steel Under Hot Working Conditions, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, 28, p 2233–2244
N. Cabansa, N. Akdut, J. Penning, and B.C. DeConnman, High-Temperature Deformation Properties of Austenitic Fe-Mn Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, 37, p 3305–3315
A. Momeni, K. Dehghani, G.R. Ebrahimi, and H. Keshmiri, Modeling the Flow Curve Characteristics of 410 Martensitic Stainless Steel Under Hot Working Condition, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, 4, p 2898–2904
A. Momeni and K. Dehghani, Prediction of Dynamic Recrystallization Kinetics and Grain Size for 410 Martensitic Stainless Steel During Hot Deformation, Met. Mater. Int., 2010, 16, p 843–849
A. Momeni, K. Dehghani, M. Heidari, and M. Vaseghi, Modeling the Flow Curve of AISI, 410 Martensitic Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2012, 21, p 2238–2243
U. Kivisakk, A Test Method for Dewpoint Corrosion of Stainless Steels in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid, Corros. Sci., 2003, 45, p 485–495
L. Zhang, J.A. Szpunar, R.W. Basu, J.X. Dong, and M.C. Zhang, Influence of Cold Deformation on the Corrosion Behavior of Ni-Fe-Cr alloy 028, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 616, p 235–242
C.M. Sellars and W.J. Mc, Tegart, On the Mechanism of Hot Deformation, Acta Metall., 1966, 14, p 1136–1138
F.A. Slooff, J. Zhou, J. Duszczyk, and L. Katgerman, Constitutive Analysis of Wrought Magnesium Alloy Mg-Al4-Zn1, Scr. Mater., 2007, 57, p 759–762
D.H. Yu, Modeling High-Temperature Tensile Deformation Behavior of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy Considering Strain Effects, Mater. Des., 2013, 51, p 323–330
C.H. Liao, H.Y. Wu, S. Lee, F.J. Zhu, H.C. Liu, and C.T. Wu, Strain-Dependent Constitutive Analysis of Extruded AZ61Mg Alloy Under Hot Compression, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 4774–4782
Y.H. Li, D.D. Wei, J.D. Hu, Y.H. Li, and S.L. Chen, Constitutive Model for Hot Deformation Behavior if T24 Ferritic Steel, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2012, 53, p 425–430
D. Samatary, S. Mandal, and A.K. Bhaduri, Constitutive Analysis to Predict High Temperature Flow Stress in Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel, Mater. Des., 2010, 31, p 981–984
H. Dehghan, S.M. Abbasi, A. Momeni, and A. Karimi-Taheri, On the Constitutive Modeling and Microstructural Evolution of Hot Compressed A286 Iron-Base Superalloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 564, p 13–19
Y.C. Lin, D.X. Wen, J. Deng, G. Liu, and J. Chen, Constitutive Models for High-Temperature Flow Behavior of a Ni-Based Superalloy, Mater. Des., 2014, 59, p 115–123
Y.C. Lin, X.S. Chen, and J. Zhong, Constitutive Modeling for Elevated Temperature Flow Behavior of 42CrMo Steel, Compos. Mater. Sci., 2008, 42, p 470–477
S. Mandal, V. Rakesh, P.V. Sivaprasad, S. Venugopal, and K.V. Kasiviswanathan, Constitutive Equations to Predict High Temperature Flow Stress in a Ti-Modified Austenitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 500, p 114–121
X.N. Peng, H.Z. Guo, and A.F. Shi, C, Qin and Z.L. Zhao, Constitutive Equations for High Temperature Flow Stress of TC4-DT Alloy Incorporating Strain, Strain Rate and Temperature, Mater. Des., 2013, 50, p 198–206
D.G. Cram, H.S. Zurob, Y.J.M. Brechet, and C.R. Hutchinson, Modelling Discontinuous Dynamic Recrystallization Using a Physically Based Model for Nucleation, Acta Mater., 2009, 57, p 5218–5228
P. Bernard, S. Bag, K. Huang, and R.E. Loge, A Two-Site Mean Field Model of Discontinuous Dynamic Recrystallization, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 7357–7367
P.J. Zerilli and R.W. Armstring, Dislocation-Mechanics-Based Constitutive Relations for Material Dynamic Calculations, J. Appl. Mech., 1941, 8, p 77–91
S. Malinov and W. Sha, Application of Artificial Neural Networks for Modelling Correlations in Titanium Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 365, p 202–211
S. Mandal, P.V. Sivaprasad, and S. Venugopal, Capability of a Feed-Forward Artificial Neural Network to Predict the Constitutive Flow Behavior of As Cast 304 Stainless Steel Under Hot Deformation, J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 2007, 129, p 242–247
G.Z. Quan, W.Q. Lv, Y.P. Mao, Y.W. Zhang, and J. Zhou, Prediction of Flow Stress in a Wide Temperature Range Involving Phase Transformation for As-Cast Ti–6Al–2Zr–1Mo–1 V Alloy by Artificial Neural Network, Mater. Des., 2013, 50, p 51–61
G. Ji, F. Li, Q. Li, H. Li, and Z. Li, Prediction of the Hot Deformation Behavior for Aermet100 Steel Using an Artificial Neural Network, Comp. Mater. Sci., 2010, 48, p 626–632
B. Li, Q. Pan, and Z. Yin, Microstructural Evolution and Constitutive Relationship of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy Containing Small Amount of Sc and Zr During Hot Deformation Based on Arrhenius-type and Artificial Neural Network Models, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 584, p 406–416
Y.C. Lin and X.M. Chen, A Critical Review of Experimental Results and Constitutive Descriptions for Metals and Alloys in Hot Working, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 1733–1759
H.J. McQueen and N.D. Ryan, Constitutive Analysis in Hot Working, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 322, p 43–63
C.G. Shastry, P. Parameswaran, M.D. Mathew, K. Bhanu, S. Rao, and S.L. Mannan, The Effect of Strain Rate and Temperature on the Elevated Temperature Tensile Flow Behavior of Service-Exposed 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 465, p 109–115
D.X. Wen, Y.C. Lin, J. Chen, X.M. Chen, J.L. Zhang, and Y.J. Liang, Work-Hardening Behaviors of Typical Solution-Treated and Aged Ni-Based Superalloys During Hot Deformation, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 618, p 372–379
P. Wanjara, M. Jahazi, H. Monajati, S. Yue, and J.P. Immarigeon, Hot working Behavior of Near-α Alloy IMI834, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 396, p 50–60
Y.H. Liu, Z.K. Yao, Y.Q. Ning, Y. Nan, and H.Z. Guo, The Flow Behavior and Constitutive Equation in Isothermal Compression of FGH4096-GH4133B Dual Alloy, Mater. Des., 2014, 63, p 829–837
Z.N. Yang, F.C. Zhang, L. Qu, Z.G. Yan, Y.Y. Xiao, R.P. Liu, and X.Y. Zhang, Formation of Duplex Microstructure in Zr–2.3Nb Alloy and Its Plastic Behaviour at Various Strain Rates, Int. J. Plast., 2013, 54, p 163–177
ASTM E209, Standard Practice for Compression Tests of Metallic Materials at Elevated Temperatures with Conventional or Rapid Heating Rates and Strain Rates. Annual Book of ASTM Standard, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 2010
Y.Q. Cheng, H. Zhang, Z.H. Chen, and K.F. Xian, Flow Stress Equation of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Sheet During Warm Tensile Deformation, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2008, 208, p 29–34
D. Samantaray, S. Mandal, and A.K. Bhaduri, A Critical Comparison of Various Data Processing Methods in Simple Uni-axial Compression Testing, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 2797–2802
S. Mandal, M. Jayalakshmi, A.K. Bhaduri, and V.S. Sarma, Effect of Strain Rate on the Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior in a Nitrogen-Enhanced 316L(N), Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45, p 5646–5656
C. Zener and J.H. Hollomon, Effect of Strain Rate Upon Plastic Flow of Steel, J. Appl. Phys., 1944, 15, p 22–32
H. Mirazdeh, J.M. Cabrera, and A. Najafizadeh, Consitutive Relationships for Hot Deformation of Austenite, Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 6441–6448
M.E. Wahabi, J.M. Cabrera, and J.M. Prado, Hot Working of Two AISI, 304 Steels: A Comparative Study, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 343, p 116–125
M. Aghaie-Khafri and F. Adhami, Hot Deformation of 15-5 PH Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 1052–1057
E.X. Pu, W.J. Zheng, J.Z. Xiang, Z.G. Song, and J. Li, Hot Deformation Characteristics and Processing Map Analysis of Superaustenitic Stainless Steel S32654, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 598, p 174–182
W.S. Lee and C.Y. Liu, The Effects of Temperature and Strain Rate on the Dynamic Flow Behavior of Different Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 426, p 101–113
S. Srinivasulu and A. Jain, A Comparative Analysis of Training Methods for Artificial Neural Network Rainfall-Runoff Models, Appl. Soft Comput., 2006, 6, p 295–306
P. Zhang, C. Hua, Q. Zhu, C.Q. Ding, and H.Y. Qin, Hot Compression Deformation and Constitutive Modeling of GH4698 alloy, Mater. Des., 2015, 62, p 1153–1160
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the financial support of the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2011CB610403), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51134011 and 51431008), the China National Funds for Distinguished Young Scientists (No. 51125002), and the Fundamental Research Fund of Northwestern Polytechnical University (No. JC20120223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Liu, F., Cheng, J.J. et al. Arrhenius-Type Constitutive Model for High Temperature Flow Stress in a Nickel-Based Corrosion-Resistant Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 1394–1406 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1986-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1986-7