Abstract
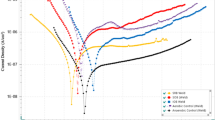
Microbially induced corrosion (MIC) poses significant threats to reliability and safety of engineering materials and structures. While most MIC studies focus on prokaryotic bacteria such as sulfate-reducing bacteria, the influence of fungi on corrosion behaviors of metals has not been adequately reported. In this study, 304 stainless steel and titanium were exposed to two very common fungi, Paecilomyces variotii, Aspergillus niger and their mixtures under highly humid atmosphere. The initial corrosion behaviors within 28 days were studied via scanning Kelvin probe, which showed marked surface ennoblement and increasingly heterogeneous potential distribution upon prolonged fungus exposure. Using stereomicroscopy, fungus growth as well as corrosion morphology of 304 stainless steel and titanium were also evaluated after a long-term exposure for 60 days. The presence of fungi decreased the corrosion resistance for both 304 stainless steel and titanium. Titanium showed higher resistance to fungus growth and the induced corrosion. Exposure to the mixed strains resulted in the highest fungus growth rate but the mildest corrosion, possibly due to the decreased oxygen level by increased fungal activities.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.A. Videla and L.K. Herrera, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion: Looking to the Future, Int. Microbiol., 2005, 8, p 169
D. Walsh, D. Pope, M. Danford, and T. Huff, The Effect of Microstructure on Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion, JOM, 1993, 45, p 22–30
B.J. Little and J.S. Lee, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion: An Update, Int. Mater. Rev., 2014, 59, p 384–393
J. Xu, K. Wang, C. Sun, F. Wang, X. Li, J. Yang, and C. Yu, The Effects of Sulfate Reducing Bacteria on Corrosion of Carbon Steel Q235 Under Simulated Disbonded Coating by Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53, p 1554–1562
Z.H. Dong, W. Shi, H.M. Ruan, and G.A. Zhang, Heterogeneous Corrosion of Mild Steel Under SRB-Biofilm Characterised by Electrochemical Mapping Technique, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53, p 2978–2987
X. Wang, J. Xu, and C. Sun, Effects of Sulfate-Reducing Bacterial on Corrosion of 403 Stainless Steel in Soils Containing Chloride Ions, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2013, 8, p 821–830
J. Duan, S. Wu, X. Zhang, G. Huang, M. Du, and B. Hou, Corrosion of Carbon Steel Influenced by Anaerobic Biofilm in Natural Seawater, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 54, p 22–28
M. Stipaničev, F. Turcu, L. Esnault, E.W. Schweitzer, R. Kilian, and R. Basseguy, Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel in Presence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in Seawater Environment, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 113, p 390–406
M.A. Shirakawa, I. Beech, R. Tapper, M. Cincotto, and W. Gambale, The Development of a Method to Evaluate Bioreceptivity of Indoor Mortar Plastering to Fungal Growth, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegr., 2003, 51, p 83–92
I.-U. Haq, S. Ali, and M. Qadeer, Influence of Dissolved Oxygen Concentration on Intracellular pH for Regulation of Aspergillus niger Growth Rate During Citric Acid Fermentation in a Stirred Tank Bioreactor, Int. J. Biol. Sci., 2005, 1, p 34
Y. Li, L. Wadsö, L. Larsson, and J. Bjurman, Correlating Two Methods of Quantifying Fungal Activity: Heat Production by Isothermal Calorimetry and Ergosterol Amount by Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry, Thermochim. Acta, 2007, 458, p 77–83
C.J. McNamara, T.D. Perry IV, R. Leard, K. Bearce, J. Dante, and R. Mitchell, Corrosion of Aluminum Alloy 2024 by Microorganisms Isolated from Aircraft Fuel Tanks, Biofouling, 2005, 21, p 257–265
M. Stoica, M. Brumă, and G. Cârâc, Electrochemical Study of AISI, 304 Stainless Steel During the Exposure at the Disinfectant Solutions with Fungal Suspensions, Mater. Corros., 2010, 61, p 1017–1025
E. Juzeliūnas, R. Ramanauskas, A. Lugauskas, K. Leinartas, M. Samulevičienė, A. Sudavičius, and R. Juškėnas, Microbially Influenced Corrosion of Zinc and Aluminium—Two-Year Subjection to Influence of Aspergillus niger, Corros. Sci., 2007, 49, p 4098–4112
S. Yuan and S. Pehkonen, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel by Aerobic Pseudomonas NCIMB 2021 Bacteria: AFM and XPS study, Colloid Surf. B, 2007, 59, p 87–99
T. Wu, J. Xu, M. Yan, C. Sun, C. Yu, and W. Ke, Synergistic Effect of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Elastic Stress on Corrosion of X80 Steel in Soil Solution, Corros. Sci., 2014, 83, p 38–47
E. Lunarska, J. Birn, and P. Domżalicki, Hydrogen Uptake by Structural Steels at Cathodic Protection in Sea Water Inoculated with Sulfate Reducing Bacteria, Mater. Corros., 2007, 58, p 13–19
H.A. Videla and L.K. Herrera, Understanding Microbial Inhibition of Corrosion. A Comprehensive Overview, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegr., 2009, 63, p 896–900
C. Xu, Y. Zhang, G. Cheng, and W. Zhu, Localized Corrosion Behavior of 316L Stainless Steel in the Presence of Sulfate-Reducing and Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 443, p 235–241
B. Little and R. Ray, A Review of Fungal Influenced Corrosion, Corros. Rev., 2001, 19, p 401–418
S. Day, M. Whalen, K. King, G. Hust, L. Wong, J. Estill, and R. Rebak, Corrosion Behavior of Alloy 22 in Oxalic Acid and Sodium Chloride Solutions, Corrosion, 2004, 60, p 804–814
N. Muthukumar, A. Rajasekar, S. Ponmariappan, S. Mohanan, S. Maruthamuthu, S. Muralidharan, P. Subramanian, N. Palaniswamy, and M. Raghavan, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion in Petroleum Product Pipelines—A Review, Indian J. Exp. Biol., 2003, 41, p 1012–1022
C. Galhaup and D. Haltrich, Enhanced Formation of Laccase Activity by the White-Rot Fungus Trametes pubescens in the Presence of Copper, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2001, 56, p 225–232
Z.-S. Wang, Y.-X. Gu, and Q.-S. Yuan, Effect of Nutrition Factors on the Synthesis of Superoxide Dismutase, Catalase, and Membrane Lipid Peroxide Levels in Cordyceps militaris Mycelium, Curr. Microbiol., 2006, 52, p 74–79
D.J. Kosman, Iron Metabolism in Aerobes: Managing Ferric Iron Hydrolysis and Ferrous Iron Autoxidation, Coordin. Chem. Rev., 2013, 257, p 210–217
B. Little, P. Wagner, and F. Mansfeld, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Metals and Alloys, Int. Mater. Rev., 1991, 36, p 253–272
N. Muthukumar, S. Mohanan, S. Maruthamuthu, P. Subramanian, N. Palaniswamy, and M. Raghavan, Role of Brucella sp. and Gallionella sp. in Oil Degradation and Corrosion, Electrochem. Commun., 2003, 5, p 421–425
J. Liao, H. Fukui, T. Urakami, and H. Morisaki, Effect of Biofilm on Ennoblement and Localized Corrosion of Stainless Steel in Fresh Dam-Water, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 1393–1403
W. Wang, P.E. Jenkins, and Z. Ren, Electrochemical Corrosion of Carbon Steel Exposed to Biodiesel/Simulated Seawater Mixture, Corros. Sci., 2012, 57, p 215–219
S. Chen, P. Wang, and D. Zhang, Corrosion Behavior of Copper Under Biofilm of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Corros. Sci., 2014, 87, p 407–415
H. Lin and G. Frankel, Atmospheric Corrosion of Cu During Constant Deposition of NaCl, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2013, 160, p C336–C344
M. Stratmann and H. Streckel, The Investigation of the Corrosion of Metal Surfaces, Covered with Thin Electrolyte Layers—A New Experimental Technique, Berich. Bunsen Gesell., 1988, 92, p 1244–1250
M. Rohwerder, G.S. Frankel, M. Stratmann, P. Leblanc, Application of Scanning Kelvin Probe in Corrosion Science, Analytical Methods in Corrosion Science and Engineering, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2005, p 605–648
W. Wang, X. Zhang, and J. Wang, Heterogeneous Electrochemical Characteristics of Biofilm/Metal Interface and Local Electrochemical Techniques Used for This Purpose, Mater. Corros., 2009, 60, p 957–962
M. Sun, K. Xiao, C. Dong, X. Li, and P. Zhong, Electrochemical and Initial Corrosion Behavior of Ultrahigh Strength Steel by Scanning Kelvin Probe, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22, p 815–822
J. Qiu, Passivity and Its Breakdown on Stainless Steels and Alloys, Surf. Interface Anal., 2002, 33, p 830–833
B.J. Little, J.S. Lee, and R.I. Ray, The Influence of Marine Biofilms on Corrosion: A Concise Review, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 54, p 2–7
A. Bressel, J.W. Schultze, W. Khan, G.M. Wolfaardt, H.P. Rohns, R. Irmscher, and M.J. Schöning, High Resolution Gravimetric, Optical and Electrochemical Investigations of Microbial Biofilm Formation in Aqueous Systems, Electrochim. Acta, 2003, 48, p 3363–3372
C. Marconnet, C. Dagbert, M. Roy, and D. Féron, Stainless Steel Ennoblement in Freshwater: From Exposure Tests to Mechanisms, Corros. Sci., 2008, 50, p 2342–2352
C. Dong, H. Luo, K. Xiao, Y. Ding, P. Li, and X. Li, Electrochemical Behavior of 304 Stainless Steel in Marine Atmosphere and Its Simulated Solution, Anal. Lett., 2013, 46, p 142–155
F.N. Afshar, J. de Wit, H. Terryn, and J. Mol, Scanning Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy as a Means of Predicting the Electrochemical Characteristics of the Surface of a Modified AA4xxx/AA3xxx (Al Alloys) Brazing Sheet, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 88, p 330–339
I.B. Beech and J. Sunner, Biocorrosion: Towards Understanding Interactions Between Biofilms and Metals, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2004, 15, p 181–186
Y. Duan, S.-M. Li, J. Du, and J.-H. Liu, Corrosion Behavior of Q235 Steel in the Presence of Pseudomonas and Iron Bacteria, Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2010, 26, p 3203–3211
N.O. San, H. Nazır, and G. Dönmez, Evaluation of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Inhibition on Ni-Co Alloy Coatings by Aeromonas salmonicida and Clavibacter michiganensis, Corros. Sci., 2012, 65, p 113–118
A. Jayaraman, E.T. Cheng, J.C. Earthman, and T.K. Wood, Importance of Biofilm Formation for Corrosion Inhibition of SAE 1018 Steel by Axenic Aerobic Biofilms, J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 1997, 18, p 396–401
A. Jayaraman, J.C. Earthman, and T.K. Wood, Corrosion Inhibition by Aerobic Biofilms on SAE 1018 Steel, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 1997, 47, p 62–68
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51401018), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program Project, No. 2014CB643300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
a) 304 stainless steel and b) titanium surfaces after 28 days of exposure to nutrient solution (TIFF 776 kb)
Figure S2
EDS analyses on a) bare surface and b) corrosion product of 304 stainless steel exposed to P. variotii (TIFF 895 kb)
Figure S3
EDS analyses on a) bare surface and b) corrosion product of 304 stainless steel exposed to A. niger (TIFF 860 kb)
Figure S4
Potential distribution on bare surfaces of a) 304 stainless steel and b) titanium; c) Gaussian fitting curve of potential distribution on bare stainless steel (TIFF 280 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Zhou, F., Xiao, K. et al. Microbially Influenced Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel and Titanium by P. variotii and A. niger in Humid Atmosphere. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 24, 2688–2698 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1558-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1558-2