Abstract
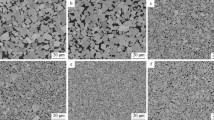
The initial WC grain-size distribution, as one of the most important factors influencing the properties of alloys, has been focused on for a long time in some fields other than cemented carbides. In the present work, five groups of WC-6Ni cemented carbides were prepared and the effect of initial WC grain-size distribution on the microstructure and properties of the hard alloys was studied. The results indicate that initial WC grain-size distribution has significant influence on the microstructure and properties of WC-6Ni cemented carbides, except density. When the mass ratio of coarse-WC and fine-WC is 7:3, WC-6Ni cemented carbide samples with initial WC grain-size distribution of WC-1(4.8 μm) and WC-4(0.7 μm) show a relatively good combination properties, while the cemented carbide samples with WC-5(0.4 μm) as the fine-WC component exhibit higher values on some properties, mainly hardness and immersion corrosion resistance in acid and alkali.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Bonny, P. De Baets, J. Van Wittenberghe, Y. Perez Delgado, J. Vleugels, O. Vander Biest, and B. Lauwers, Influence of Electrical Discharge Machining on Sliding Friction and Wear of WC-Ni Cemented Carbide, Tribol Int., 2010, 43, p 2333–2344
A.D. Krawitz, E.F. Drake, and B. Clausen, The Role of Residual Stress in the Tension and Compression Response of WC-Ni, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 3595–3601
E.O. Correa, J.N. Santos, and A.N. Klein, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of WC Ni-Si Based Cemented Carbides Developed by Powder Metallurgy, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2010, 28, p 572–575
S. Imasato, K. Tokumoto, T. Kitada, and S. Sakaguchi, Properties of Ultra-Fine Binderless Cemented Carbide RCCFN, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 1995, 13, p 305–312
K.H. Shi, K.C. Zhou, Z.Y. Li, X.Q. Zan, S.Z. Xu, and Z.Y. Min, Effect of Adding Method of Cr on Microstructure and Properties of WC-9Ni-2Cr Cemented Carbides, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2013, 38, p 1–6
H. Engqvist, G.A. Botton, N. Axdn, and S. Hogmark, A Study of Grain Boundaries in a Binderless Cemented Carbide, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 1998, 16, p 309–313
K. Mannesson, I. Borgh, A. Borgenstam, and J. Ågren, Abnormal Grain Growth in Cemented Carbides: Experiments and Simulations, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2011, 29, p 488–494
K. Mannesson, J. Jeppsson, A. Borgenstam, and J. Ågren, Carbide Grain Growth in Cemented Carbides, Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 1912–1923
H. Saito, A. Iwabuchi, and T. Shimizu, Effects of Co Content and WC Grain Size on Wear of WC Cemented Carbide, Wear, 2006, 261, p 126–132
J.H. Xi, Y.J. Xie, G.C. Yao, and Y.H. Liu, Effect of Grain Composition on Properties of Inert Anodes, J. Funct. Mater., 2007, 3, p 393–396 (in Chinese)
H. Huang, Particle Grade Technique and Application on Energetic Materials, Energ. Mater., 2001, 9, p 161–164 (in Chinese)
H.W. Ouyang, Y. Liu, H.B. Wang, and B.Y. Huang, Calculation Method for Random Packing of Sphere Particles, Mater. Sci. Eng. Powder Metal., 2002, 7, p 87–92 (in Chinese)
M.M. Khruschov, Resistance of Metals to Wear by Abrasion as Related to Hardness. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Lubrication and Wear, 1957 (London), p 655–659.
B.Q. Sun, Study of Strength and Structure of WC-Co Hard Alloy(II), Rare Met. Cem. Carbides, 2004, 32, p 29–34 (in Chinese)
J. Gurland, The Fracture Strength of Sintered Tungsten Carbide-Cobalt Alloys in Relation to Composition and Particle Spacing, Trans. TMS, 1963, 227, p p1146
C.H. Yi, H.Y. Fan, J. Xiong, Z.X. Guo, G.B. Dong, W.C. Wan, and H.S. Chen, Effect of WC Content on the Microstructures and Corrosion Behavior of Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets, Ceram. Int., 2013, 39, p 503–509
E.J. Wentzel and C. Allen, Erosion-Corrosion Resistance of Tungsten Carbide Hard Metals with Different Binder Compositions, Wear, 1995, 181–183, p 63–69
S. Hochstrasser-Kurz, Y. Mueller, C. Latkoczy, S. Virtanen, and P. Schmutz, Analytical Characterization of the Corrosion Mechanisms of WC-Co by Electrochemical Methods and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectroscopy, Corros. Sci., 2007, 49, p 2002–2020
S. Sutthiruangwonga, G. Moria, and R. Kösters, Passivity and Pseudopassivity of Cemented Carbides, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2005, 23, p 129–136
Acknowledgments
Mr K. L. Dong and Q. Jiang of Zi Gong Cemented Carbide Corporation Limited are acknowledged by their support with specimen preparation. Thanks to Ms C. L. Chen and X. M. Li from the same company for the help in microstructure observation and property test.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Kh., Zhou, Kc., Li, Zy. et al. Optimization of Initial WC Grain-Size Distribution in WC-6Ni Cemented Carbides. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 23, 3222–3228 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1117-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1117-2