Abstract
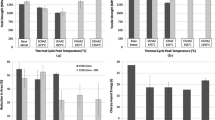
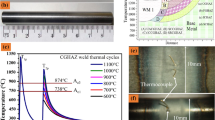
The behaviour of γ’ phase to thermal and mechanical effects during rapid heating of Astroloy, a powder metallurgy nickel-based superalloy has been investigated. The thermo-mechanical-affected zone (TMAZ) and heat-affected zone (HAZ) microstructures of an inertia friction welded (IFW) Astroloy were simulated using a Gleeble thermo-mechanical simulation system. Detailed microstructural examination of the simulated TMAZ and HAZ and those present in actual IFW specimens showed that γ’ particles persisted during rapid heating up to a temperature where the formation of liquid is thermodynamically favored and subsequently re-solidified eutectically. The result obtained showed that forging during the thermo-mechanical simulation significantly enhanced resistance to weld liquation cracking of the alloy. This is attributable to strain-induced rapid isothermal dissolution of the constitutional liquation products within 150 μm from the center of the forged sample. This was not observed in purely thermally simulated samples. The microstructure within the TMAZ of the as-welded alloy is similar to the microstructure in the forged Gleeble specimens.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.H. Haakens and J.H.G. Matthey, New Approach to the Weldability of Nickel-Base as Cast and Powder Metallurgy Superalloys, Weld. J., 1982, 61, p 25–30
W.A. Owczarski, D.S. Duvall, and C.P. Sullivan, Model for Heat-Affected Zone Cracking in Nickel-Base Superalloys, Weld. J., 1966, 45(4), p 145–155
J.J. Pepe and W.F. Savage, Effects of Constitutional Liquation in 18-Ni Maraging Steel Weldment, Weld. J., 1967, 46(9), p S411
O.A. Ojo, N.L. Richards, and M.C. Chaturvedi, Liquid Film Migration of Constitutionally Liquated Gamma ‘ in Weld Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) of Inconel 738LC Superalloy, Scr. Mater., 2004, 51(2), p 141–146
O.A. Ojo and M.C. Chaturvedi, On the Role of Liquated γ’ Precipitates in Weld Heat Affected Zone Microfissuring of a Nickel-Based Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 403(1–2), p 77–86
M. Preuss, P.J. Withers, J.W.L. Pang, and G.J. Baxter, Residual Stresses in Inertia Friction Welded Aero Engine Materials, ISIS, Science Highlights, 2003, p 1–3
T.L. Oberle, C.D. Loyd, and M.R. Calton, Inertia Welding Dissimilar Metals, Weld. J., 1967, 46(6), p 511–516
Y.C. Kim, A. Fuji, and T.H. North, Residual-Stress and Plastic Strain in AISI, 304L Stainless-Steel Titanium Friction Weld, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1995, 11(4), p 383–388
A.D. Romig, Jr., J.C. Lippold, and M.J. Cieslak, Analytical Electron Microscope Investigation of the Phase Transformations in a Simulated Heat-Affected Zone in Alloy 800, Metall. Trans. A, 1988, 19A(1), p 35–50
O. Reiso, N. Ryum, and J. Strid, Melting of Secondary-Phase Particles in Al–Mg–Si Alloys, Metall. Trans. A, 1993, 24(12), p 2629–2641
B. Radhakrishnan and R.G. Thompson, Phase Diagram Approach to Study Liquation Cracking in Alloy 718, Metall. Trans. A, 1991, 22A(4), p 887–902
L. Wang, M. Preuss, P.J. Withers, G. Baxter, and P. Wilson, Energy-Input-Based Finite Element Process Modeling of Inertia, Weld. Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2005, 36(4), p 513–523
M. Soucail and Y. Bienvenu, Dissolution of the Phase in a Nickel Base Superalloy at Equilibrium and under Rapid Heating, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, 220A, p 215–222
B. Radhakrishnan and R.G. Thompson, Liquid-Film Migration (LFM) in the Weld Hea Affected Zone (HAZ) Of A Ni-Base Superalloy, Scr. Metall. Mater., 1990, 24(3), p 537–542
S.W. Barker and G.R. Purdy, On Liquid Film Migration in Aluminium-Copper Alloys, Acta Mater., 1998, 46(2), p 511–524
R. Nakkalil, N.L. Richards, and M.C. Chaturvedi, Influence of Solidification Mode on Heat Affected Zone Microfissuring in a Nickel–Iron Base Superalloy, Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, 41(12), p 3381–3392
R. Hultgren, P.D. Desai, D.T. Hawkins, M. Gleiser, and K.K. Kelly, Selected Values of the Thermodynamic Properties of Binary Alloys, USA, Vol 192. American Society for Metals, Metals Park, 1973
D. Shahriari, M.H. Sadeghi, A. Akbarzadeh, and M. Cherraghzadeh, The Influence of Heat Treatment and Hot Deformation Conditions on Gamma’ Precipitate Dissolution of Nimonic 115 Superalloy, International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 45, p 841–850
L.X. Zhou and T.N. Baker, Effects of Strain-Rate and Temperature on Deformation Behavior of IN 718 during High-Temperature Deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1994, 177, p 1–9
A.R. Mashreghi, H. Monajatizadeh, M. Jahazi, and S. Yue, High Temperature Deformation of Nickel Base Superalloy Udimet 520, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2004, 20, p 161–166
S.I. Oh, S.L. Semiatin, and J.J. Jonas, An Analysis of the Isothermal Hot Compression Test, Metall. Trans. A, 1992, 23, p 963–975
S.C. Medeiros, W.G. Frazier, and Y. Prasad, Hot Deformation Mechanisms in a Powder Metallurgy Nickel-Base Superalloy IN 625, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, 31, p 2317–2325
M.C. Somani, K. Muraleedharan, Y. Prasad, and V. Singh, Mechanical Processing and Microstructural Control in Hot Working of Hot Isostatically Pressed P/M IN-100 Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 245, p 88–99
F.S. Buffington and M. Cohen, Self-Diffusion in Alpha-Iron under Uniaxial Compressive Stress, Trans. AIME, 1952, 194, p 859–860
A.F. Forestieri and L.A. Girifalco, The Effect of Plastic Deformation on Self-Diffusion in Silver, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1959, 10, p 99–105
T. Watanabe and S. Karashim, On the Strain-Enhanced Diffusion of α-Iron, Phys. Status Solidi, 1970, 42, p 749–756
T. Watanabe and S. Karashim, An Analysis of High Temperature Creep in Alpha Iron Based on Super Jog Mechanism, Trans. Jpn. Inst. Metals, 1970, 11, p 159–163
V.G. Gavriljuk, Decomposition of Cementite in Pearlitic Steel Due to Plastic Deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 345, p 81–89
A. Seeger, The Generation of Lattice Defects by Moving Dislocations, and its Application to the Temperature Dependence of the Flow-Stress of FCC Crystals, Philos Mag., 1955, 46, p 1194–1217
http://www.bss.phy.cam.ac.uk/~amd3/teaching/A_Donald/Crystalline_solids_2.htm. Retrieved 20-10-2011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oluwasegun, K.M., Olawale, J.O., Ige, O.O. et al. Microstructural Characterization of Thermomechanical and Heat-Affected Zones of an Inertia Friction Welded Astroloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 23, 2834–2846 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1067-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1067-8