Abstract
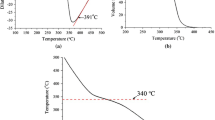
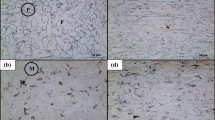
The mechanical properties of ultrafine lath-shaped low-carbon steel plates were studied. Results indicated that the hardness and tensile strength of the conventional low-carbon steel are HRC 19 and 410 MPa, respectively. With the decreased grain size of the ultrafine lath-shaped steel plates, the hardness and tensile strength of the test samples rapidly increase. Mechanical properties are at their optimum when grain size reaches 90 nm. Furthermore, both the hardness and the tensile strength values reach their maximum, which are HRC 53.5 and 1217 MPa, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Okayasu, K. Sato, M. Mizuno, D.Y. Hwang, and D.H. Shin, Fatigue Properties of Ultra-Fine Grained Dual Phase Ferrite/Martensite Low Carbon Steel, Int. J. Fatigue, 2008, 30(8), p 1358–1365
G. Salishchev, R. Zaripova, R. Galeev, and O. Valiakhmetov, Nanocrystalline Structure Formation During Severe Plastic Deformation in Metals and Their Deformation Behaviour, Nanostruct. Mater., 1995, 6(5–8), p 913–916
N. Tsuji, R. Ueji, Y. Minamino, and Y. Saito, A New and Simple Process to Obtain Nano-Structured Bulk Low-Carbon Steel with Superior Mechanical Property, Scripta Mater., 2002, 46(4), p 305–310
N. Tsuji, Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, and S. Tanigawa, Ultra-fine Grained Bulk Steel Produced by Accumulative Roll-Bonding (ARB) Process, Scripta Mater., 1999, 40(7), p 795–800
C.Y. Yu and L. Liu, Quenching Cooling and Quenching media, Liaoning Science and Technology Press, Shenyang, 2010 (in Chinese)
J.R. Tarpani, W.W. Bose Filho, and D. Spinelli, Grain size Effects in the Quasi-Static Fracture Resistance of a Thermally Embrittled RPV Steel (Annealed Microstructures), J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2002, 11(4), p 414–421
A. Shafiei Mohammadabadi and K. Dehghani, A New Model for Inverse Hall-Petch Relation of Nanocrystalline Materials, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2008, 17(5), p 662–666
J.E. Schaffer, Structure-Property Relationships in Conventional and Nanocrystalline NiTi Intermetallic Alloy Wire, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2009, 18(5), p 582–587
K.T.V. Rao and R.O. Ritchie, Mechanical Properties of Al–Li Alloys. I. Fracture Toughness and Microstructure, Mater. Sci. Technol. Lond, 1989, 5(9), p 882–895
J. Cui, Y. Fu, N. Li, J. Sun, J. He, and Y. Dai, Study on Fatigue Crack Propagation and Extrinsic Toughening of an Al–Li Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 281(1), p 126–131
H. Azizi-Alizamini, M. Militzer, and W.J. Poole, A Novel Technique for Developing Bimodal Grain Size Distributions in Low Carbon Steels, Scripta Mater., 2007, 57(12), p 1065–1068
T.S. Wang, Z. Li, B. Zhang, X.J. Zhang, J.M. Deng, and F.C. Zhang, High Tensile Ductility and High Strength in Ultrafine-Grained Low-Carbon Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 2798–2801
T. Akita, M. Gotoh, S.V. Dobatkin, K. Kitagawa, and Y. Hirose, Influence of Annealing on Strength of Ultrafine Grained Low Carbon Steels by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, 638–642, p 1899–1904
X.C. Li, X.T. Feng, S.G. Cai, and W. Chen, Study of Mechanical Properties and Forming Properties of Ultra-fine Grain Ferrite Steels, J. Plast. Eng., 2009, 16(1), p 162–166
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50371073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Jing, T., Lu, M. et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ultrafine Lath-Shaped Low Carbon Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 21, 1496–1499 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-011-0055-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-011-0055-5