Abstract
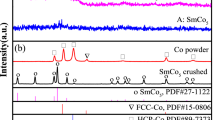
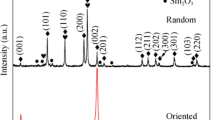
SmCo5 alloys with Sn additions (0.2-2.0 at.%) were prepared by mechanical milling of arc-melted samples. The nano-phase structures and magnetic properties of as-milled powders were investigated. The Sn additions resulted in development of nanocrystalline structures producing exchange-coupled magnets with better remanence magnetization to maximum magnetization ratios (M r/M max), typically 0.92 at 9.9 kOe coercivity. In addition, it was observed that the Sn concentrations lead to higher M r/M max ratios and maximum magnetization accompanying lower coercivity. X-ray diffraction revealed formation of 2:17 and 2:7 phases in 1:5 matrix, which were found to be dependent on Sn percentage. It appeared that higher Sn concentrations promoted 2:17 phase and helped in the formation of nano-sized phases.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.C. Jiles, Recent Advances and Future Directions in Magnetic Materials, Acta Mater., 2003, 51, p 5907–5939 (in English)
A. Menth, H. Negal, and R.S. Perkins, New High Performance Permanent Magnets Based on Rare Earth Transition Metal Compounds, Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1978, 8, p 21–47 (in English)
O. Gutfleisch, Controling the Properties of High Energy Density Permanent Magnetic Materials by Different Processing Routes, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2003, 33, p R157–R172 (in English)
K.J. Strant, Cobalt-Rare Earth Alloys as Promising New Permanent Magnet Materials, Cobalt, 1967, 9(36), p 133–143 (in English)
V.P. Menushenkov, Phase Transformation and Coercivity in Rare-Earth Permanent Magnets, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2005, 290–291, p 174–1277 (in English)
M.F. de Campos, F.J.G. Landgraf, N.H. Saito, S.A. Romero, A.C. Neiva, F.P. Missell, E. de Morais, S. Gama, E.V. Obrucneva, and B.V. Jalnin, Chemical Composition and Coercivity of Smco5 Magnets, J. Appl. Phys., 1998, 84(1), p 368–373 (in English)
E.A. Nesbit, New Permanent Magnetic Materials containing Rare Earth Metals, J. Appl. Phys., 1969, 40, p 1259–1265 (in English)
Y. Zhang, A. Gabay, Y. Wang, and G.C. Hadjipanayis, Microstructure, Microchemistry, and Coercivity in Sm-Co-Cu and Pr-Co-Cu Alloys, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2004, 272–276, p 1899–1900 (in English)
A.M. Gaby, P. Larson, I.I. Mazin, and G.C. Hadjipanayis, Magnetic States and Structural Transformation in Sm(Co, Cu)5 and Sm(Co, Fe, Cu)5 Permanent Magnets, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2005, 38, p 1337–1341 (in English)
S. Washko, J. Gerboc, and J. Orehotsky, Magnetic and Crystallographic Properties of SmCo Based Ternary Alloys, IEEE Trans. Magn. Mag., 1976, 12(6), p 974–976 (in English)
A.A. Kundig, R. Goplan, T. Ohkubo, and K. Hono, Coercivity Enhancement in Melt-Spun SmCo5 by Sn Addition, Scr. Mater., 2006, 54, p 2047–2051 (in English)
M.L. Kahn, J.-L. Bobet, F. Weill, and B. Chevalier, Modification of the Magnetic Properties of SmCo5 Particles Depending on the Grinding Atmosphere, J. Alloys Compd., 2002, 334, p 285–292
N. Tang, Z. Chen, Y. Zhang, G.C. Hadjipanayis, and F. Yang, Nanograined YCo5-Based Powders with high Coercivity, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2000, 219, p 173–177 (in English)
G.C. Hadjipanayis, Nanophase Hard Magnets, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1999, 200, p 373–391 (in English)
K.M. Choadary, A.K. Glri, K. Pellerin, S.A. Majetich, and J.H.J. Scott, Annealing effect on the Coercivity of SmCo5 Nanoparticles, J. Appl. Phys., 1999, 85(8), p 4331–4333 (in English)
H.P. Klug and L.E. Alexander, Method of Integral Breadths, X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials, 2nd ed., Wiley, New York, 1974, p 661–665 (in English)
Z.D. Zhang, W. Liu, J.P. Liu, and D.J. Sellmyer, Metastable Phases in Rare-Earth Permanent-Magnet Materials, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2000, 33, p R217–R246 (in English)
C. Orquiz-Mela, J.A. Matutes-Aquino, Nanocrystalline Pr0.5Sm0.5Co5 Alloy obtained by Mechanical Milling, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2008, doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.02.123 (in English)
J.T. Elizalde Galindo, H.A. Davies, and J.A. Matutes-Aquino, Structural and Magnetic Properties of Mechanically Milled Y1−x Pr x Co5 compounds [x = 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5], Mater. Charact., 2007, 58, p 805–808 (in English)
H.A. Davies, Nanocrystalline Exchange-Enhanced Hard Magnetic Alloys, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1996, 157/158, p 11–14 (in English)
Z. Chen, Y. Zhang, and G.C. Hadjipanayis, Nanocomposite PrCo5/Pr2Co17 Magnets With Enhanced Maximum Energy Product, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2000, 219, p 178–182 (in English)
W. Rave and K. Ramstock, Micromagnetic Calculation of the Grain size dependence of Remanence and Coercivity in Nanocrystalline Permanent Magnets, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1997, 171, p 69–82 (in English)
R. Skomski, J.M.D. Coey, Permanent Magnetism, Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol, Philadelphia, 1999, p 186–191, 298–301
K.H.J. Buschow, Handbook of Magnetic Materials, Vol 10, Elsevier, North-Holland, New York, 1997, p 503–504 (in English)
M.F. de Campos, F.J.G. landgral, R. Machado, D. Rodringues, S.A. Romero, A.C. Neiva, and F.P. Missell, A Model relating Remanence and Microstructure of SmCo5 Magnets, J. Alloys Compd., 1998, 267, p 257–264 (in English)
R.W. Gao, D.H. Zhang, W. Li, X.M. Li, and J.C. Zhang, Hard Magnetic property and δM(H) plot for Sintered NdFeB Magnet, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2000, 208, p 239–243 (in English)
R.W. McCallum, Determination of the Saturation Magnetization, Anisotropy Field, Mean Field Interaction, and Switching Field Distribution for Nanocrystalline Hard Magnets, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2005, 292, p 135–142 (in English)
K. Kang, L.H. Lewis, J.S. Jiang, and S.D. Bader, Recoil Hysteresis of Sm-Co/Fe Exchange-Spring Bilayers, J. Appl. Phys., 2005, 98, p 1139061–1139067 (in English)
Y. Kato and M. Tsutsumi, An Analysis of Magnetization Reversal Process, IEEE. Trans. Magn., 1992, 28(5), p 2686–2688
T. Schrefl, J. Fidler, and D. Suss, Micromagnetic Modeling of Nanocomposite Magnets, Institute of Applied and Technical Physics, Vienna University of Technology, Wiedner Hauptstraβe 8-1040 Vienna, Austria (in English).
H. Chiriac, M. Marinescu, P. Tiberto, and F. Vinai, Reversible Magnetization Behavior and Exchange Coupling in Two-Phase NdFeB Melt Spun Ribbons, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 304–306, p 957–960 (in English)
J.S. Jiang, H.G. Kaper, and G.K. Leaf, Hysteresis in Layered Spring Magnets, Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B, 2001, 1(2), p 219–232 (in English)
Y. Gao, J. Zhu, Y. Weng, E.B. Park, and C.J. Yang, The Enhanced Exchange Coupled Interaction in Nanocrystalline Nd2Fe14B/Fe3B + αFe Alloys With Improved Microstructure, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1999, 191, p 146–152 (in English)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Prof. Dr. M. F. de Campos of EEIMVR-Universidade Fluminense, Avdos Trabalhadores, Brazil and Prof. Dr. R. William McCallum of Iowa State University Ames, USA for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaigham, H., Khalid, F.A. Magnetic Properties and Nanocrystalline Phases in Sn Containing SmCo5 Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 20, 1304–1309 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9752-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9752-8