Abstract
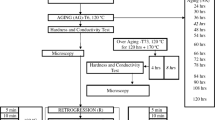
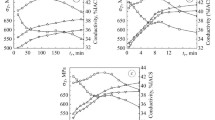
A retrogression and reaging (RRA) treatment was performed on 2195 Al-Li Alloy. The exposure times were from 5 to 60 min, and the temperatures were from 200 to 250 °C. Samples that were exposed to a salt spray test had overall similar mechanical properties as compared to those that were not exposed. The percent elongation, however, was significantly deteriorated due to the salt spray exposure. The mechanical properties of the 2195 samples were compared to those of 2099 samples exposed to similar treatments in an earlier study.
































Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Cina, Reducing Stress Corrosion Cracking in Aluminum Alloys, U.S. Patent 3,856,584, 24 December 1974
R.S. Kaneko, RRA: Solution for Stress Corrosion Problems with T6 Temper Aluminum, Met. Prog., 1980, 117, p 41–43
M. Talianker and B. Cina, Retrogression and Reaging and the Role of Dislocations in the Stress Corrosion of 7000-Type Aluminum Alloys, Metall. Trans. A, 1989, 20A, p 2087–2092
J.K. Park, Influences of Retrogression and Reaging Treatments on the Strength and Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance of Aluminum Alloy 7075-T6, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1988, 103, p 223–231
J.K. Park and A.J. Ardell, Microstructure of the Commercial 7075 Al Alloy in the T651 and T7 Tempers, Metall. Trans. A, 1983, 14A, p 1957–1965
J.K. Park and A.J. Ardell, Effect of Retrogression and Reaging Treatments on the Microstructure of Al-7075-T651, Metall. Trans. A, 1984, 15A, p 1531–1543
P. Fleck, D. Calleros, M. Madsen, T. Trinh, D. Hoang, E.W. Lee, J. Foyos, and O.S. Es-Said, Retrogression and Reaging of 7075 T6 Aluminum Alloy, Aluminum Alloys, Their Physical and Mechanical Properties—Proceedings ICAA7, Part 1(Charlottesville, VA), Trans Tech Publications, 2000, p 649–654
P. Fleck, K. Koziar, E. Fromer, P. Herbe, G. Davila, M. Lead, J. Foyos, E.W. Lee, and O.S. Es-Said, Retrogression and Reaging of 7249 Plates, Light-Weight Alloys for Aerospace Applications, K.V. Jata, Ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2001, p 99–108
P. Fleck, K. Koziar, J. Davila, H. Pech, E. Fromer, M. Leal, J. Foyos, E.W. Lee, and D. Tenney, A Review of the Effect of Retrogression and Reaging on Aluminum Alloy 7249, LiMat3, Center for Advanced Aerospace Materials, Puhang University of Science, Pusan, Korea, 2001, p 559–564
J. Na, G. Xiang, and Z. Zi-Qioa, Microstructure Evolution of Aluminum Lithium Alloy 2195 Undergoing Commercial Production, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2010, 20, p 740–745
J.H. Sanders, Investigation of Grain Boundary Chemistry in Al-Li 2195 Welds using Auger Electron Spectroscopy [J], Thin Solid Films, 1996, 227(1/2), p 121–127
M.C. Chatuvedi and D.L. Chen, Effect of Specimen Orientation and Welding on the Fracture and Fatigue Properties of 2195 Al-Li Alloy [J], Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 389, p 465–469
M.L. Bairwa, S.G. Desai, and P.P. Date, Identification of Heat Treatments for Better Formability in an Aluminum Lithium Alloy Sheet, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2005, 14, p 623–633
M. Romios, R. Tiraschi, C. Parrish, H. Babel, J.R. Ogren, and O.S. Es-Said, Design of Multistep Aging Treatments of 2099 (C458) Al-Li Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2005, 14(5), p 641–646
“2195-T8R78 Al-Li Plates” Alcan Aerospace Brochure, April 2010, http://www.alcanaerospace.com
“ASTM B117” Ascott Analytical Equipment Limited and National Exposure Testing, April 2010, http://www.ascott-analytical.com/ASTMB117/
“ASTM E8” Instron Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, April 2010, http://www.instron.us/wa/home/default_en.aspx
O.S. Es-Said, W.E. Frazier, and E.W. Lee, The Effect of Retrogression and Re-Aging on the Properties of the 7249 Aluminum Alloys, JOM, 2003, p 45–48
N. Ward, A. Tran, A. Abad, E.W. Lee, M. Hahn, E. Fordan, and O.S. Es-Said, The Effects of Retrogression and Reagging on Aluminum Alloy 2099 (C458), J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (Accepted)
Registration Record Series, Teal Sheets, May 2010, http://www.aluminum.org
E.A. Starke, Jr. and C.P. Blankenship, Jr., Aluminum Lithium Alloys, Aluminum-Lithium Alloys for Aerospace Applications, Proceedings of a Workshop, NASA, George Marshall Space Flight Center, Alabama, May 17–19, 1994
C. Giummarra, B. Thomas, and R. Rioja, New Aluminum Lithium Alloys for Aerospace Applications, Proceedings of the Light Metals Technology Conference, 2007, http://www.alcoa.com
N. Aizpuru, D. Le, J. McDonald, L. McLennan, S. Tewfik, E.W. Lee, D. Piatkowski, J. Foyos, J. Ogren, and O.S. Es-Said, The Effects of Flash Annealing on the Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Previously used AM2 Mats Composed of AL 6061-T6, Eng. Fail. Anal. J., 2005, 12, p 691–698
F.S. Bovard, Advanced Aluminum Technologies, NSRP—Product Design & Materials Technology Panel Meeting, Collection of Power Point Presentation Slides, 14 Feb 2008, http://www.nsrp.org
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ward, N., Tran, A., Abad, A. et al. The Effects of Retrogression and Reaging on Aluminum Alloy 2195. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 20, 1003–1014 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9739-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9739-5