Abstract
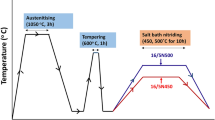
Hydroturbine steels, such as 13Cr-4Ni martensitic steels, are generally subjected to heavy-erosive wear and loss of efficiency due to solid particulate entrainment in the water. Surface-modified steels have proven to give better performance in terms of erosive wear resistance. In the present study, an attempt is made to investigate the effect of angle of impingement and particle size on slurry-jet erosion behavior of pulsed plasma nitrided and laser hardened 13Cr-4Ni steels. Laser hardening process has shown good performance at all angles of impingement due to martensitic transformation of retained austenite. Plastic deformation mode of material removal was also an evident feature of all laser-hardened surface damage locations. However, pulsed-plasma nitrided steels have exhibited chip formation and micro-cutting mode of erosive wear. Erosion with 150-300 μm size was twice compared to 150 μm size slurry particulates.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.S. Mann, Erosion Visualization and Characteristics of Two Dimensional Diffusion Treated Martensitic Stainless Steel Hydrofoils Wear 217(1998) 56–61
B.S. Mann, V. Arya, Abrasive and Erosive Wear Characteristics of Plasma Nitriding and HVOF Coatings: Their Application in Hydro Turbines Wear 249 (2001) 354–360
B.S. Mann, V. Arya, An Experimental Study to Correlate Water Jet Impingement Erosion Resistance and Properties of Metallic Materials and Coatings Wear 253 (2002) 650–661
Y.M. Kim, J.U. Kim, J.G. Han, Investigation on the Pulsed DC Plasma Nitriding with Optical Emission Spectroscopy Surf. Coat. Technol. 151-152 (2002) 227–232
R.J.K. Wood, The Sand Erosion Performance of Coatings Mater. Design 20 (1999)179–191
K.H. Loa, F.T. Chenga, C.T. Kwok, H.C. Man, Effects of Laser Treatments on Cavitation Erosion and Corrosion of AISI 440C Martensitic Stainless Steel Mater. Lett. 58 (2003) 88–93
C.T. Kwok, K.H. Lo, F.T. Cheng, H.C. Man, Effect of Processing Conditions on the Corrosion Performance of Laser Surface-Melted AISI 440C Martensitic Stainless Steel Surf. Coat. Technol. 166 (2003) 221–230
Y.I. Oka, K. Okamura, and T. Yoshida, Practical Estimation of Erosion Damage Caused by Solid Particle Impact Part 1: Effects of Impact Parameters on a Predictive Equation, Wear, 2005, 259(1–6), p 95–101
H.M. Clark, K.K. Wong, Impact Angle, Particle Energy and Mass Loss in Erosion by Dilute Slurries Wear 186-187 (1995) 454–464
G.W. Stachowiak, Particle Angularity and its Relationship to Abrasive and Erosive Wear. Wear 241 (2000) 214–219
D.W. Wheeler, R.J.K. Wood, Erosion of Hard Surface Coatings for Use in Offshore Gate Valves Wear 258 (2005) 526–536
C.T. Kwok, H.C. Man, F.T. Cheng Cavitation Erosion and Pitting Corrosion Behaviour of Laser Surface-Melted Martensitic Stainless Steel UNS S42000 Surf. Coat. Technol. 126 (2000) 238–255
H.M. Clark, R.B. Hartwich, A Re-Examination of the ‘Particle Size Effect’ in Slurry Erosion Wear 248 (2001) 147–161
D.J. O’Flynn, M.S. Bingley, M.S.A. Bradley, A.J. Burnett, A Model to Predict the Solid Particle Erosion Rate of Metals and its Assessment Using Heat-Treated Steels Wear 248 (2001) 162–177
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Dr. B.S. Mann, Additional director, Surface Coatings and Treatment Laboratory, Corporate R&D Division, BHEL, Vikasnagar, Hyderabad, India for his help in providing the material for this investigation. We also thank ARCI, Hyderabad for their assistance in Laser treatment of our Cr-Ni alloys. The authors are grateful to Department of Science and Technology (DST), India for their financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manisekaran, T., Kamaraj, M., Sharrif, S. et al. Slurry Erosion Studies on Surface Modified 13Cr-4Ni Steels: Effect of Angle of Impingement and Particle Size. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 16, 567–572 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-007-9068-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-007-9068-5