Abstract
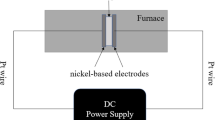
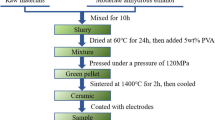
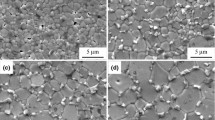
The effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO–Bi2O3 varistor ceramics was studied in the present work. Results demonstrate that the Bi-rich phase ZnBi38O60 is generated at the ZnO grain boundaries in the prepared varistor ceramics over a range of 850–1000°C. As the sintering temperature increases, the Bi-rich insulator layer tends to widen, and the average grain size increases to 13.22 μm. The switching field, breakdown strength (\(E_{{1{\text{mA}}}}\)), and nonlinear coefficient (α) increase, while the leakage current density (\(J_{L}\)) decreases, because of an increase in barrier height (\(\varphi_{B}\)). In addition, the sintering temperature promotes a decrease in the dielectric constant (\(\varepsilon_{a}\)) and an increase in dielectric loss. The ZnO–Bi2O3 varistor ceramic sintered at 1000°C exhibits excellent overall electrical properties, with a switching field of 228.04 V/mm, \(E_{{1{\text{mA}}}}\) of 379.76 V/mm, α of 6.02, \(J_{L}\) of 140 μA/cm2, \(\varphi_{B}\) of 0.39 eV, and \(\varepsilon_{a}\) of 172.87 at 1 kHz.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.K. Gupta, Application of zinc oxide varistors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 1817 (2010).
L.M. Levinson and H.R. Philipp, The physics of metal oxide varistors. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 1332 (1975).
M.P. Ahmad, A.V. Rao, K.S. Babu, and G.N. Rao, Effect of carbon-doping on structural and dielectric properties of zinc oxide. J. Adv. Dielectr. 10, 2050017 (2020).
H. Jiang, X. Ren, X. Lao, A. Kong, M. Zhong, Y. Sun, Y. Wu, Z. Yao, and L. Shi, Effect of NiO doping on grain growth and electrical properties of ZnO-based varistors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42, 3898 (2022).
M.A. Badruddin, M.S. Shaifudin, A.M.I.A.A. Mohd, W.M.I.W.M. Kamaruzzaman, N.A.M. Nasir, N. Yusof, and M.S.M. Ghazali, Electrical and microstructural evaluation of ZnO varistor ceramics with different CaSiO3 contents. Mater. Chem. Phys. 289, 126464 (2022).
A. Vojta and D.R. Clarke, Microstructural origin of current localization and “puncture” failure in varistor ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 81, 985 (1997).
E.R. Leite, M.A.L. Nobre, and E. Longo, Microstructural development of ZnO varistor during reactive liquid phase sintering. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 5391 (1996).
A. Bouchekhlal and F. Hobar, Effect of sintering temperature on microstructure and nonlinear electrical characteristics of ZnO varistor. J. Adv. Dielectr. 8, 1850014 (2018).
J. Li, K. Tang, S. Yang, and D. Zhu, Effects of Sb2O3 on the microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO–Bi2O3-based varistor ceramics fabricated by two-step solid-state reaction route. Ceram. Int. 47, 19394 (2021).
X. Huang, G. Pan, J. Li, D. Zhu, and Q. Yan, Effects of SiO2 on the microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO-based varistors (ZBSCCM) prepared by two-step sinering routework. Ceram. Int. 49, 37263 (2023).
A.M.D. Rubia, J.F. Fernandez, and A.C. Caballero, Equilibrium phases in the Bi2O3-rich region of the ZnO–Bi2O3 system. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25, 2215 (2005).
C.W. Nahm, Effect of Bi2O3 doping on microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO-V2O5-Mn3O4 semiconducting ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 903 (2017).
T. Tian, L. Zheng, M. Podlogar, H. Zeng, S. Bernik, K. Xu, X. Ruan, X. Shi, and G. Li, Novel ultrahigh-performance ZnO-based varistor ceramics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 35924 (2021).
P. Meng, J. Hu, H. Zhao, and J. He, High voltage gradient and low residual-voltage ZnO varistor ceramics tailored by doping with In2O3 and Al2O3. Ceram. Int. 42, 19446 (2016).
X. Wang, X. Ren, Z. Li, W. You, H. Jiang, W. Yu, L. Jin, Z. Yao, and L. Shi, A unique tuning effect of Mg on grain boundaries and grains of ZnO varistor ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 2633 (2021).
F. Kharchouche, Effect of sintering temperature on microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO-0.5mol.%V2O5–0.5mol.%Cr2O3 varistor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 3891 (2018).
M. Zhao, W. Cui, Z. Liu, and H. Chen, Effect of Bi2O3 on the ZnVMnCoTiO based varistor ceramic sintered at 800 °C. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 19724 (2021).
J. Li, K. Tang, S. Yang, and D. Zhu, Effects of doping Y2O3 on the microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO–Bi2O3-based varistor ceramics. J. Electroceram. 46, 131 (2021).
M. Zhao, H. Song, W. Cui, Z. Liu, and H. Chen, Low temperature sintering and characterization of 0.25–1 mol.% Bi2O3 doped ZnBiMnNbO based varistor ceramics. Ceram. Int. 47(16), 23362 (2021).
X. Xiao, L. Zheng, L. Cheng, T. Tian, X. Ruan, and G. Li, Effect of Cr2O3 on the property and microstructure of ZnO–Bi2O3 varistor ceramics in different sintering temperature. Ceram. Int. 41, S557 (2015).
D. Szwagierczak, J. Kulawik, and A. Skwarek, Influence of processing on microstructure and electrical characteristics of multilayer varistors. J. Adv. Ceram. 8, 408 (2019).
M.A. de la Rubia, M. Peiteado, J.F. Fernandez, and A.C. Caballero, Compact shape as a relevant parameter for sintering ZnO–Bi2O3 based varistors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 87, 1209 (2004).
R. Metz, H. Delalu, J.R. Vignalou, N. Achard, and M. Elkhatib, Electrical properties of varistors in relation to their true bismuth composition after sintering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 63, 157 (2000).
L.M. Levinson and H.R. Philipp, Metal oxide varistor-A multijunction thin-film device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 24, 75 (1974).
J. Shen, Y. Zhang, M. Li, R. Bao, M. Shen, C. Huang, G. Zhang, Y. Ke, H. Li, and S. Jiang, Effects of Fe and Al co-doping on the leakage current density and clamp voltage ratio of ZnO varistor. J. Alloy. Compd. 747, 1018 (2018).
W. Cao, Y. Guo, J. Su, and J. Liu, Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructural evolution of ZnO varistors. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 1266 (2023).
H.I. Hsiang, C.C. Chen, and C.C. Kao, Effect of ZnBi2O4 and Bi2O3 addition on the densification, microstructure, and varistor properties of ZnO varistors. Ceram. Int. 49, 2244 (2023).
T.K. Gupta and W.G. Carlson, A grain-boundary defect model for instability/stability of a ZnO varistor. J. Mater. Sci. 20, 3487 (1985).
F.A. Selim, T.K. Gupta, P.L. Hower, and W.G. Carlson, Low voltage ZnO varistor: Device process and defect model. J. Appl. Phys. 51, 765 (1980).
T. Tian, L. Zheng, S. Bernik, Z. Man, X. Shi, X. Ruan, and G. Li, Influence of Cr2O3 doping on the electrical characteristics of novel ZnO-Cr2O3-based varistor ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 159, 112111 (2023).
W. Liang, H. Zhao, S. Fan, H. Wang, Q. Xie, and Y. Zhu, Improvement of voltage gradient and leakage current characteristics of Mn2O3 and In2O3 added SnO2-ZnO-Ta2O5 based varistor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 124, 105582 (2021).
J. Li, K. Tang, and D. Zhu, Effect of Ho2O3 doping on the microstructure and electrical properties of ZnO–Bi2O3-Sb2O3-Cr2O3-Co2O3-MnO2-based varistors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 153, 107180 (2023).
H. Wang, H. Zhao, W. Liang, S. Fan, and J. Kang, Effect of sintering process on the electrical properties and microstructure of Ca-doped ZnO varistor ceramics. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 133, 105880 (2021).
A.X. Zhao, J. Liang, J. Sun, J. Guo, S. Dursun, K. Wang, and C.A. Randall, Cold sintering ZnO based varistor ceramics with controlled grain growth to realize superior breakdown electric field. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 430 (2021).
M. Zhao, Y. Wang, T. Sun, and H. Song, Effect of bismuth and vanadium as the varistor forming element in ZnO-based ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 8206 (2020).
M. Zhao, X. Lin, W. Cui, Z. Liu, H. Chen, L. Deng, and Y. Du, Effect of Nb2O5 on ZnBiMnO varistor ceramic prepared by solid-state sintering at 850 ℃. Ceram. Int. 49, 67 (2023).
S. Ma, Z. Xu, R. Chu, J. Hao, J. Hao, W. Li, L. Cheng, and G. Li, Influence of SnO2 on ZnO–Bi2O3-Co2O3 based varistor ceramics. Ceram. Int. 41, 12490 (2015).
H. Bai, M. Li, Z. Xu, R. Chu, J. Hao, H. Li, C. Chen, and G. Li, Influence of SiO2 on electrical properties of the highly nonlinear ZnO–Bi2O3-MnO2 varistors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37, 3965 (2017).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Doctoral Fund Project of Henan Polytechnic University (Grant No. B2020-45 and Grant No. B2019-20), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (Grant No. NSFRF210451), the Young Core Instructor Foundation of Henan Polytechnic University (Grant No. 2022XQG-12 and 2023XQG-10), and the Henan Province Scientific and Technological Project (Grant No. 222102230026).
Funding
The Funding was provided by Doctoral Fund Project of Henan Polytechnic University (B2020-45, Jingjing Tian; B2019-20, Heng Tian), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (NSFRF210451, Jingjing Tian), the Young Core Instructor Foundation of Henan Polytechnic University (2022XQG-12, Jingjing Tian; 2023XQG-10, Heng Tian), and the Henan Province Scientific and Technological Project (222102230026, Jingjing Tian).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Wu, Y., Tian, H. et al. The Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Microstructure and Electrical Properties of ZnO–Bi2O3 Varistor Ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11135-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11135-4