Abstract
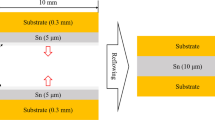
The sintering process of Cu nanoparticles is challenging due to the oxidation of Cu and the formation of voids in the die-attach layer. In this work, a simple and cost-effective bimodal-sized Cu composite paste was prepared for a high-strength Cu-Cu joint. The joint microstructure and sintering properties were systematically investigated by adjusting the mass ratio of the particle dimensions from 80 nm to 300 nm and varying the sintering parameters. Die attachment by pressure (20 MPa)-assisted sintering in air at 250°C was rapidly achieved using bimodal-sized Cu particles. The joint sintered for 1 min exhibited shear strength of 85.63 MPa, while 5-min sintering was able to obtain a dense bondline structure, and the shear strength reached 102.46 MPa. The sintered layers in nitrogen had the highest thermal conductivity of 284 W/m K and low resistivity of 4.42 µΩ cm. These results confirm that bimodal-sized Cu composite paste can be considered as an inexpensive potential die-attach material for high-temperature electronics packaging.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.A. Bajwa, Y. Qin, R. Reiner, R. Quay, and J. Wilde, Assembly and packaging technologies for high-temperature and high-power GaN devices. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 5(10), 1402 (2015).
S. Ji, Z. Zhang, and F. Wang, Overview of high voltage sic power semiconductor devices: development and application. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 1(3), 254 (2017).
A. Matallana, E. Ibarra, I. López, J. Andreu, J.I. Garate, X. Jordà, and J. Rebollo, Power module electronics in HEV/EV applications: new trends in wide-bandgap semiconductor technologies and design aspects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 113, 109264 (2019).
L.A. Navarro, X. Perpina, P. Godignon, J. Montserrat, V. Banu, M. Vellvehi, and X. Jorda, Thermomechanical assessment of die-attach materials for wide bandgap semiconductor devices and harsh environment applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 29(5), 2261 (2014).
F. Roccaforte, P. Fiorenza, G. Greco, R. Lo Nigro, F. Giannazzo, F. Iucolano, and M. Saggio, Emerging trends in wide band gap semiconductors (SiC and GaN) technology for power devices. Microelectron. Eng. 187, 66 (2018).
S. Sun, Q. Guo, H. Chen, M. Li, and C. Wang, Solderless bonding with nanoporous copper as interlayer for high-temperature applications. Microelectron. Reliab. 80, 198 (2018).
C. Chen, Z. Zhang, Q. Wang, B. Zhang, Y. Gao, T. Sasamura, Y. Oda, N. Ma, and K. Suganuma, Robust bonding and thermal-stable Ag-Au joint on ENEPIG substrate by micron-scale sinter Ag joining in low temperature pressure-less. J. Alloys Compd. 828, 154397 (2020).
X. Liu and H. Nishikawa, Low-pressure Cu-Cu bonding using in-situ surface-modified microscale Cu particles for power device packaging. Scr. Mater. 120, 80 (2016).
N. Kumar and A. Maurya, Development of lead free solder for electronic components based on thermal analysis. Mater. Today Proc. 62(4), 2163 (2022).
C.-H. Hsiao, W.-T. Kung, J.-M. Song, J.-Y. Chang, and T.-C. Chang, Development of Cu-Ag pastes for high temperature sustainable bonding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 684, 500 (2017).
R. Rashidi and H. Naffakh-Moosavy, Metallurgical, physical, mechanical and oxidation behavior of lead-free chromium dissolved Sn-Cu-Bi solders. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 13, 1805 (2021).
S. Li, Y. Liu, H. Ye, X. Liu, F. Sun, X. Fan, and G. Zhang, Sintering mechanism of Ag nanoparticle-nanoflake: a molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 16, 640 (2022).
J. Yan, A review of sintering-bonding technology using Ag nanoparticles for electronic packaging. Nanomaterials (Basel) 11(4), 927 (2021).
C. Chen and K. Suganuma, Large-scale ceramic–metal joining by nano-grained Ag particles paste sintering in low-temperature pressure-less conditions. Scr. Mater. 195, 113747 (2021).
H. Yan, P. Liang, Y. Mei, and Z. Feng, Brief review of silver sinter-bonding processing for packaging high-temperature power devices. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 6(3), 25 (2020).
T.F. Chen and K.S. Siow, Comparing the mechanical and thermal-electrical properties of sintered copper (Cu) and sintered silver (Ag) joints. J. Alloys Compd. 866, 158783 (2021).
H.Q. Zhang, S.L. He, G.D. Qu, Z.Y. Deng, G.S. Zou, Q. Jia, E. Deng, and W. Guo, Improved thermal conductivity and reliability through graphene reinforced nanopaste for power devices in new energy vehicles. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 1, 1 (2023).
C.H. Yin, K. Wumaeraili, Y. Zhang, Y.C. Wu, J.H. Zhang, W. Guo, Y. Zhu, X.G. Song, Q. Jia, and H.Q. Zhang, Novel Ag-Cu foam sheet with multi-layer composite structure for high performance joining of SiC power chips. Mater Charact 209, 113696 (2024).
H. Nakako, D. Ishikawa, C. Sugama, Y. Kawana, M. Negishi, Y. Ejiri, In sintering copper die-bonding paste curable under pressureless conditions, PCIM Europe 2017, in International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, (2017), pp. 1–5
J. Li, T. Shi, X. Yu, C. Cheng, J. Fan, G. Liao, Z. Tang, Low-temperature and low-pressure Cu-Cu bonding by pure Cu nanosolder paste for wafer-level packaging, in 2017 IEEE 67th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), (2017) p. 976
J. Li, Q. Liang, C. Chen, T. Shi, G. Liao, Z. Tang, Cu-Cu bonding by low-temperature sintering of self-healable Cu nanoparticles, in 2019 IEEE 69th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), (2019), p. 661
J.-L. Jo, K. Anai, S. Yamauchi, T. Sakaue, The properties of Cu sinter paste for pressure sintering at low temperature, in 2019 IEEE 69th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), (2019), p. 76
H. Nakako, D. Ishikawa, C. Sugama, Y. Kawana, M. Negishi, Y. Yanaka, Y. Ejiri, In relationship between bonding properties and porosity of sintered Cu bonding, PCIM Europe 2019, in International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, (2019), p. 1
T. Ishizaki, A. Kuno, A. Tane, M. Yanase, F. Osawa, T. Satoh, and Y. Yamada, Reliability of Cu nanoparticle joint for high temperature power electronics. Microelectron. Reliab. 54(9–10), 1867 (2014).
T. Furukawa, M. Shiraishi, Y. Yasuda, A. Konno, M. Mori, T. Morita, S. Watanabe, T. Arai, M. Nakamura, D. Kawase, In high power density side-gate HiGT modules with sintered Cu having superior high-temperature reliability to sintered Ag, in 2017 29th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and IC's (ISPSD), (2017), p. 263
H.-J. Huang, M.-B. Zhou, X.-P. Zhang, Extraordinarily enhanced sintering performance of pressureless sinterable Cu nanoparticle paste for achieving robust die-attach bonding by using reducing hybrid solvent, in 2021 IEEE 71st Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), (2021), p. 583
S. Koga, H. Nishikawa, M. Saito, and J. Mizuno, Fabrication of nanoporous Cu sheet and application to bonding for high-temperature applications. J. Electron. Mater. 49(3), 2151 (2020).
J. Li, Q. Liang, T. Shi, J. Fan, B. Gong, C. Feng, J. Fan, G. Liao, and Z. Tang, Design of Cu nanoaggregates composed of ultra-small Cu nanoparticles for Cu-Cu thermocompression bonding. J. Alloys Compd. 772, 793 (2019).
H.-J. Huang, X. Wu, M.-B. Zhou, X.-P. Zhang, A highly reliable die bonding approach for high power devices by low temperature pressureless sintering using a novel Cu nanoparticle paste, in 2020 IEEE 70th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), (2020), p. 1697
J. Li, Y. Xu, X. Zhao, Y. Meng, Z. Yin, Y. Wang, and T. Suga, Enhancement and mechanism of copper nanoparticle sintering in activated formic acid atmosphere at low temperature. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 10(5), 054004 (2021).
P.-W. Chou, J.-M. Song, Z.-Y. Xie, M. Akaike, T. Suga, M. Fujino, and J.-Y. Lin, Low temperature de-oxidation for copper surface by catalyzed formic acid vapor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 456, 890 (2018).
J. Liu, H. Chen, H. Ji, and M. Li, Highly conductive Cu-Cu joint formation by low-temperature sintering of formic acid-treated Cu nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(48), 33289 (2016).
F. Mu, H. Ren, L. Liu, Y. Wang, G. Zou, T. Suga, In Nano-Cu paste sintering in Pt-catalyzed formic acid vapor for Cu bonding at a low temperature, in 2019 International Conference on Electronics Packaging (ICEP), (2019), p. 365
H.J. Huang, X. Wu, M.B. Zhou, and X.P. Zhang, Superior strength and strengthening mechanism of die attachment joints by using bimodal-sized Cu nanoparticle paste capable of low-temperature pressureless sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32(3), 3391 (2021).
Z. Huang, J. Wen, Y. Zhang, Q. Liu, H. Li, J. Tong, P. Liang, G. Yang, C. Cui, High strength and density Cu-Cu joints formation by low temperature and pressure sintering of different mass ratio of Cu micron-nanoparticles paste, in 2021 22nd International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT), (2021), p. 1
Y. Peng, Y. Mou, J. Liu, and M. Chen, Fabrication of high-strength Cu-Cu joint by low-temperature sintering micron–nano Cu composite paste. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(11), 8456 (2020).
Y. Gao, H. Zhang, W. Li, J. Jiu, S. Nagao, T. Sugahara, and K. Suganuma, Die bonding performance using bimodal Cu particle paste under different sintering atmospheres. J. Electron. Mater. 46(7), 4575 (2017).
D. Tomotoshi and H. Kawasaki, Surface and interface designs in copper-based conductive inks for printed/flexible electronics. Nanomaterials (Basel) 10(9), 1689 (2020).
X. Wang, Z. Zhang, Y. Feng, and F. Xiao, Anti-oxidative copper nanoparticle paste for Cu-Cu bonding at low temperature in air. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33(2), 817 (2021).
Y. Gao, W. Li, C. Chen, H. Zhang, J. Jiu, C.F. Li, S. Nagao, and K. Suganuma, Novel copper particle paste with self-reduction and self-protection characteristics for die attachment of power semiconductor under a nitrogen atmosphere. Mater. Des. 160, 1265 (2018).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the R&D Program of the Beijing Municipal Education Commission (KZ202210005005), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52205324), and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (L233038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Lu, Z., Jia, Q. et al. Sintering Mechanism of Bimodal-Sized Cu Nanoparticle Paste for Power Electronics Packaging. J. Electron. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11021-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11021-z