Abstract
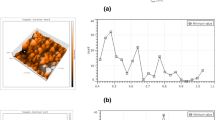
Oxygen plasma etching has been performed to roughen the surface structure of an Al-doped ZnO (AZO) seed layer. The distribution of Ag nanoparticles was optimized to improve the characteristics of a film and facilitate its application as a touch sensing electrode. First, an intermittent procedure was performed to optimize the quality of the AZO seed layer. After the optimal parameters were obtained according to the figure-of-merit, the surface of the seed layer was roughened, and the depth of surface roughening was affected by adjusting the etching power of the oxygen plasma, and the surface roughness uniformity was affected by adjusting the etching time. Finally, by changing the etching oxygen flow rate, the width of the rough structure was further affected. The above three steps can optimize the surface roughness structure and effectively improve the uniform distribution of Ag nano-particles. To improve the sensitivity (SE) and stability (ST) of the film, the density of nano-Ag particles was modulated. The characteristics of film carriers were measured with a Hall effect analyzer. The surface morphology of the seed layer and the crystallinity change of the film were examined using electron microscopy, x-ray diffraction, ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy. The results revealed that a favorable film quality was achieved by performing three intermittent procedures. When the AZO seed layer surface was etched with a power of 50 W for 5 min, a 50-sccm etching oxygen flow and a 90-W nano-Ag deposition power were applied for 20 s, the density and distribution of the nano-Ag particles was favorable, and the SE and ST of the film were optimal. Under these conditions, the film’s resistance was 3.21 × 10−3 Ω-cm, its SE was 45.04%–52.48%, and its ST error was within 7.44%.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
N.M. Le and B.-T. Lee, Highly conducting and highly transparent oxide/metal/oxide structures for ultraviolet-C light sources utilizing a thin Cu wetting interlayer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(37), 323 (2017).
Y.-D. Ko, K.-C. Kim, and Y.-S. Kim, Effects of substrate temperature on the Ga-doped ZnO films as an anode material of organic light emitting diodes. Superlattices Microstruct. 51, 941 (2012).
Y.-S. Lin and Y.-H. Huang, Study of optoelectronics and microstructures on the AZO/nano-layer metals/AZO sandwich structures. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electr. 24, 3058 (2013).
L. Wang, C. Hu, and L. Shao, The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 1227 (2017).
R.A. Maniyara, V.K. Mkhitaryan, T.L. Chen, D.S. Ghosh, and V. Pruneri, An antireflection transparent conductor with ultralow optical loss and electrical resistance. Nat. Commun. 7, 13771 (2016).
H. Moon, P. Won, J. Lee, and S.H. Ko, Low-haze, annealing-free, very long Ag nanowire synthesis and its application in a flexible transparent touch panel. Nanotechnology 27, 295201 (2016).
H.J. Choi, S.G. Yoon, J.H. Lee, and J.Y. Lee, Crystallized indium-tin oxide (ITO) thin films grown at low temperature onto flexible polymer substrates. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 1, Q106 (2012).
C.-C. Wu, Highly flexible touch screen panel fabricated with silver-inserted transparent ITO triple-layer structures. RSC Adv. 22, 11862 (2018).
X. Yin, W. Que, D. Fei, F. Shen, and Q. Guo, Ag nanoparticle/ZnO nanorods nanocomposites derived by a seed-mediated method and their photocatalytic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 524, 13 (2012).
P. Makvandi, C. Wang, E. Zare, A. Borzacchiello, L. Niu, and F. Tay, Metal-based nanomaterials in biomedical applications: antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity aspects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1910021 (2020).
B.Y. Oh, M.C. Jeong, D.S. Kim, W. Lee, and J.M. Myoung, Post-annealing of Al-doped ZnO films in hydrogen atmosphere. J. Cryst. Growth 281, 475–480 (2005).
S. Fareed, A. Jamil, F. Afsar, F. Sher, C. Li, X. Xu, and M.A. Rafiq, Selective oxygen sensor prepared using Ni-doped zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 5677 (2019).
D. Valerini, L. Tammaro, F. Di Benedetto, G. Vigliotta, L. Capodieci, R. Terzi, and A. Rizzo, Aluminum-doped zinc oxide coatings on polylactic acid films for antimicrobial food packaging. Thin Solid Film 645, 187–192 (2018).
A. Dey, Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: a review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 229, 206 (2018).
F. Liu, B. Wang, X. Yang, Y. Guan, R. Sun, Q. Wang, X. Liang, P. Sun, and G. Lu, High-temperature stabilized zirconia-based sensors utilizing MNb2O6 (M: Co, Ni and Zn) sensing electrodes for detection of NO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 232, 523 (2016).
K. Suematsu, K. Watanabe, A. Tou, Y. Sun, and K. Shimanoe, Ultraselective toluene-gas sensor: nanosized gold loaded on zinc oxide nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 90, 1959 (2018).
L. Bocquet and E. Charlaix, Nanofluidics, from bulk to interfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 39, 1073 (2010).
M. Travagliati, D. Nardi, C. Giannetti, V. Gusev, P. Pingue, V. Piazza, G. Ferrini, and F. Banfi, Interface nano-confined acoustic waves in polymeric surface phononic crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 021906 (2015).
K. Gold, B. Slay, M. Knackstedt, and A. Gaharwar, Antimicrobial activity of metal and metal-oxide based nanoparticles. Adv. Ther. 1, 1700033 (2018).
G. Benetti, M. Gandolfi, M. Van Bael, L. Gavioli, C. Giannetti, C. Caddeo, and F. Banfi, Photoacoustic sensing of trapped fluids in nanoporous thin films: device engineering and sensing scheme. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 27947 (2018).
V. Saxena, P. Chandra, and L. Pandey, Design and characterization of novel Al-doped ZnO nanoassembly as an effective nanoantibiotic. Appl. Nanosci. 8, 1925 (2018).
J. Huang, X. Li, and W. Zhou, Safety assessment of nanocomposite for food packaging application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 45, 187 (2015).
K. Wegner, P. Piseri, H. Tafreshi, and P. Milani, Cluster beam deposition: a tool for nanoscale science and technology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, R439 (2006).
F. Cao, L. Zhang, H. Wang, Y. You, Y. Wang, N. Gao, J. Ren, and X. Qu, Defect-rich adhesive nanozymes as efficient antibiotics for enhanced bacterial inhibition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 16236 (2019).
R. Pantani, G. Gorrasi, G. Vigliotta, M. Murariu, and P. Dubois, PLA-ZnO nanocomposite films: water vapor barrier properties and specific end-use characteristics. Eur. Polym. J. 49, 3471 (2013).
A.S.M.I. Uddin and G.-S. Chung, Synthesis of highly stable silver-loaded vertical ZnO nanowires array and its acetylene sensing properties. Surf. Rev. Lett. 23, 1550087 (2016).
N. Maréchal, E. Quesnel, and Y. Pauleau, Silver thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 241, 34 (1994).
S. Kang, R. Nandi, J.-K. Sim, J.-Y. Jo, U. Chatterjee, and C.-R. Lee, Characteristics of an oxide/metal/oxide transparent conducting electrode fabricated with an intermediate Cu–Mo metal composite layer for application in efficient CIGS solar cell. RSC Adv. 7, 48113 (2017).
E. Aydin and N.D. Sankir, AZO/metal/AZO transparent conductive oxide thin films for spray pyrolyzed copper indium sulfide based solar cells. Thin Solid Films 653, 29 (2018).
D. Valerini, L. Tammaro, F. Villani, A. Rizzo, I. Caputo, G. Paolella, and G. Vigliotta, Ag functionalization of Al-doped ZnO nanostructured coatings on PLA substrate for antibacterial applications. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 4830 (2020).
M. Chuang and F. Chen, Synergistic plasmonic effects of metal nanoparticle—decorated PEGylated graphene oxides in polymer solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 7397 (2015).
W. Oliver and G. Pharr, An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
M. Chiodi, C.P. Cheney, P. Vilmercati, E. Cavaliere, N. Mannella, H.H. Weitering, and L. Gavioli, Enhanced dopant solubility and visible-light absorption in Cr-N codoped TiO2 nanoclusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 311 (2012).
M.G. Blaber, M.D. Arnold, and M.J. Ford, Search for the ideal plasmonic nanoshell: the effects of surface scattering and alternatives to gold and silver. J. Phys. Chem. C 8, 3041 (2009).
E. Cavaliere, G. Benetti, M. Van Bael, N. Winckelmans, S. Bals, and L. Gavioli, Exploring the optical and morphological properties of Ag and Ag/TiO2 nanocomposites grown by supersonic cluster beam deposition. Nanomaterials 7, 442 (2017).
G. Torrisi, I. Crupi, S. Mirabella, and A. Terrasi, Robustness and electrical reliability of AZO/Ag/AZO thin film after bending stress. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 165, 88 (2017).
G. Benetti, E. Cavaliere, R. Brescia, S. Salassi, R. Ferrando, A. Vantomme, L. Pallecchi, S. Pollini, S. Boncompagni, and B. Fortuni, Tailored Ag–Cu–Mg multielemental nanoparticles for wide-spectrum antibacterial coating. Nanoscale 11, 1626 (2019).
A. Tangerman and E.G. Winkel, Extra-oral halitosis: an overview. J. Breath Res. 4, 017003 (2010).
N.M. Vuong, N.D. Chinh, B.T. Huy, and Y.-I. Lee, CuO-decorated ZnO hierarchical nanostructures as efficient and established sensing materials for H2S gas sensors. Sci. Rep. 6, 26736 (2016).
Z. Zeng, X. Huang, Z. Yin, H. Li, Y. Chen, H. Li, Q. Zhang, J. Ma, F. Boey, and H. Zhang, Fabrication of graphene nanomesh by using an anodic aluminum oxide membrane as a template. Adv. Mater. 24, 4138–4142 (2012).
P. Mendez-Pfeiffer, L. Urzua, E. Sanchez-Mora, A. Gonzalez, J. Romo-Herrera, J. Arciniega, and L. Morales, Damage on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus using white light photoactivation of Au and Ag nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 125, 213102 (2019).
X. Zhou, S. Lee, Z. Xu, and J. Yoon, Recent progress on the development of chemosensors for gases. Chem. Rev. 115, 7944 (2015).
F. Cao, L. Zhang, H. Wang, Y. You, Y. Wang, N. Gao, J. Ren, and X. Qu, Defect-rich adhesive nanozymes as efficient antibiotics for enhanced bacterial inhibition. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 58, 16236–16242 (2019).
S.H. Ahn and L.J. Guo, Large-area roll-to-roll and roll-to-plate nanoimprint lithography: a step toward high-throughput application of continuous nanoimprinting. ACS Nano 3, 2304 (2009).
J.Y. Park, S.W. Choi, and S.S. Kim, A model for the enhancement of gas sensing properties in SnO2-ZnO core-shell nanofibres. J. Phy. D 44, 205403 (2011).
T. Rakshit, S. Santra, I. Manna, and S.K. Ray, Enhanced sensitivity and selectivity of brush-like SnO2 nanowire/ZnO nanorod heterostructure based sensors for volatile organic compounds. RSC Adv. 4, 36749 (2014).
H.-J. Choi, S.-J. Choi, S. Choo, I.-D. Kim, and H. Lee, Hierarchical ZnO nanowires-loaded Sb-doped SnO2-ZnO micrograting pattern via direct Imprinting-assisted hydrothermal growth and its selective detection of acetone molecules. Sci. Rep. 6, 18731 (2016).
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported as projects of the I-Shou University, Taiwan R.O.C. under Grants ISU112-01-01A, ISU111-01-02A and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan R.O.C., under Grants MOST108-2221-E-214-028 and MOST111-2918-I-214 -001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y-SL: Writing—Original Draft Preparation and Writing—Review and Editing, C-HT and Y-CTJ: Formal Analysis, Investigation and Data Curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YS., Teng, CH. & James, YC.T. Improving the Uniform Distribution of Nano-Ag in Al-Doped ZnO Film to Enhance Its Application in Soft Touch Sensing Electrodes. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 7907–7919 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10704-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10704-3