Abstract
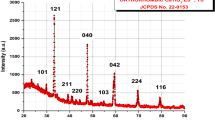
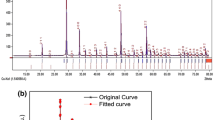
The thermoluminescence (TL) kinetic parameters and radioluminescence results (RL) of RE3+ (RE = Pr, Sm, Tb, Ho, Er)-doped barium tantalate phosphors have been studied for different concentrations. The concentration quenching occurring at the RL intensity of Pr3+ after 1.5 mol% was associated with a cross-relaxation between 3P0 → 3H4 and 1D2 → 3H4, while the RL emissions of Tb3+ were observed corresponding to transitions of5D4 → 7FJ. The asymmetry ratio of RL is relatively high compared to the PL asymmetry ratio for Sm3+, which may be attributed to the RL mechanism leading to some decrease in the local symmetry of Sm3+ ions. The Ho3+ and Er3+ show the characteristic green and red emissions corresponding to radiative transitions. Also, the spectral properties of the phosphors have been discussed by comparing the RL results, the reported PL results of Pr3+, Sm3+, Ho3+, Er3+ , and the PL results of Tb3+ , which were examined in the study. After being irradiated by x-ray and short-wave UV light (254 nm), TL glow curves for Pr3+, Tb3+, and Er3+ doped phosphors were compared in the range of 50 °C and 400 °C at a heating rate of 2 °C s−1. TL glow peaks for Pr3+, Tb3+, and Er3+ formed at temperatures of 77 °C and 208 °C, 87 °C and 263 °C, and 158 °C and 267 C, respectively. The kinetic data were estimated by applying computerized glow curve deconvolution (CGCD) where TL glow curves of BaTa2O6:RE3+ (RE = Pr, Tb, Er) consist of 5, 6, and 7 estimated glow peaks with figure-of-merit values of 1.06, 1.60, and 1.09, respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Xu, X. Zhao, and Y. Zhu, Synthesis of hexagonal BaTa2O6 nanorods and influence of defects on the photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 25825 (2006).
G.K. Layden, Polymorphism of BaTa2O6. Mater. Res. Bull. 2, 533 (1967).
T. Vanderah, R. Roth, T. Siegrist, W. Febo, J. Loezos, and W.W. Ng, Subsolidus phase equilibria and crystal chemistry in the system BaO-TiO2-Ta2O5. Solid State Sci. 5, 149 (2003).
M. İlhan, M.İ Katı, İÇ. Keskin, and L.F. Güleryüz, Evaluation of structural and spectroscopic results of tetragonal tungsten bronze MTa2O6:Eu3+ (M = Sr, Ba, Pb) phosphors and comparison on the basis of Judd–Ofelt parameters. J. Alloys Compd. 901, 163626 (2022).
M. İlhan, İÇ. Keskin, L.F. Güleryüz, and M.İ Katı, A comparison of spectroscopic properties of Dy3+-doped tetragonal tungsten bronze MTa2O6 (M = Sr, Ba, Pb) phosphors based on Judd–Ofelt parameters. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 16606 (2022).
M. İlhan, and L.F. Güleryüz, Cathodoluminescence and photoluminescence of BaTa2O6:Sm3+ phosphor depending on the sintering temperature. Chem. Pap. 76, 6963 (2022).
S.C. Navale, V. Samuel, A.B. Gaikwad, and V. Ravi, A co-precipitation technique to prepare BaTa2O6. Ceram. Int. 33, 297 (2007).
M. İlhan, A. Mergen, and C. Yaman, Mechanochemical synthesis and characterisation of BaTa2O6 ceramic powders. Ceram. Int. 37, 1507 (2011).
M. İlhan, A. Mergen, and C. Yaman, Removal of iron from BaTa2O6 ceramic powder produced by high energy milling. Ceram. Int. 39, 5741 (2013).
G.K. Layden, Dielectric and structure studies of hexagonal BaTa2O6. Mater. Res. Bull. 3, 349 (1968).
H. Kato, and A. Kudo, New tantalate photocatalysts for water decomposition into H2 and O2. Chem. Phys. Lett. 295, 487 (1998).
H. Kato, and A. Kudo, Photocatalytic water splitting into H2 and O2 over various tantalate photocatalysts. Catal. Today 78, 561 (2003).
M. İlhan, A. Mergen, C. Sarıoğlu, and C. Yaman, Heat capacity measurements on BaTa2O6 and derivation of its thermodynamic functions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 128, 707 (2017).
M. Ilhan, R. Samur, H. Demirer, and F. Mindivan, Photoluminescence and concentration quenching of Pr3+ doped BaTa2O6 phosphor. Metalurgija 54, 407 (2015).
M. İlhan, İÇ. Keskin, Z. Çatalgöl, and R. Samur, NIR photoluminescence and radioluminescence characteristics of Nd3+ doped BaTa2O6 phosphor. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 15, 1594 (2018).
M.K. Ekmekçi, M. İlhan, A.S. Başak, and S. Deniz, Structural and luminescence properties of Sm3+ doped TTB-type BaTa2O6 ceramic phosphors. J. Fluoresc. 25, 1757 (2015).
M. İlhan, M.K. Ekmekçi, A. Mergen, and C. Yaman, Synthesis and optical characterization of red-emitting BaTa2O6:Eu3+ phosphors. J. Fluoresc. 26, 1671 (2016).
M. İlhan, M.K. Ekmekçi, A. Mergen, and C. Yaman, Photoluminescence characterization and heat treatment effect on luminescence behavior of BaTa2O6:Dy3+ phosphor. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 14, 1134 (2017).
M. İlhan, Synthesis, structure and photoluminescence properties of Ho3+ doped TTB–BaTa2O6. Solid State Sci. 38, 160 (2014).
M. İlhan, Synthesis, structural properties and visible–near infrared photoluminescence of trivalent erbium (Er3+) doped BaTa2O6 phosphor. AKU J. Sci. Eng. 17, 675 (2017).
J. Singh, J. Manam, and F. Singh, Synthesis and thermoluminescence studies of γ-irradiated Dy3+ doped SrGd2O4 phosphor. Mater. Res. Bull. 94, 113 (2017).
B. Sanyal, M. Goswami, S. Shobha, V. Prakasan, S.P. Chawla, M. Krishnan, and S.K. Ghosh, Synthesis and characterization of Dy3+ doped lithium borate glass for thermoluminescence dosimetry. J. Non Cryst. Solids 475, 184 (2017).
M. Isik, E. Bulur, and N.M. Gasanly, TL and TSC studies on TlGaSe2 layered single crystals. J. Lumin. 144, 163 (2013).
V. Pagonis, G. Kitis, and C. Furetta, Numerical and Practical Exercises in Thermoluminescence (New York: Springer, 2006).
İÇ. Keskı̇n, Radioluminescence results, thermoluminescence analysis and kinetic parameters of Y2O3:Ln3+ (Ln: Dy, Nd, Sm) nanophosphors obtained by sol–gel method. Ceram. Int. 48, 20579 (2022).
T. Yanagida, Study of rare-earth-doped scintillators. Opt. Mater. 35, 1987 (2013).
M. İlhan, Synthesis, structural characterization, and photoluminescence properties of TTB-type PbTa2O6:Eu3+ phosphor. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 14, 1144 (2017).
B.D. Cullity, and S.R. Stock, Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 3rd ed., (Hoboken: Prentice Hall, 2001).
I.E. Wachs, Infrared spectroscopy of supported metal oxide catalysts. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 105, 143 (1995).
K.H. Lee, K.W. Chae, C.I. Cheon, and J.S. Kim, Photoluminescence and structural characteristics of double tungstates A (M1–xPrx)W2O8 (A= Li, Cs, M= Al, Sc, La). J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 30, 243 (2010).
K.H. Lee, K.W. Chae, C.I. Cheon, and J.S. Kim, Effect of Crystal Structural environment of Pr3+ on photoluminescence characteristics of double tungstates. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 48, 183 (2011).
D. Balaji, A. Durairajan, D. Thangaraju, K.K. Rasu, and S.M. Babu, Investigation of structural and luminescent properties of Pr3+ activated CsGd(WO4)2 by sol–gel synthesis. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 178, 762 (2013).
R. Naccache, F. Vetrone, A. Speghini, M. Bettinelli, and J.A. Capobianco, Cross-relaxation and upconversion processes in Pr3+ singly doped and Pr3+/Yb3+ codoped nanocrystalline Gd3Ga5O12: the sensitizer/activator relationship. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 7750 (2008).
F.B. Xiong, F.X. Xu, H.F. Lin, Y.P. Wang, E. Ma, and W.Z. Zhu, Synthesis and luminescent properties of novel thermal-stable orangish-red-emitting LnNbO4:Sm3+ (Ln=La, Y) phosphors. Appl. Phys. A 126, 908 (2020).
A.K. Vishwakarma, and M. Jayasimhadri, Pure orange color emitting Sm3+ doped BaNb2O6 phosphor for solid-state lighting applications. J. Lumin. 176, 112 (2016).
A.Y. Madkhli, Ü.H. Kaynar, M.B. Coban, M. Ayvacikli, A. Canimoglu, and N. Can, Characterization, room and low temperature photoluminescence of yttrium aluminium borate activated with Sm3+ ions. Mater. Res. Bull. 161, 112167 (2023).
J. Hakami, Ü.H. Kaynar, M. Ayvacikli, M.B. Coban, J.G. Guinea, P.D. Townsend, M. Oglakci, and N. Can, Structural and temperature-dependent luminescence of terbium doped YAl3(BO3)4 phosphor synthesized by the combustion method. Ceram. Int. 48, 32256 (2022).
İÇ. Keskin, M. Türemiş, M.İ Katı, S. Gültekin, Y.T. Arslanlar, A. Çetin, and R. Kibar, Detailed luminescence (RL, PL, CL, TL) behaviors of Tb3+ and Dy3+ doped LiMgPO4 synthesized by sol–gel method. J. Lumin. 225, 117276 (2020).
C.S. McCamy, Correlated color temperature as an explicit function of chromaticity coordinates. Color Res. Appl. 17, 142 (1992).
M. İlhan, M.K. Ekmekçi, and İÇ. Keskin, Judd-Ofelt parameters and x-ray irradiation results of MNb2O6:Eu3+ (M= Sr, Cd, Ni) phosphors synthesized via a molten salt method. RSC Adv. 11, 10451 (2021).
T. Xie, R. Lei, J. Wang, F. Huang, S. Zhao, B. Li, and S. Xu, Multi-functionalities of photoluminescence, x-ray excited luminescence and optical temperature sensing in Er3+ and Er3+/Yb3+ doped Gd2Zr2O7 phosphors. J. Alloys Compd. 905, 164226 (2022).
L. Teng, W. Zhang, W. Chen, J. Cao, X. Sun, and H. Guo, Highly efficient luminescence in bulk transparent Sr2GdF7:Tb3+ glass ceramic for potential x-ray detection. Ceram. Int. 46, 10718 (2020).
Y. Zhou, J. Chen, O.M. Bakr, and O.F. Mohammed, Metal halide perovskites for x-ray imaging scintillators and detectors. ACS Energy Lett. 6, 739 (2021).
J. Tous, K. Blazek, M. Kucera, M. Nikl, and J.A. Mares, Scintillation efficiency and x-ray imaging with the RE-doped LuAG thin films grown by liquid phase epitaxy. Radiat. Meas. 47, 311 (2012).
X. Zhang, G. Zhou, J. Zhou, H. Zhou, P. Kong, Z. Yu, and J. Zhan, Energy transfer from Bi3+ to Ho3+ triggers brilliant single green light emission in LaNbTiO6:Ho3+, Bi3+ phosphors. RSC Adv. 4, 13680 (2014).
H.R. Gonçalves, Y. Messaddeq, A. Chiasera, Y. Jes, M. Ferrari, and S.J.L. Ribeiro, Erbium-activated silica–zirconia planar waveguides prepared by sol–gel route. Thin Solid Films 516, 3094 (2008).
M. Mortier, Between glass and crystal: glass–ceramics, a new way for optical materials. Philos. Mag. 82, 745 (2002).
V. Dubey, J. Kaur, and S. Agrawal, Effect of europium doping levels on photoluminescence and thermoluminescence of strontium yttrium oxide phosphor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 31, 27 (2015).
Y. Gong, Y. Wang, Y. Li, X. Xu, and W. Zeng, Fluorescence and phosphorescence properties of new long-lasting phosphor Ba4(Si3O8)2:Eu2+, Dy3+. Opt. Exp. 19, 4310 (2011).
S. Kumar, A.K. Gathania, A. Vij, and R. Kumar, Gamma induced thermoluminescence and color centers study of Dy doped LiF micro-cubes. Ceram. Int. 42, 14511 (2016).
Y. Horowitz, The annealing characteristics of LiF:Mg, Ti. Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 30, 219 (1990).
A. Wiatrowska, and E. Zych, Lu2O3:Pr, Hf storage phosphor: compositional and technological issues. Materials 7, 157 (2014).
H.G. Balian, and N.W. Eddy, Figure-of-merit (FOM), an improved criterion over the normalized chi-squared test for assessing goodness-of-fit of gamma-ray spectral peaks. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 145, 389 (1977).
S.K. Misra, and N.W. Eddy, IFOM, a formula for universal assessment of goodness-of-fit of gamma ray spectra. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 166, 537 (1979).
M. Balarin, Half-width and asymmetry of glow peaks and their consistent analytical representation. J. Therm. Anal. 17, 319 (1979).
R. Chen, V. Pagonis, and J.L. Lawless, Evaluated thermoluminescence trapping parameters—What do they really mean? Radiat. Meas. 91, 21 (2016).
S. Gültekin, S. Yıldırım, O. Yılmaz, İÇ. Keskin, M.İ Katı, and E. Çelik, Structural and optical properties of SrAl2O4:Eu2+/Dy3+ phosphors synthesized by flame spray pyrolysis technique. J. Lumin. 206, 59 (2019).
Acknowledgments
We performed the spectroscopic and structural analyzes ourselves.
Funding
No funding supported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
We accept the ethical statement.
Human and animal rights
Our article does not include humans and animals.
Consent to publications
We have consent for the publication and there is no private information.
Data availability
There is no such situation.
Code availability
There is no such situation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Keskin, İ.Ç., İlhan, M. Thermoluminescence Kinetic Parameters and Radioluminescence of RE3+ (RE = Pr, Sm, Tb, Ho, Er)-Doped Barium Tantalate Phosphors. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 5614–5630 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10501-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10501-y