Abstract
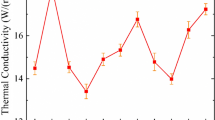
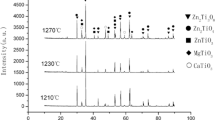
MO-ZrO2-Ta2O5 (M = Zn, Co) ceramics were prepared by solid-phase reaction method. Thermo-gravimetric-differential thermal behavior, crystal structure, and microwave dielectric properties of ZnO-ZrO2-Ta2O5 and CoO-ZrO2-Ta2O5 ceramics were compared in this paper. Both of them exhibited monoclinic wolframite structure. Densest microstructures with uniform grains were obtained at 1400°C and 1425°C in the cases of M = Zn and Co, respectively. ZnO-ZrO2-Ta2O5 and CoO-ZrO2-Ta2O5 exhibited comparable εr ~ 20.26 and 24.30, while the former had Q × f ~ 60, 983 GHz and the latter had Q × f ~ 95,300 GHz. The grain growth exponent and activation energy obtained from the phenomenological kinetic equation indicated the growth process of ceramics. The grain growth of Zn-based ceramic was dominated by interfacial reactions and lattice diffusion. For the other one, the grain growth mechanisms were grain boundary diffusion and lattice diffusion at high temperatures. The grain growth progress of them both affected by lattice diffusion. The growth process of ZnO-ZrO2-Ta2O5 ceramics was faster than that of CoO-ZrO2-Ta2O5 ceramic. However, the grains were overgrown and grew slowly at 1425°C and 1450°C, which was caused by the excessive high temperature.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Rangan, T.S. Rappaport, and E. Erkip, Millimeter wave cellular wireless networks: potentials and challenges. Proc. IEEE 102(3), 366–385 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2014.2299397.
T.S. Rappaport, S. Shu, R. Mayzus, Z. Hangd, and F. Gutierrezt, Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5G cellular: it will work! IEEE Access 1(1), 335–349 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2013.2260813.
J.K. Plourde, and C.L. Ren, Application of dielectric resonators in microwave components. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory 29(8), 754–770 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.1981.1130444.
J. Petzelt, S. Kamba, G.V. Kozlov, and A.A. Volkov, Dielectric properties of microwave ceramics investigated by infrared and submillimetre spectroscopy. Ferroelectrics 176(1), 145–165 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150199608223607.
C.F. Shih, W.M. Li, K.S. Tung, and W.D. Hsu, Low-loss microwave dielectric material base on magnesium titanate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93(9), 2448–2451 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.03790.x.
Q.W. Liao, L.X. Li, P. Zhang, X. Ding, X. Ren, and W. Zhang, A microwave dielectric material for microstrip patch antenna substrate. J. Mater. Res. 26(19), 2503–2510 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.281.
H.W. Lee, J.H. Park, S. Nahm, D.W. Kim, and J.G. Park, Low-temperature sintering of temperature-stable LaNbO4 microwave dielectric ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 45(1), 21–24 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2009.09.008.
H. Jantunen, R. Rautioaho, A. Uusimäki, and S. Leppävuori, Compositions of MgTiO3-CaTiO3 ceramic with two borosilicate glasses for LTCC technology. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 20(14–15), 2331–2336 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-2219(00)00145-X.
L. Fang, Q. Yu, C.Z. Hu, and H. Zhang, High dielectric constant and low-loss dielectric ceramics of Ba5LnZnNb9O30 (Ln = La, Nd and Sm). Mater. Lett. 61(19), 4140–4143 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2007.01.068.
S.D. Ramarao, and V. Murthy, Crystal structure refinement and microwave dielectric properties of new low dielectric loss AZrNb2O8 (A: Mn, Zn, Mg and Co) ceramics. Scr. Mater 69(3), 274–277 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.04.018.
Z. Feng, C.F. Xing, J.X. Bi, X.S. Jiang, and H.T. Wu, Sintering characteristics and microwave dielectric properties of low loss CoZrNb2O8 ceramics achieved by reaction sintering process. J. Alloys Compd. 686, 923–929 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.06.219.
Q.W. Liao, L.X. Li, X. Ren, X.X. Yu, and D. Guo, A low sintering temperature low loss microwave dielectric material ZnZrNb2O8. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95(11), 3363–3365 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2012.05450.x.
H.L. Pan, C.F. Xing, J.X. Bi, X.S. Jiang, and H. Wu, Sintering characteristics and microwave dielectric properties of low loss ZnZrNb2O8 ceramics achieved by reaction sintering process. J. Alloys Compd. 687(6), 274–279 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.06.029.
X.S. Lyu, L.X. Li, S. Zhang, H. Sun, S. Li, J. Ye, B.W. Zhang, and J.T. Li, A new low-loss dielectric material ZnZrTa2O8 for microwave devices. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36(3), 931–935 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.11.015.
W.S. Xia, L.Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, S.E. Jin, Y.P. Xu, Z.W. Zuo, and L.W. Shi, Extrinsic effects on microwave dielectric properties of high-Q MgZrTa2O8 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(11), 11325–11330 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5256-0.
Y. Zhang, S.H. Ding, T.X. Song, and Y.C. Zhang, Microwave dielectric properties of temperature stable MO-ZrO2-Ta2O5 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 798, 194–203 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.251.
W.Y. Du, Y.L. Ai, W.H. Chen, W. He, J.J. Zhang, Y.Q. Fan, and Y.X. Gong, Grain growth kinetics and growth mechanism of columnar Al2O3 crystals in xNb2O5-7.5La2O3- Al2O3 ceramic composites. Ceram. Int. 45(6), 6788–6794 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.171.
D.W. Ni, K.B. Andersen, and V. Esposito, Sintering and grain growth kinetics in La0.85Sr0.15MnO3-Ce0.9Gd0.1O1.95 (LSM-CGO) porous composite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34(15), 3769–3778 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.04.044.
W. Zhang, L. Chen, C.G. Xu, X.M. Lv, Y.J. Wang, J.H. Ouyang, and Y. Zhou, Grain growth kinetics and densification mechanism of (TiZrHfVNbTa)C high-entropy ceramic under pressureless sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 110(30), 57–64 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.08.070.
L. Chen, Y.L. Ai, Q.J. Yu, W.H. Chen, W. He, J.J. Zhang, and X.X. Min, Study on the growth kinetics of Al2O3 columnar crystal in Al2O3 matrix composite ceramics prepared by microwave sintering. J. Cryst. Growth 507, 395–401 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2018.11.039.
X.C. Wang, J. Zhao, E.Z. Cui, Z.F. Sun, and H. Yu, Grain growth kinetics and grain refinement mechanism in Al2O3 /WC/TiC/graphene ceramic composite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41(2), 1391–1398 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.10.019.
B.W. Hakki, and P.D. Coleman, A dielectric resonator method of measuring inductive capacities in the millimeter rang. IEEE Trans. 8(4), 402–410 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1109/tmtt.1960.1124749.
W.E. Courtney, Analysis and evaluation of a method of measuring the complex permittivity and permeability microwave insulators. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory 18(8), 476–485 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.1970.1127271.
J. Liu, J. Baeyens, Y.M. Deng, X.L. Wang, and H.L. Zhang, High temperature Mn2O3/Mn3O4 and Co3O4/CoO systems for thermo-chemical energy storage. J. Environ. Manag. 267, 110582 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110582.
N. Nekokar, M. Pourabdoli, A.G. Hamidi, and D. Uner, Effect of mechanical activation on thermal energy storage properties of Co3O4/CoO system. Adv. Powder Technol. 29(2), 333–340 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.11.020.
C.L. Huang, J.L. Huang, and T.H. Hsu, Microwave dielectric properties of novel Na2Mg5−xZnx (MoO4)6 (x = 0–0.09) ceramics for ULTCC applications. Mater. Res. Bull 141, 141111355 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111355.
R. Gupta, D.H. Kim, and H.T. Kim, Microwave dielectric properties and thermal conductivities of low-temperature sintered (Na1−xKx)2MoO4 (x ≤ 0.2) ceramics. Ceram Int. 48, 15282–15292 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.02.062.
H. Deng, T.H. Yuan, R.D. Li, F.H. Zeng, G.H. Liu, and X. Zhou, Spark plasma sintering of pure tungsten powder: densification kinetics and grain growth. Powder Technol. 310, 264–271 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.01.050.
J.E. Burke and D. Turnbull, Recrystallization and grain growth. Progr. Met. Phys. 3, 220–292 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1016/0502-8205(52)90009-9.
A.J. Ardell, On the coarsening of grain boundary precipitates. Acta Metall. 20(4), 601–609 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(72)90015-6.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51902268); the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2021YFG0235).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X., Zhang, Y., Ding, S. et al. Structure, Dielectric Properties, and Grain Growth Kinetics of MO-ZrO2-Ta2O5 (M = Zn, Co) Microwave Ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 2614–2625 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10224-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10224-0