Abstract
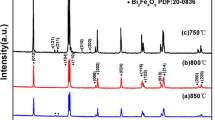
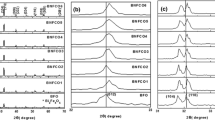
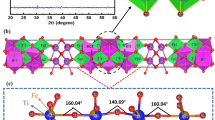
To understand the multiferroic behavior of the Y and Mn co-doped Bi0.9La0.1FeO3 system, we have synthesized Bi0.9La0.1FeO3 with the co-doped composition of Bi(0.9−a)YaLa0.1Fe (1−b)MnbO3 (a = 0.05, b = 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, and a = 0.10, b = 0.10) using the solid-state reaction method. The role of Y and Mn co-doping on the structural, magnetic, ferroelectric, and dielectric properties were studied by various characterization techniques, such as x-ray diffraction, vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), polarization–electric field (P–E) loop tracer, and dielectric measurements. X-ray diffraction studies show that a 5% doped sample is single phasic nature and crystallizes in rhombohedral (R3c) symmetry, whereas higher doped samples are dual-phase in nature with minor impurity Bi2Fe4O9 and crystallize in rhombohedral (R3c) and cubic (Pm-3 m) modulation in structural parameters with Y and Mn doping. The modulation in magnetic behavior with Y and Mn doping has been investigated and studied in the context of modification in the different interactions. P–E loop behavior is observed for lower Y (5%) and Mn (5, 10, 15%) doped samples, whereas a lossy/leaky loop is found for higher doped samples (Y-5, 10%, and Mn-20%). Lastly, the real and imaginary parts of dielectric permittivity indicate doping-induced increases in the values of ε′ and ε″.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Eerenstein, N.D. Mathur, and J.F. Scott, Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442, 759–765 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05023.
J. Dho, X. Qi, H. Kim, J.L. MacManus-Driscoll, and M.G. Blamire, Large Electric Polarization and Exchange Bias in Multiferroic BiFeO3. Adv. Mater. 18, 1445–1448 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200502622.
N.A. Hill and A. Filippetti, Why are There Any Magnetic Ferroelectrics? J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 242–245, 976–979 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(01)01078-2.
U. Nuraini and S. Suasmoro, Crystal Structure and Phase Transformation of BiFeO3 Multiferroics on the Temperature Variation. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 817, 012059 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/817/1/012059.
A.J. Jacobson and B.E.F. Fender, A Neutron Diffraction Study of the Nuclear and Magnetic Structure of BiFeO3. J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 8, 844–850 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3719/8/6/015.
W. Prellier, M.P. Singh, and P. Murugavel, The Single-Phase Multiferroic Oxides: From Bulk to Thin Film. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 17, R803–R832 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/17/30/R01.
J. Silva, A. Reyes, H. Esparza, H. Camacho, and L. Fuentes, BiFeO3: A Review on Synthesis, Doping and Crystal Structure. Integr. Ferroelectr. 126, 47–59 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2011.574986.
J. Schiemer, R. Withers, L. Noren, L. Yun, L. Bourgeois, and G. Stewart, Detailed Phase Analysis and Crystal Structure Investigation of a Bi1-xCaxFeO3-x/2 Perovskite-Related Solid Solution Phase and Selected Property Measurements Thereof. Chem Mater. 21, 4223–4232 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm901757h.
D. Varshney, A. Kumar, and K. Verma, Effect of A Site and B Site Doping on Structural, Thermal and Dielectric Properties of BiFeO3 Ceramics. J Alloys Compd 509, 8421–8426 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.05.106.
G.L. Yuan, K.Z. Baba-Kishi, J.M. Liu, S.W. Or, Y.P. Wang, and Z.G. Liu, Multiferroic Properties of Single-Phase Bi0.85La0.15FeO3 Lead-Free Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89, 3136–3139 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2006.01186.x.
H. Wu, Y.B. Lin, J.J. Gong, F. Zhang, M. Zeng, M.H. Qin, Z. Zhang, Q. Ru, Z.W. Liu, X.S. Gao, and J.M. Liu, Significant Enhancements of Dielectric and Magnetic Properties in Bi(Fe1-xMgx)O3–x/2 Induced by Oxygen Vacancies. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46, 145001 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/46/14/145001.
S.T. Zhang, Y. Zhang, M.H. Lu, C.L. Du, Y.F. Chen, Z.G. Liu, Y.Y. Zhu, N.B. Ming, and X.Q. Pan, Substitution-Induced Phase Transition and Enhanced Multiferroic Properties of Bi1-xLaxFeO3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 162901 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2195927.
N. Jeon, D. Rout, I.W. Kim, and S.J.L. Kang, Enhanced Multiferroic Properties of Single-Phase BiFeO3 Bulk Ceramics by Ho Doping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 072901 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3552682.
P. Uniyal and K.L. Yadav, Room Temperature Multiferroic Properties of Eu Doped BiFeO3. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 07D914 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3072087.
G.L. Yuan, S.W. Or, J.M. Liu, and J.M. Liu, Structural Transformation and Ferroelectromagnetic Behavior in Single-Phase Bi1-XNdxFeO3 Multiferroic Ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 052905 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2266992.
Z. Yan, K.F. Wang, J.F. Qu, Y. Wang, Z.T. Song, and S.L. Feng, Processing and Properties of Yb-Doped BiFeO3 Ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 082906 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2775034.
A. Ravalia, M. Vagadia, P.S. Solanki, S. Gautam, K.H. Chae, K. Asokan, N.A. Shah, and D.G. Kuberkar, Role of Defects in BiFeO3 Multiferroic Films and Their Local Electronic Structure by X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy. J Appl Phys 116, 153701 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4898196.
A. Ablat, E. Muhemmed, C. Si, J. Wang, H. Qian, R. Wu, N. Zhang, R. Wu, and K. Ibrahim, Electronic Structure of BiFe1−xMnxO3 Thin Films Investigated by X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy. J Nanomater (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/123438.
H. Liu, Z. Liu, and K. Yao, Improved Electric Properties in BiFeO3 Films by the Doping of Ti. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 41, 123–128 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-006-0514-x.
X. Qi, J. Dho, R. Tomov, M.G. Blamire, and J.L. MacManus-Driscoll, Greatly Reduced Leakage Current and Conduction Mechanism in aliovalent-Ion-Doped BiFeO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 062903 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1862336.
A. Mukherjee, M. Banerjee, S. Basu, P.M.G. Nambissan, and M. Pal, Gadolinium Substitution Induced Defect Restructuring in Multiferroic BiFeO3 Case Study by Positron Annihilation Spectroscopy. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46, 495309 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/46/49/495309.
A. Mukherjee, S. Basu, G. Chakraborty, and M. Pal, Effect of Y-Doping on the Electrical Transport Properties of Nanocrystalline BiFeO3. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 014321 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4734005.
S.J. Chiu, Y.T. Liu, G.P. Yu, H.Y. Lee, and H.J. Huang, The Structure and Ferroelectric Property of La-doped BiFeO3/SrTiO3 Artificial Superlattice Structure by RF Sputtering: Effect of Deposition Temperature. Thin Solid Films 529, 85–88 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2012.02.033.
M. Zhong, N.P. Kumar, E. Sagar, Z. Jian, H. Yemin, and P.V. Reddy, Structural Magnetic and Dielectric Properties of Y Doped BiFeO3. Mater. Chem. Phys. 173, 126–131 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.01.047.
M.B. Bellakki and V. Manivannan, Citrate-gel Synthesis and Characterization of Yttrium-Doped Multiferroic BiFeO3. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 53, 184–192 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-009-2076-1.
V. Srinivas, A.T. Raghavender, and K. Vijaya Kumar, Structural and Magnetic Properties of Mn Doped BiFeO3 Nanomaterials. Phys Resear Int (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4835328.
S. Chauhan, M. Kumar, S. Chhoker, S.C. Katyal, H. Singh, M. Jewariya, and K.L. Yadav, Multiferroic, Magnetoelectric and Optical Properties of Mn-Doped BiFeO3 Nanoparticles. Solid State Commun 152, 525–529 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2011.12.037.
J.Z. Huang, Y. Wang, Y. Lin, M. Li, and C.W. Nan, Effect of Mn Doping on Electric and Magnetic Properties of BiFeO3 Thin Films by Chemical Solution. J Appl Phys 106, 063911 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3225559.
J. Silva, A. Reyes, R. Castaneda, H. Esparza, H. Camacho, J. Matutes, and L. Fuentes, Structure and Electromagnetic Properties of Bi1−xYxFe0.95Mn0.05O3 (x=0.05, 0.075, 0.10). Ferroelectrics 426, 103–111 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2012.671624.
R. Palkar, D.C. Kundaliya, and S.K. Malik, Effect of Mn Substitution on Magnetoelectric Properties of Bismuth Ferrite System. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 4337 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1558992.
S. Mukherjee, L.A.W. Basu, N.T.K. Green, and M. Thanh, Pal, Enhanced Multiferroic Properties of Y and Mn Codoped Multiferroic BiFeO3 Nanoparticles. J Mater Sci. 50, 1891–1900 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8752-8.
M. Mukherjee, S. Banerjee, N.T.K. Basu, L.A.W. Thanh, and M. Green, Pal, Enhanced Magnetic and Electrical Properties of Y and Mn co-doped BiFeO3 Nanoparticles. Physica B 448, 199–203 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2014.03.082.
D. Varshney, A. Kumar, and K. Verma, Effect of A Site and B Site Doping on Structural, Thermal and Dielectric Properties of BiFeO3 Ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 8421–8426 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.05.106.
K. Momma and F. Izumi, VESTA 3 for Three-Dimensional Visualization of Crystal, Volumetric and Morphology Data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 44, 1272–1276 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889811038970.
P. Trivedi, F. Singh, B. Vyas, H. Kundalia, D.K. Shukla, S. Rayaprol, and D.G. Kuberkar, Stiffening of Phonons with Enhanced Hybridization and Structural Phase Transformation Upon Pr-Doping in BiFeO3. Physica B Phys Condens Matt 571, 247–251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.07.021.
R.A. Young ed., The Rietveld Method. (New York: Oxford University Press), 1993).
RA Agarwal, S Sanghi, AN Ahlawat, and Monica, Phase Transformation, Dielectric and Magnetic Properties of Nb-Doped Bi0.8Sr0.2FeO3 Multiferroics, J. Appl. Phys., 111, 113917 (2012); doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4728981
F. Huang, Z. Wang, Lu. Xiaomei, J. Zhang, K. Min, W. Lin, R. Ti, Xu. TingTing, Ju. He, C. Yue, and J. Zhu, Peculiar Magnetism of BiFeO3 Nanoparticles with Size Approaching the Period of the Spiral Spin Structure. Sci Rep 3, 2907 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02907.
D.K. Rana, S.K. Kundu, R.J. Choudhary, and S. Basu, Enhancement of Electrical and Magnetodielectric Properties of BiFeO3 Incorporated PVDF Flexible Nanocomposite Films. Mater Resear Expr 6, 0850d9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab26de.
A. Khomchenko, I.O. Troyanchuk, D.V. Karpinsky, S. Das, V.S. Amaral, M. Tovar, V. Sikolenko, and J.A. Paixão, Structural Transitions and Unusual Magnetic Behaviour in Mn-doped Bi1−xLaxFeO3 Perovskites. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 084102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4759435.
R.P. Maiti, S. Basu, and D. Chkaravorty, Synthesis of Nanocrystalline YFeO3 and its Magnetic Properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3274–3277 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.05.061.
B. Deka, S. Ravi, A. Perumal, and D. Pamu, Effect of Mn Doping on Magnetic and Dielectric Properties of YFeO3. Ceram Int 43, 1323–1334 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.10.087.
Wu. Jiangtao, N. Li, Xu. Jun, S. Zhou, Y. Jiang, and Z. Xie, Synthesis, Phase Diagram and Magnetic Properties of (1–x)BiFeO3-xLaMnO3 Solid Solution. J. Alloy. Compd. 634, 142–147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.01.283.
A. Wrzesinska, A. Khort, M. Witkowski, J. Szczytko, J. Ryl, J. Gurgul, D.S. Kharitonov, K. Łątka, T. Szumiata, and A. Wypych-Puszkarz, Structural, Electrical and Magnetic Study of La-, Eu-, and Er-Doped Bismuth Ferrite Nanomaterials Obtained by Solution Combustion Synthesis. Sci Rep 11, 22746 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01983-z.
R. Das, T. Sarkar, and K. Mandal, Multiferroic Properties of Ba2+ and Gd3+ Co-Doped Bismuth Ferrite: Magnetic, Ferroelectric and Impedance Spectroscopic Analysis. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 45, 455002 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/45/45/455002.
S.K. Pradhan and B.K. Roul, Effect of Gd Doping on Structural, Electrical and Magnetic Properties of BiFeO3 Electroceramic. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 72, 1180–1187 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2011.07.017.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Prof. D.G. Kuberkar, Saurashtra University, Rajkot for his guidance and motivation. The authors are thankful to the Department of Physics, Saurashtra University, Rajkot for providing the XRD and P–E loop facility. The authors thank Prof. A. K. Nigam, TIFR, for magnetization measurements. M.V. acknowledges DST, India for the INSPIRE faculty award (DST/INSPIRE/04/2017/003059). ABR is thankful to IUAC New Delhi for UFR-65319 and UGC-DAE, CSR, Indore for CSR-IC-ISUM-64/ CRS-347/2020-21/949 Project funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support or personal relationships that could have appeared to affect the work reported in this paper. We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. We further confirm that the authorship order listed in the manuscript has been approved by all of us.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jose, P.J., Rathod, U., Savaliya, C. et al. Studies on Multiferroic Behavior of Y-Mn Co-Doped Bi0.9La0.1FeO3. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 6689–6698 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09972-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09972-2