Abstract
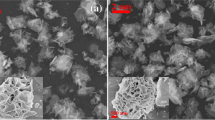
A high-density and low-cost hydrogen generation technology is required for hydrogen energy systems. Non-noble multimetallic Co-Mn-B nanoparticles can serve as a good catalyst because of their low cost and ability to produce hydrogen gas during the catalytic semi-methanolysis process. This work reports the synthesis, characterization, and the use of Co-Mn-B catalyst supported on Eupergit CM as a very active and reusable catalyst for the generation of hydrogen from the semi-methanolysis of ammonia borane (AB). Solid materials were characterized by x-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Rates of hydrogen generation were used to determine the kinetics of semi-methanolysis reaction. The parameters examined, namely the percentage of NaOH, percentage of metal loading, amount of catalyst particles, and AB concentrations and temperatures, were 1–5 (wt)%, 5–10 (wt)%, 5–50 mg, 0.5–3 mmol, and 30–60°C, respectively. Total turnover frequency (TOF) value, hydrogen generation rate, and activation energy (Ea) were obtained at 30°C as 15,751 h−1, 17,324 mL gcat−1min−1 (3 mmol AB and 25 mg Co-Mn-B/Eupergit CM), and 43.936 kJ mol−1, respectively.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Momirlan, and T.N. Veziroglu, The properties of hydrogen as fuel tomorrow in sustainable energy system for a cleaner planet. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 30, 795–802 (2005).
H.N. Abdelhamid, Dehydrogenation of sodium borohydride using cobalt embedded zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. J. Solid State Chem. 297, 122034 (2021).
R.J. Keaton, J.M. Blacquiere, and R.T. Baker, Base metal catalyzed dehydrogenation of ammonia-borane for chemical hydrogen storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 1844 (2007).
H.C. Kazici, S. Yilmaz, T. Sahan, F. Yildiz, O.F. Er, and H. Kivrak, A comprehensive study of hydrogen production from ammonia borane via PdCoAg/AC nanoparticles and anodic current in alkaline medium: experimental design with response surface methodology. Front. Energy 14, 578–589 (2020).
H.C. Kazici, F. Yildiz, M.S. Izgi, B. Ulas, and H. Kivrak, Novel activated carbon supported trimetallic PdCoAg nanoparticles as efficient catalysts for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44, 10561–10572 (2019).
H.C. Kazici, F. Salman, M.S. Izgi, and O. Sahin, Synthesis of metal-oxide-supported triple nano catalysts and application to H-2 production and H2O2 oxidation. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 3634–3644 (2020).
H.N. Abdelhamid, Salts induced formation of hierarchical porous ZIF-8 and their applications for CO2 sorption and hydrogen generation via NaBH4 hydrolysis. Macromol. Chem. Phys 221, 2000031 (2020).
P.A. Storozhenko, R.A. Svitsyn, V.A. Ketsko, A.K. Buryak, and A.V. Ul’yanov, Ammineborane: synthesis and physicochemical characterization. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 50, 980–985 (2005).
C.T.F. Lo, K. Karan, and B.R. Davis, Kinetic studies of reaction between sodium borohydride and methanol, water, and their mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 46, 5478–5484 (2007).
B.H. Liu, Z.P. Li, and S. Suda, Nickel- and cobalt-based catalysts for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of borohydride. J. Alloy. Compd. 415, 288–293 (2006).
Q.L. Yao, K. Yang, X.L. Hong, X.S. Chen, and Z.H. Lu, Base-promoted hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane catalyzed by noble-metal-free nanoparticles. Catal. Sci. Technol. 8, 870–877 (2018).
O. Sahin, M. Kaya, M.S. Izgi, and C. Saka, The effect of microwave irradiation on a co-b-based catalyst for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of NaBH4 solution. Energy Sourc. Part a-Recov. Utiliz. Environ. Effects 37, 462–467 (2015).
Q.L. Yao, W.M. Shi, G. Feng, Z.H. Lu, X.L. Zhang, D.J. Tao, D.J. Kong, and X.S. Chen, Ultrafine Ru nanoparticles embedded in SiO2 nanospheres: Highly efficient catalysts for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. J. Power Sourc. 257, 293–299 (2014).
Q.L. Yao, Z.H. Lu, Y.S. Jia, X.S. Chen, and X. Liu, In situ facile synthesis of Rh nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes as highly active catalysts for H-2 generation from NH3BH3 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 40, 2207–2215 (2015).
N. Cao, J. Su, W. Luo, and G.Z. Cheng, Graphene supported Ru@Co core-shell nanoparticles as efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane and methylamine borane. Catal. Commun. 43, 47–51 (2014).
M. Navlani-Garcia, K. Mori, Y. Kuwahara, and H. Yamashita, Recent strategies targeting efficient hydrogen production from chemical hydrogen storage materials over carbon-supported catalysts. Npg Asia Mater. 10, 277–292 (2018).
T. Hugle, M.F. Kuhnel, and D. Lentz, Hydrazine borane: a promising hydrogen storage material. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 7444–7446 (2009).
P.P.V. Ramachandran, and P.D. Gagare, Preparation of ammonia borane in high yield and purity, methanolysis, and regeneration. Inorg. Chem. 46, 7810 (2007).
F.H. Stephens, V. Pons, and R.T. Baker, Ammonia-borane: the hydrogen source par excellence? Dalton Trans. 25, 2613–2626 (2007).
T. Umegaki, J.M. Yan, X.B. Zhang, H. Shioyama, N. Kuriyama, and Q. Xu, Boron- and nitrogen-based chemical hydrogen storage materials. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 34, 2303 (2009).
W.W. Zhan, Q.L. Zhu, and Q. Xu, Dehydrogenation of ammonia borane by metal nanoparticle catalysts. ACS Catal 6, 6892–6905 (2016).
Storozhenko PA, Svitsyn RA, Ketsko VA, Buryak AK, Ul’yanov AV. Ammine borane: synthesis and physicochemical characterization. Russ J. Inorg. Chem. 50, 1066-71, (2005)
M. Yurderi, A. Bulut, I.E. Ertas, M. Zahmakiran, and M. Kaya, Supported copper-copper oxide nanoparticles as active, stable and low-cost catalyst in the methanolysis of ammonia-borane for chemical hydrogen storage. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 165, 169–175 (2015).
D.D. Ke, J. Wang, H.M. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Zhang, X. Zhao, S.M. Han, Hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane catalyzed by poly(amidoamine) dendrimers-modified reduced graphene oxide nanosheets supported Ag(0.3)Co(0.7 )nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34, 2350-2358 (2018).
H.N. Abdelhamid, A review on hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 46, 726–765 (2021).
R.M. da Silva, P.M.P. Souza, F.A.N. Fernandes, L.R.B. Goncalves, and S. Rodrigues, Co-immobilization of dextransucrase and dextranase in epoxy-agarose- tailoring oligosaccharides synthesis. Process Biochem. 78, 71–81 (2019).
P. Torres, A. Datla, V.W. Rajasekar, S. Zambre, T. Ashar, M. Yates, M.L. Rojas-Cervantes, O. Calero-Rueda, V. Barba, M.J. Martinez, A. Ballesteros, and F.J. Plou, Characterization and application of a sterol esterase immobilized on polyacrylate epoxy-activated carriers (Dilbeads (TM)). Catal. Commun. 9, 539–545 (2008).
M.S. Izgi, O. Sahin, E. Onat, and C. Saka, Epoxy-activated acrylic particulate polymersupported Co-Fe-Ru-B catalyst to produce H2 from hydrolysis of NH3BH3. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 45, 22638–22648 (2020).
J. Hannauer, U.B. Demirci, G. Pastor, C. Geantet, J.M. Herrmannb, and P. Miele, Hydrogen release through catalyzed methanolysis of solid sodium borohydride. Energy Environ. Sci. 3, 1796 (2010).
X. Zhang, Y.T. Qian, Y.C. Zhu, and K.B. Tang, Synthesis of Mn2O3 nanomaterials with controllable porosity and thickness for enhanced lithium-ion batteries performance. Nanoscale 6, 1725–1731 (2014).
M.S. Izgi, M.S. Ece, H.C. Kazici, O. Sahin, and E. Onat, Hydrogen production by using Ru nanoparticle decorated with Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 core-shell microspheres. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 45, 30415–30430 (2020).
N. Sahiner, and A.O. Yasar, A new application for colloidal silica particles: natural, environmentally friendly, low-cost, and reusable catalyst material for H-2 production from NaBH4 methanolysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 11245–11252 (2016).
F. Ali, S.B. Khan, and A.M. Asiri, Chitosan coated cellulose cotton fibers as catalyst for the H-2 production from NaBH4 methanolysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44, 4143–4155 (2019).
H. Erdogan, O. Metin, and S. Ozkar, Hydrogen generation from the methanolysis of ammonia borane catalyzed by in situ generated, polymer stabilized ruthenium(0) nanoclusters. Catal. Today 170, 93–98 (2011).
S.B. Kalidindi, U. Sanyal, and B.R. Jagirdar, Nanostructured Cu and Cu@Cu2O core shell catalysts for hydrogen generation from ammonia-borane. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10, 5870–5874 (2008).
S.B. Kalidindi, A.A. Vernekar, and B.R. Jagirdar, Co-Co2B, Ni-Ni3B and Co-Ni-B nanocomposites catalyzed ammonia-borane methanolysis for hydrogen generation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 770–775 (2009).
D.H. Sun, V. Mazumder, O. Metin, and S.H. Sun, Methanolysis of ammonia borane by CoPd nanoparticles. ACS Catal. 2, 1290–1295 (2012).
N. Tunc, and M. Rakap, Preparation and characterization of Ni-M (M: Ru, Rh, Pd) nanoclusters as efficient catalysts for hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane methanolysis. Renew. Energy 155, 1222–1230 (2020).
D. Ozhava, N.Z. Kilicaslan, and S. Ozkar, PVP-stabilized nickel(0) nanoparticles as catalyst in hydrogen generation from the methanolysis of hydrazine borane or ammonia borane. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 162, 573–582 (2015).
S. Caliskan, M. Zahmakiran, and S. Ozkar, Zeolite confined rhodium(0) nanoclusters as highly active, reusable, and long-lived catalyst in the methanolysis of ammonia-borane. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 93, 387–394 (2010).
J.H. Kim, K.T. Kim, Y.M. Kang, H.S. Kim, M.S. Song, Y.J. Lee, P.S. Lee, and J.Y. Lee, Study on degradation of filamentary Ni catalyst on hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. J. Alloy. Compd. 379, 222–227 (2004).
H.B. Dai, X.D. Kang, and P. Wang, Ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized in montmorillonite used as catalyst for methanolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 35, 10317–10323 (2010).
Y. Shang, R. Chen, and G. Jiang, Kinetic study of NaBH4 hydrolysis over carbon-supported ruthenium. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 33, 6719–6726 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazıcı, H.Ç., İzgi, M.S. & Şahin, Ö. Co-Mn-B Nanoparticles Supported on Epoxy-Based Polymer as Catalyst for Evolution of H2 from Ammonia Borane Semi-Methanolysis. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 2356–2368 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09491-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09491-0