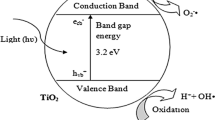
Abstract
The problem of water pollution has become an urgent global issue. As one approach for addressing this problem, in this work, rod-like ZnO nanostructures were synthesized by a simple electrodeposition method, which can purify wastewater by photocatalytic reaction. ZnO was deposited on indium tin oxide (ITO) conductive glass by electrodeposition, and then the surface of the sample was modified by 1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane to make the surface super-hydrophobic. ZnO nanorods with a “photocatalytic and self-cleaning” synergistic effect were obtained. The morphology and structure of the samples were analyzed by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and x-ray diffraction (XRD). FESEM images show that different deposition times, water bath temperatures, electrolysis times, and electrodeposition voltages have different effects on the surface morphology of the materials. XRD patterns show that the crystal structure of nano-ZnO is a hexagonal wurtzite crystalline structure. The optical properties of the samples were characterized by UV–Vis spectrophotometry. The hydrophobicity of the materials was characterized using a droplet shape analyzer. Photocatalysis results show that the modification can improve the photocatalytic efficiency of the materials. The results show that the material has excellent optical properties, and because of its super-hydrophobicity, there are no residual small particles on the surface after the photocatalytic reaction. Therefore, this material not only has high photocatalytic performance, but can also be recycled for treatment of water pollution.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Feng, J. Chen, L.Y. Guo, S.Y. Lei, and Y.R. Ni, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 8160 (2012).
A.A. Firooz, R.A. Mirzaie, and F. Kamrani, J. Struct. Chem. 59, 739 (2018).
Y.L. Chen, L.C. Kuo, M.L. Tseng, H.M. Chen, C.K. Chen, H.J. Huang, R.S. Liu, and D.P. Tsai, Opt. Express 21, 7240 (2013).
A.P. Bhirud, S.D. Sathaye, R.P. Waichal, L.K. Nikam, and B.B. Kale, Green Chem. 14, 2790 (2012).
F. Yan, S.W. Zhang, Y. Liu, H.F. Liu, F.Y. Qu, X. Cai, and X. Wu, Mater. Res. Bull. 59, 98 (2014).
C.Q. Zhu, B.A. Lu, Q. Su, E.Q. Xie, and W. Lan, Nanoscale 4, 3060 (2012).
M.B. Nayan, K. Namratha, and A.K. Byrappa, Physiol. Plant. 54, 451 (2006).
S.C. Shen, W.K. Ng, Z.Y. Zhong, Y.C. Dong, L.S.O. Chia, and R.B.H. Tan, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 1311 (2010).
J.S. Huang, and C.F. Lin, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 1897 (2008).
S.E. Ahn, J.S. Lee, H. Kim, S. Kim, B.H. Kang, H.K. Kang, and G.T. Kim, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 5022 (2004).
E. Danielson, V. Dhamodharan, A. Porkovich, P. Kumar, and M. Sowwan, Sci. Rep. 9, 17370 (2019).
A.M. Bagamadova, and A.K. Omaev, Tech. Phys. Lett. 41, 874 (2015).
C.L. Hong, E. Park, I. Shin, and J. Hong, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 41, 358 (2020).
D.L. Ramirez, K.N. Alvarez, G. Riveros, M. Ejos, and M.G. Lobos, Ecs Trans. 58, 117 (2013).
L. Shi, L. Liang, J. Ma, S.F. Zhong, F.X. Wang, and J.M. Sun, Ceram. Int. 40, 3495 (2014).
M. Ahmad, E. Ahmed, Y.W. Zhang, N.R. Khalid, J.F. Xu, M. Ullah, and Z.L. Hong, Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 697 (2013).
H. Agil, and N. Akduran, Adv. J. Sci. Eng. 1, 122 (2020).
O.M. Ozkendir, Adv. J. Sci. Eng. 1, 7 (2020).
M. Mirzaei, and M. Mirzaei, Phys. E 42, 2147 (2010).
A.S. Rad, A. Mirabi, M. Peyravi, and M. Mirzaei, Can. J. Phys. 95, 958 (2017).
M. Motahharinia, H.A. Zamani, and H.K. Maleh, Eur. Chem. Commun. 2, 760 (2020).
V.R. Shinde, C.D. Lokhande, R.S. Mane, and S.H. Han, Appl. Surf. Sci. 245, 407 (2005).
S.B. Kim, W.W. Lee, J. Yi, and W.L. Park, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 3910 (2012).
Y. Zhang, F. Fang, C. Wang, and L.D. Wang, Polym. Compos. 35, 1204 (2014).
Z.W. Liang, H. Cui, K. Wang, and P.H. Yang, CrystEngComm 14, 1723 (2012).
S.Y. Lin, Z.K. Xu, C.L. Wang, and D.X. Zhao, Ceram. Int. 42, 16424 (2016).
S.S. Shinde, P.S. Shinde, C.H. Bhosale, and K.Y. Rajpure, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 104, 425 (2011).
P. Shukla, I. Fatimah, S.B. Wang, H.M. Ang, and M.O. Tadé, Catal. Today 157, 410 (2010).
N. Shah, K. Bhangaonkar, D.V. Pinjari, and S.T. Mhaske, J. Adv. Nanomater. 2, 133 (2017).
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by Hubei Key Laboratory of Forensic Science (Hubei University of Police, No. 2018KFKT05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Li, X., Zhang, Q. et al. Electrodeposition of ZnO Nanorods with Synergistic Photocatalytic and Self-Cleaning Effects. Journal of Elec Materi 50, 4954–4961 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-08958-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-08958-w