Abstract
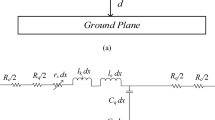
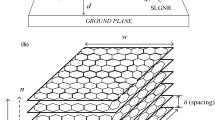
In this study, a thermally aware electrical equivalent single conductor along with an analytical model to evaluate the parasitic parameters of multilayer graphene nanoribbon (MLGNR) as an on-chip very-large-scale integration interconnect is proposed and its performance is analyzed in terms of delay, power dissipation, and power delay product (PDP) with variable temperatures ranging from 200 K to 500 K for 32 nm, 22 nm, and 16 nm technology nodes. It was observed that with a rise in the temperature, there is a sharp decrease in the mean free path of the GNR interconnect, which further dominates its own resistance at variable global lengths (500–2000 μm) for all three technology nodes. The Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis (SPICE) simulation tool is used to estimate and compare the performance of MLGNR in terms of signal delay, power dissipation, and PDP for three different technology nodes. It is revealed from the results that the propagation delay and PDP increase with increasing temperature. A similar analysis was also done for the copper interconnect and it was found that the MLGNR gives better performance in terms of delay, power dissipation, and PDP, at long interconnects (2000 μm) over a temperature range of 200–500 K for deep submicron technology nodes (32 nm, 22 nm, and 16 nm).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.M. Rossnagel and T.S. Kuan, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B: Microelectron. Nano Struct. Proces. Measurem. Phenom. 22, 240 (2004).
W. Steinhogl, G. Schindler, G. Steinlesberger, M. Traving, and M. Engelhardt, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 023706 (2005).
E.T. Ogawa, L. Ki-Don, V.A. Blaschke, and P.S. Ho, IEEE Trans. Reliab. 51, 403 (2002).
J.A. Davis and J.D. Meindl, Interconnect Technology and Design for Gigascale Integration, 1st ed. (Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media, 2003), pp. 1–398.
F. Kreupl, A.P. Graham, G.S. Duesberg, W. Steinhogl, M. Liebau, E. Unger, and W. Honlein, Microelectron. Eng. 64, 399 (2002).
N. Srivastava and K. Banerjee, in Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International conference on Computer-aided design. IEEE Computer Society (2005), pp. 383–390
M.K. Rai and S. Sarkar, Physic. Status Solid. (a) 208, 735 (2011).
M.K. Rai and S. Sarkar, J. Comput. Electron. 12, 796 (2013).
H. Li, W.Y. Yin, K. Banerjee, and J.F. Mao, IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 55, 1328 (2008).
A. Naeemi and J.D. Meindl, in Interconnect Technology Conference, IITC International. IEEE (2008), pp. 183–185
A.K. Geim and K.S. Novoselov, Nanosci. Technol. Collect. Rev. Nat. J. 11, 183 (2010).
S. Rakheja, V. Kumar, and A. Naeemi, in Proceedings of the IEEE (2013), pp. 1740–1765.
N. Srivastava and K. Banerjee, JOM 56, 30 (2004).
J. Hone, M. Whitney, C. Piskoti, and A. Zettl, Phys. Rev. B 59, R2514 (1999).
P. Kim, L. Shi, A. Majumder, and P.L. McEuen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 215502 (2001).
A.A. Balandin, S. Ghosh, W. Bao, I. Calizo, D. Tewldebrham, F. Miao, and C.N. Lau, Nano Lett. 8, 902 (2008).
C. Xu, H. Li, and K. Banerjee, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56, 1567 (2009).
H. Li, X. Xu, N. Srivastava, and K. Banerjee, IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 56, 1799 (2009).
V. Kumar, S. Rakheja, A. Naeemi, and I.E.E.E. Trans, Electron. Devices 59, 2753 (2012).
T. Ragheb and Y. Massoud, in Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design. IEEE Press (2008), pp. 593–597.
W.S. Zhao, W.Y. Yin, and I.E.E.E. Trans, Electromagn. Compat. 56, 638 (2014).
K. Singh and B. Raj, J. Electron. Mater. 44, 4825 (2015).
K. Singh and B. Raj, J. Comput. Electron. 14, 469 (2015).
V.R. Kumar, M.K. Majumder, N.R. Kukkam, and B.K. Kaushik, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 14, 484 (2015).
M.Y. Han, B. Ozyilmaz, Y. Zhang, and P. Kim, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 206805 (2007).
A. Naeemi and J.D. Meindl, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56, 1822 (2009).
D. Gunlycke, H.M. Lawler, and C.T. White, Phys. Rev. B 75, 085418 (2007).
V. Perebeinos and P. Avouris, Phys. Rev. B 81, 195442 (2010).
J.P. Cui, W.S. Zhao, W.Y. Yin, J. Hu, and I.E.E.E. Trans, Electromagn. Compat. 54, 126 (2012).
M.K. Rai, B.K. Kaushik, and S. Sankar, J. Comput. Electron. 15, 407 (2016).
Predictive technology model, http://ptm.asu.edu. Accessed 01 December, 2018.
D. Das, H. Rahaman, and I.E.E.E. Trans, Nanotechnol. 10, 1362 (2011).
ITRS, International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductor, Edition (2013), http://www.itrs2.net/itrs-reports.html. Accessed 01 December, 2018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, H., Sandha, K.S. Thermally Aware Modeling and Performance Analysis of MLGNR as On-Chip VLSI Interconnect Material. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 4902–4912 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07281-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07281-9