Abstract
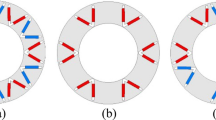
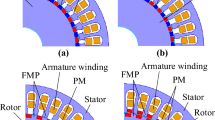
This paper proposes a dual-permanent-magnet-excited machine (DPMEM). It employs three sets of permanent magnets (PMs). The first set of PMs is magnetized radially, and located among the rotor slots. The second set is also magnetized radially, while equipped under the short stator iron teeth. The third set is magnetized circumferentially, and deployed in the slots formed by the long stator iron teeth and the second set of PMs. Two adjacent PMs magnetized circumferentially have opposite directions of magnetization, resulting in the so-called flux-focusing effect. Compared with the existing DPMEMs, the torque density of the proposed machine can be improved significantly, so as to exhibit promising potential for low-speed large-torque applications. Its operation principle is revealed by studying field harmonics in the air gap. The influences on overall performance of the proposed machine arising from the magnetization patterns, slot-pole combination and parameters are also studied by using the finite element method (FEM). Comparative study on the different machines formed by the combination of the three sets of PMs is performed by using the FEM. The results indicate that the proposed type of DPMEM contains six detailed types of PM machines, and can offer high torque density with low torque ripple, a high power factor and efficiency when compared with the six PM machines. Moreover, the magnetization pattern A or E and the ratio of p1 and p2 close to 1 are the best choice when designing this machine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.L. Li, K.T. Chau, M. Cheng, B. Kim, and R.D. Lorenz, IEEE Trans. Magn. 51, 1 (2015).
Y.T. Gao, R.H. Qu, D.W. Li, and F.X. Chen, IEEE Trans. Magn. 53, 1689 (2012).
Y.D. Deng, W. Fan, K. Ling, and C.Q. Su, J. Electron. Mater. 41, 1698 (2012).
J.M. Silveyra, P. Xu, V. Keylin, V. DeGeorge, A. Leary, and M.E. McHenry, J. Electron. Mater. 45, 219 (2016).
O. Lyan, V. Jankunas, E. Guseinoviene, A. Pasilis, A. Senulis, A. Knolis, and E. Kurt, J. Electron. Mater. 47, 4437 (2018).
X.L. Li, K.T. Chau, and Y.B. Wang, Energies 9, 1 (2016).
B. Kin, Energies 10, 1 (2017).
B. Kim and T.A. Lipo, IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 50, 3656 (2014).
W. Zhao, J. Zheng, J. Wang, G. Liu, J. Zhao, and Z. Fang, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63, 2072 (2016).
L. Xu, G. Liu, W. Zhao, Y. Yang, and R. Cheng, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64, 179 (2017).
S. Jia, R. Qu, J. Li, D. Li, and W. Kong, IEEE Trans. Magn. 53, 1 (2017).
H. Yang, H.Y. Lin, Z.Q. Zhu, S.H. Fang, and Y.K. Huang, Energies 9, 1 (2016).
R. Hosoya and S. Shimomura, in 8th International Conference on Power Electronics—ECCE Asia (2011), pp. 2208–2215.
R. Hosoya, H. Shimada, and S. Shimomura, in IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (2011), pp. 2790–2797.
S. Kazuhiro, R. Hosoya, and S. Shimomura, in 15th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (2012), pp. 1–6.
L. Jian, Y. Shi, C. Liu, G. Xu, Y. Gong, and C.C. Chan, IEEE Trans. Magn. 49, 2381 (2013).
W. Zhao, X. Sun, J. Ji, and G. Liu, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 26, 1 (2016).
Q. Wang and S. Niu, IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 32, 424 (2017).
Q. Wang, S. Niu, and X. Luo, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64, 6908 (2017).
Y. Shi, S. Niu, J. Wei, L. Jian, and R. Liu, IEEE Trans. Magn. 51, 1 (2015).
S. Niu, S.L. Ho, and W.N. Fu, IEEE Trans. Magn. 50, 805 (2014).
L. Jian, Y. Shi, J. Wei, Y. Zheng, and Z. Deng, Energies 8, 10127 (2015).
K. Xie, D. Li, R. Qu, and Y. Gao, IEEE Trans. Magn. 53, 1 (2017).
C. Shi, D. Li, R. Qu, H. Zhang, Y. Gao, and Y. Huo, IEEE Trans. Magn. 53, 1 (2017).
D.K. Jang and J.H. Chang, IEEE Trans. Magn. 50, 877 (2014).
K. Atallah, S.D. Calverley, and D. Howe, in IEE Proceedings—Electric Power Applications (2001), pp. 135–143.
Y. Shi, L. Jian, J. Wei, Z. Shao, W. Li, and C.C. Chan, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63, 1425 (2016).
G. Peng, J. Wei, Y. Shi, Z. Shao, and L. Jian, Energies 11, 1 (2018).
L. Jian, Y. Shi, J. Wei, and Y. Zheng, J. Appl. Phys. 11, 17A713-1 (2015).
X. Zhu, J. Ji, L. Xu, and M. Kang, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 28, 1 (2018).
W. Hua and M. Cheng, in CES/IEEE 5th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (2006), pp. 1–5.
M. Dou and R. Fu, in 15th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (2012), pp. 1–5.
Y. Shi and L. Jian, Energies 11, 1 (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Wei, J., Deng, Z. et al. Design and Analysis of a Dual-Permanent-Magnet-Excited Machine for Low-Speed Large-Torque Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 1400–1411 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6809-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6809-1