Abstract
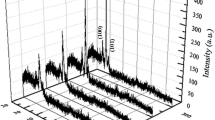
Zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films were deposited on commercial glass substrates at room temperature by RF magnetron sputtering. The effect of the sputtering variables such as RF power, argon flow and deposition time on the structural, electrical and optical properties was studied and discussed using a full 3k design of experiments. The properties of the deposited films were determined from x-ray diffraction, 3D optical microscopy, four-point probe and UV–Vis spectroscopy measurements. The x-ray diffraction patterns revealed a wurtzite-like crystalline structure of the ZnO films, with preferential orientation along the (002) direction. Depending on deposition parameters, the thickness of the films varied in the range of 23–163 nm and their resistivity was in the range from 100 Ω cm to 105 Ω cm. Additionally, all films show good optical transmittance (higher than 70%) in the visible spectral region and energy band gap values in the range of 2.27–2.31 eV. On the other hand, a multiple linear regression analysis was performed to predict the responses (average thickness, resistivity, and energy band gap) in terms of the significant factors. The results suggest that the time, power-time and flow-time are significant predictors for the thickness model; meanwhile, flow, flow2, power-flow, and power-time are significant for the resistivity model. In the energy band gap model, power, flow, time and flow2 were significant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Adachi, Properties of Group-IV, III–V II–VI Semiconductors (Hoboken: Wiley, 2005), p. 11.
M. Hadis and O. Umit, Zinc Oxide Fundam. Materials and Device Technology (Hoboken: Wiley, 2009), p. 1.
R. Kumar, G. Kumar, O. Al-Dossary, and A. Umar, Mater. Express (2015). https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2015.1204.
M.I. Medina-Montes, S.H. Lee, M. Pérez, L.A. Baldenegro-Pérez, M.A. Quevedo-López, B. Gnade, and R. Ramírez-Bon, J. Electron. Mater. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-011-1608-y.
M.I. Medina-Montes, H. Arizpe-Chávez, L.A. Baldenegro-Pérez, M.A. Quevedo-López, and R. Ramírez-Bon, J. Electron. Mater. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-012-1994-9.
R. Singh, M. Kumar, and S. Chandra, J. Mater. Sci. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0372-5.
P.B. Taunk, R. Das, D.P. Bisen, R.K. Tamrakar, and N. Rathor, Int. J. Mod. Sci. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kijoms.2015.11.002.
E. Heredia, C. Bojorge, J. Casanova, H. Cánepa, A. Craievich, and G. Kellermann, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.046.
H. Belkhalfa, H. Ayed, A. Hafdallah, M.S. Aida, and R.T. Ighil, Optik (Stuttg) (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.11.126.
R. Kumar, G. Kumar, and O. Al-Dossary, Mater. Express A 5, 3 (2015).
N.E. Duygulu, A.O. Kodolbas, and A. Ekerim, J. Cryst. Growth (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2014.02.028.
L. Gao, S. Jiang, and R. Li, Thin Solid Films (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2016.02.059.
Y. Zhao, D. Jiang, M. Zhao, R. Deng, J. Qin, and S. Gao, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.055.
A. Spadoni and M.L. Addonizio, Thin Solid Films (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2015.06.035.
H.Y. Dai, C. Zhan, and J. Du, Optik (Stuttg) (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.11.154.
Y. Lu and J. Jia, Chin. Chem. Lett. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2014.06.003.
J. Liu, A. Wei, and Y. Zhao, J. Alloys Compd. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.042.
F. Gode, E. Guneri, and O. Baglayan, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.04.128.
D.C. Montgomery, Design and Analysis of Experiments (Hoboken: Wiley, 2013), p. 2013.
L. Sun, S. Wan, Z. Yu, and L. Wang, Sep. Purif. Technol. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.01.042.
M. Cuéllar, V. Pfaffen, and P.I. Ortiz, J. Electroanal. Chem. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2015.07.050.
N. Ozbay and A.S. Yargic, J. Clean. Prod. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.03.050.
E. Yucel, Y. Yucel, and B. Ibrahim, J. Mater. Sci. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0791-9.
K. Do Kim, D.W. Choi, Y. Choa, and H.T. Kim, J. Mater. Process. Technol. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.09.053.
Y. Tao, M.M. Ba-abbad, A. Wahab, N. Hanis, H. Hairom, and A. Benamor, Mater. Des. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.07.040.
A. Cuevas, R. Romero, D. Leinen, E.A. Dalchiele, J.R. Ramos-Barrado, and F. Martin, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2014.11.048.
E. Yücel, N. Güler, and Y. Yücel, J. Alloys Compd. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.067.
E. Yücel, Y. Yücel, and B. Beleli, J. Cryst. Growth (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2015.04.018.
E. Yücel, Y. Yücel, and B. Beleli, J. Alloys Compd. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.03.267.
C.L. Tien and S.W. Lin, Opt. Commun. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2006.05.044.
C. Peng, T.P. Dhakal, S.M. Garner, S. Member, P. Cimo, S. Lu, and C.R. Westgate, Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. A 14, 121 (2014).
S. Hsu, M. Weng, R. Yang, C. Fang, and J. Chou, IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2016.2572223.
Y. Lare, A. Godoy, L. Cattin, K. Jondo, T. Abachi, F.R. Diaz, M. Morsli, K. Napo, M.A. Valle, and J.C. Berne, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.02.054.
A. Purohit, S. Chander, A. Sharma, S.P. Nehra, and M.S. Dhaka, Opt. Mater. (Amst) (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2015.08.021.
S. Sharma, C. Periasamy, and P. Chakrabarti, Electron. Mater. Lett. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-015-4445-y.
X.L. Zhang, K.N. Hui, K.S. Hui, and J. Singh, Mater. Res. Bull. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.11.104.
S. Elmas, S. Özen, N. Ekem, and M.Z. Balba, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.044.
A. Mortezaali, O. Taheri, and Z.S. Hosseini, MEE (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2015.11.016.
S. Sharma, S. Vyas, C. Periasamy, and P. Chakrabarti, Superlattices Microstruct. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2014.07.032.
A. Ismail and M.J. Abdullah, J. King Saud Univ. Sci. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2012.12.004.
J.J. Valenzuela-Jáuregui, R. Ramírez-Bon, A. Mendoza-Galván, and M. Sotelo-Lerma, Thin Solid Films (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(03)00908-8.
M.D. Morales-acosta, C.G. Alvarado-beltrán, M.A. Quevedo-lópez, and B.E. Gnade, J. Non Cryst. Solids (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2012.11.025.
C. Trejo-cruz, A. Mendoza-galván, A.M. López-beltrán, and M. Gracia-jiménez, Thin Solid Films (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2009.02.134.
A. Cuevas, R. Romero, D. Leinen, E.A. Dalchiele, J.R. Ramos-barrado, and F. Martin, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2014.11.048.
C. Besleaga, G.E. Stan, A.C. Galca, L. Ion, and S. Antohe, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.05.097.
J. Hair, R.E. Anderson, and R.L. Tatham, Multivarate Data Analysis (Prentice Hall international: Upper Saddle River, 1999), p. 143.
D.C. Montgomery, E.A. Peck, and G.G. Vining, Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis (Hoboken: Wiley, 2012), p. 171.
Acknowledgements
The technical assistance of C.A. Ávila-Herrera and M.A. Hernández-Landaverde, the use of LIDTRA facilities and the support of CONACYT-Mexico (Project Number 242549) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flores-García, E., González-García, P., González-Hernández, . et al. Statistical Analysis of Sputter Parameters on the Properties of ZnO Thin Films Deposited by RF Sputtering. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 5537–5547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6422-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6422-3