Abstract
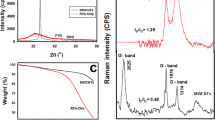
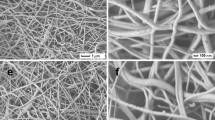
Carbon nanotubes (CNT) and carbon nanospheres were successfully synthesized from coconut fibre-activated carbon. The biomass was first carbonized then physically activated, followed by treatment using ethanol vapor at 700°C to 1100°C at 100°C intervals. The effect of synthesis temperature on the formation of the nanomaterials was studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive x-ray spectrometry, x-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared microscopy (FTIR) and thermogravimetric analysis. SEM analysis revealed that nanospheres were formed at higher temperatures of 1000°C and 1100°C, while lower temperatures of 800°C and 900°C favored the growth of CNT. At 700°C, however, no tubes or spheres were formed. TEM and FTIR were used to observe spectral features, such as the peak positions, intensity and bandwidth, which are linked to some structural properties of the samples investigated. All these observations provided facts on the nanosphere and nanotube dimensions, vibrational modes and the degree of purity of the obtained samples. The TEM results show spheres of diameter in the range 50 nm to 250 nm while the tubes had diameters between 50 nm to 100 nm. XRD analysis reveals the materials synthesized are amorphous in nature with a hexagonal graphite structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. He, H. Li, Y. Liu, H. Huang, Z. Kang, and S.-T. Lee, Colloids Surf. B 87, 326 (2011).
H. Li, X.D. He, Y.Y. Liu, H. Huang, S. Lian, S.T. Lee, and Z.H. Kang, Carbon 49, 605 (2011).
H. Li, X. He, Y. Liu, H. Yu, Z. Kang, and S.-T. Lee, Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 147 (2011).
Z. Ma, H. Ming, H. Huang, Y. Liu, and Z. Kang, New J. Chem. 36, 861 (2012).
J.S. Sagu, U. Wijayantha, K. Gamage, M. Bohm, S. Bohm, and T.K. Rout, Adv. Eng. Mater. 18, 1059 (2016).
Y. Ding, H. Alias, D. Wen, and R.A. Williams, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49, 240 (2006).
P. Estellé, Mater. Lett. 138, 162 (2015).
S. Halelfadl, P. Estellé, B. Aladag, N. Doner, and T. Maré, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 71, 111 (2013).
S. Halelfadl, T. Maré, and P. Estellé, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 53, 104 (2014).
B. Jo and D. Banerjee, Mater. Lett. 122, 212 (2014).
M.-S. Liu, M. Ching-Cheng Lin, I.T. Huang, and C.-C. Wang, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 32, 1202 (2005).
L. Lu, Z.-H. Liu, and H.-S. Xiao, Sol. Energy 85, 379 (2011).
T. Maré, S. Halelfadl, S. Van Vaerenbergh, and P. Estellé, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 66, 80 (2015).
R. Sadri, G. Ahmadi, H. Togun, M. Dahari, S.N. Kazi, E. Sadeghinezhad, and N. Zubir, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 151 (2014).
R. Saidur, K.Y. Leong, and H.A. Mohammad, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15, 1646 (2011).
X.-Q. Wang and A.S. Mujumdar, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 46, 1 (2007).
Y. Wang, F. Su, C.D. Wood, J.Y. Lee, and X.S. Zhao, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 47, 2294 (2008).
D. Antiohos, M. Romano, J. Chen, and J.M. Razal, Syntheses and Applications of Carbon Nanotubes and Their Composites, ed. S. Suzuki (Rijeka: InTech, 2013), https://doi.org/10.5772/51784.
L.-M. Peng, Z. Zhang, and S. Wang, Mater. Today 17, 433 (2014).
H. He, L.A. Pham-Huy, P. Dramou, D. Xiao, P. Zuo, and C. Pham-Huy, BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 1 (2013).
V. Amenta and K. Aschberger, WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 7, 371 (2015).
W. Shao, P. Arghya, M. Yiyong, L. Rodes, and S. Prakash, Syntheses and Applications of Carbon Nanotubes and Their Composites, ed. S. Suzuki (Rijeka: InTech, 2013), https://doi.org/10.5772/51785.
K. Shi, J. Yan, E. Lester, and T. Wu, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53, 15012 (2014).
J.O. Alves, J.A.S. Tenório, C. Zhuo, and Y.A. Levendis, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 1, 31 (2012).
H.M. Al-Swaidan, A. Ahmad, in 3rd International Conference on Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, (2011), pp. 25–31.
T.A. Hassan, V.K. Rangari, V. Fallon, Y. Farooq, S. Jeelani, in Proceedings of the Nanotechnology Conference, (2010), pp. 278–281.
S.S. Shams, L.S. Zhang, R. Hu, R. Zhang, and J. Zhu, Mater. Lett. 161, 476 (2015).
N.A. Fathy, RSC Adv. 7, 28535 (2017).
P. Gonugunta, S. Vivekanandhan, A.K. Mohanty, and M. Misra, World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2, 148 (2012).
X.-W. Chen, O. Timpe, S.B.A. Hamid, R. Schlögl, and D.S. Su, Carbon 47, 340 (2009).
I. Abdullahi, N. Sakulchaicharoen, and J.E. Herrera, Diam. Relat. Mater. 41, 84 (2014).
N. Jeong, Y. Seo, and J. Lee, Diam. Relat. Mater. 16, 600 (2007).
M.S. Shamsudin, N.A. Asli, S. Abdullah, S.Y.S. Yahya, and M. Rusop, Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2012, 1 (2012).
D. Lopez, I. Abe, and I. Pereyra, Diam. Relat. Mater. 52, 59 (2015).
S.M. Toussi, A. Fakhru’l-Razi, A. Suraya, in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 17 (IOP Publishing, 2011), p. 012003.
M. Shamsudin, N. Asli, S. Abdullah, S. Yahya, and M. Rusop, Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2012, 420619 (2012).
Y. Jiang and C. Lan, Mater. Lett. 157, 269 (2015).
S. Alam, B. Seema, and F.K. Bangash, J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 31, 46 (2009).
G. Allaedini, S.M. Tasirin, and P. Aminayi, J. Alloys Compd. 647, 809 (2015).
O.-K. Park, H.-S. Chae, G.Y. Park, N.-H. You, S. Lee, Y.H. Bang, D. Hui, B.-C. Ku, and J.H. Lee, Compos. B 76, 159 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adewumi, G.A., Inambao, F., Eloka-Eboka, . et al. Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes and Nanospheres from Coconut Fibre and the Role of Synthesis Temperature on Their Growth. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 3788–3794 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6248-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6248-z