Abstract
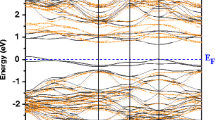
The electronic, magnetic, and optical properties of Ti-doped semiconductors Mg1−xTi x Te at concentrations of x = 0.25, 0.50, and 0.75 have been investigated in the framework of density functional theory. Spin-polarized calculations of the electronic structure of Mg1−xTi x Te revealed that these compounds are half-metallic ferromagnetic materials with 100% spin polarization at the Fermi level. Large half-metallic gaps of 1.69 eV, 1.18 eV, and 0.98 eV were obtained for these compounds with Ti concentration of 0.25, 0.50, and 0.75, respectively. In addition, the origin of the half-metallic gap in Mg1−xTi x Te is discussed based on the partial density of states. It is found that hybridization between Ti-3d and Te-5p states and the large exchange splitting of the Ti-3d states are responsible for the half-metallic property of Mg1−xTi x Te compounds. The Curie temperatures of Mg0.5Ti0.5Te and Mg0.25Ti0.75Te were predicted to be 572 K and 959 K, respectively, within the mean field approximation. The appropriate half-metallic properties of Mg1−xTi x Te (x = 0.50 and 0.75) make them appropriate electronic materials for use in spintronics applications. The optical properties of pure and Ti-doped MgTe semiconductors, such as the dielectric function, extinction coefficient, absorption coefficient, reflectivity, and optical conductivity, were also considered. It was found that Ti doping considerably changed the optical properties of the MgTe semiconductors, especially at lower frequencies, such that these materials can be used in optical devices such as photodetectors and solar cells over wider ranges of frequency than corresponding undoped material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Žutić, J. Fabian, and S.D. Sarma, Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 323 (2004).
S. Bandyopadhyay and M. Cahay, Introduction to Spintronics, 2nd ed. (Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2015).
T. Shinjo, Nanomagnetism and Spintronics (Amsterdam: Elsevier Science, 2013).
B. Azzerboni, G. Asti, L. Pareti, and M. Ghidini, Magnetic Nanostructures in Modern Technology: Spintronics, Magnetic MEMS and Recording (Berlin: Springer, 2007).
C.Y. Fong, J.E. Pask, and L.H. Yang, Half-Metallic Materials and Their Properties (Singapore: World Scientific, 2013).
S. von Oehsen, Spin-polarized Currents for Spintronic Devices: Point-Contact Andreev Reflection and Spin Filters (Göttingen: Cuvillier, 2007).
R.A. de Groot, F.M. Mueller, P.G.V. Engen, and K.H.J. Buschow, Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 2024 (1983).
M. Allaf Behbahani, M. Moradi, M. Rostami, and S. Davatolhagh, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 92, 85 (2016).
S. Berri, M. Ibrir, D. Maouche, and M. Attallah, Comput. Condens. Matter 1, 26 (2014).
S. Berri, Chin. J. Phys. 55, 195 (2017).
J. Du, S. Dong, Y.-L. Lu, H. Zhao, L. Feng, and L.Y. Wang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 428, 250 (2017).
S. Bahramian and F. Ahmadian, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 424, 122 (2017).
M. Dehghanzadeh and F. Ahmadian, Solid State Commun. 251, 50 (2017).
F. Taşkın, M. Atiş, O. Canko, S. Kervan, and N. Kervan, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 473 (2017).
X.T. Wang, T.T. Lin, H. Rozale, X.F. Dai, and G.D. Liu, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 402, 190 (2016).
R.J. Caraballo Vivas, S.S. Pedro, C. Cruz, J.C.G. Tedesco, A.A. Coelho, A.M.G. Carvalho, D.L. Rocco, and M.S. Reis, Mater. Chem. Phys. 174, 23 (2016).
Y. Hu and J.-M. Zhang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 192, 253 (2017).
H. Qiu, Z. Wang, and X. Sheng, Phys. Lett. A 377, 347 (2013).
S.E.A. Yousif and O.A. Yassin, J. Alloys Compd. 506, 456 (2010).
Y. Zhang, V. Ji, and K.-W. Xu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 162, 711 (2015).
Y. Aharbil, H. Labrim, S. Benmokhtar, M.A. Haddouch, L. Bahmad, A. Belhaj, H. Ez-Zahraouy, and A. Benyoussef, Mater. Chem. Phys. 183, 588 (2016).
S. Kervan and N. Kervan, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 382, 63 (2015).
S.F. Rabbani and I.B.S. Banu, Comput. Mater. Sci. 101, 281 (2015).
G. Jaiganesh and S.M. Jaya, Comput. Mater. Sci. 102, 85 (2015).
B. Ul Haq, R. Ahmed, A. Shaari, N. Ali, Y. Al-Douri, and A.H. Reshak, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 43, 123 (2016).
Q. Zhao, Z. Xiong, L. Luo, Z. Sun, Z. Qin, L. Chen, and N. Wu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 396, 480 (2017).
S.F. Rabbani and I.B.S. Banu, J. Alloys Compd. 695, 3131 (2017).
H.S. Saini, M.K. Kashyap, M. Kumar, J. Thakur, M. Singh, A.H. Reshak, and G.S.S. Saini, J. Alloys Compd. 649, 184 (2015).
M. Boutaleb, B. Doumi, A. Tadjer, and A. Sayede, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 397, 132 (2016).
M. Rostami, M. Moradi, Z. Javdani, and H. Salehi, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 38, 218 (2015).
Y.-S. Kim, Y.-C. Chung, and S.-C. Yi, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 126, 194 (2006).
A. Ait Raiss, Y. Sbai, L. Bahmad, and A. Benyoussef, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 385, 295 (2015).
M.S. Akhtar, M.A. Malik, S. Riaz, and S. Naseem, Mater. Chem. Phys. 160, 440 (2015).
T. Schäpers, Semiconductor Spintronics (Berlin: De Gruyter, 2016).
T. Jungwirth, J. König, J. Sinova, J. Kučera, and A.H. MacDonald, Phys. Rev. B 66, 012402 (2002).
S. Dhara, B. Sundaravel, K.G.M. Nair, R. Kesavamoorthy, M.C. Valsakumar, T.V.C. Rao, L.C. Chen, and K.H. Chen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 173110 (2006).
V. Zayets, M.C. Debnath, and K. Ando, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 565 (2004).
M.C. Debnath, V. Zayets, and K. Ando, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 091112 (2005).
K. Ramanujam, I. Masaya, T. Ken, T. Kazuki, G. Fumitaka, and A. Eisuke, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 3161 (2001).
M. Kamruzzaman, T.R. Luna, P. Jiban, and M.G.M. Anowar, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 27, 035017 (2012).
M.W. Wang, M.C. Phillips, J.F. Swenberg, E.T. Yu, J.O. McCaldin, and T.C. McGill, J. Appl. Phys. 73, 4660 (1993).
P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, G.K.H. Madsen, D. Kvasnicka, and J. Luitz, WIEN2K, An Augmented Plane Wave + Local Orbitals Program for Calculating Crystal Properties, Karlheinz Schwarz (Wien: Techn. Universität Wien, 2001).
J.P. Perdew and Y. Wang, Phys. Rev. B 45, 13244 (1992).
K. Schwarz, P. Blaha, and G.K.H. Madsen, Comput. Phys. Commun. 147, 71 (2002).
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
D. Koller, F. Tran, and P. Blaha, Phys. Rev. B 83, 195134 (2011).
F.D. Murnaghan, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 30, 244 (1944).
G. Gökoğlu, M. Durandurdu, and O. Gülseren, Comput. Mater. Sci. 47, 593 (2009).
N.A. Noor, S.M. Alay-e-Abbas, M.U. Sohaib, S.M.G. Abbas, and A. Shaukat, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 164 (2015).
A. Waag, H. Heinke, S. Scholl, C.R. Becker, and G. Landwehr, J. Cryst. Growth 131, 607 (1993).
G.V. Samsonov, Handbook of the Physicochemical Properties of the Elements (Berlin: Springer, 2012).
S. Duman, S. Bağcı, H.M. Tütüncü, and G.P. Srivastava, Phys. Rev. B 73, 205201 (2006).
A. Fleszar, Phys. Rev. B 64, 245204 (2001).
J.P. Perdew, Int. J. Quantum Chem. 28, 497 (1985).
S. Duman, S. Bağcı, H. Tütüncü, and G. Srivastava, Phys. Rev. B 73, 205201 (2006).
A. Los and V. Los, Magnetic Properties of Transition-Metal-Doped Silicon Carbide Diluted Magnetic Semiconductors (London: INTECH Open Access Publisher, 2011).
A. Delin, O. Eriksson, R. Ahuja, B. Johansson, M.S.S. Brooks, T. Gasche, S. Auluck, and J.M. Wills, Phys. Rev. B 54, 1673 (1996).
M. Grundmann, The Physics of Semiconductors: An Introduction Including Nanophysics and Applications (Berlin: Springer, 2010).
W. Schäfer and M. Wegener, Semiconductor Optics and Transport Phenomena (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2013).
D.-M. Ma, Y.-Y. Chai, V. Wang, E.-L. Li, and W. Shi, Comput. Mater. Sci. 113, 75 (2016).
H. Castán, E. Pérez, H. García, S. Dueñas, L. Bailón, J. Olea, D. Pastor, E. García-Hemme, M. Irigoyen, and G. González-Díaz, J. Appl. Phys. 113, 024104 (2013).
V. Wang, W. Xiao, L.J. Kang, R.J. Liu, H. Mizuseki, and Y. Kawazoe, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 48, 015101 (2015).
A. Abbad, W. Benstaali, H.A. Bentounes, S. Bentata, and A. Belaidi, Comput. Mater. Sci. 70, 19 (2013).
D. Novko, M. Šunjić, and V. Despoja, Phys. Rev. B 93, 125413 (2016).
N.V. Joshi, Photoconductivity: Art: Science and Technology (London: Taylor & Francis, 1990).
O.S. Martinez, R.C. Palomera, J.S. Cruz, and X. Mathew, Phys. Status Solidi 6, S214 (2009).
M.V. Gapanovich, I.N. Odin, V.V. Popova, V.F. Kozlovskii, and G.F. Novikov, Inorg. Mater. 52, 890 (2016).
G.Y. Jia, Y. Liu, J.Y. Gong, D.Y. Lei, D.L. Wang, and Z.X. Huang, J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 8822 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allaf Behbahani, M., Moradi, M. & Rostami, M. First-Principles Investigation of Electronic, Half-Metallic, and Optical Properties of Ti-Doped MgTe Semiconductors with Various Concentrations of Dopant. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 2565–2575 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6085-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6085-0