Abstract
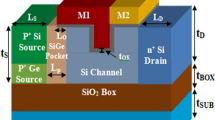
To achieve reliable transistors, we propose a new silicon-on-insulator (SOI) metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) with an amended electric field in the channel for improved electrical and thermal performance, with an emphasis on current leakage improvement. The amended electric field leads to lower electric field crowding and thereby we assume enhanced reliability, leakage current, gate-induced drain leakage (GIDL), and electron temperature. To modify the electric field distribution, an additional rectangular metal region (RMR) is utilized in the buried oxide of the SOI MOSFET. The location and dimensions of the RMR have been carefully optimized to achieve the best results. The electrical, thermal, and radiofrequency characteristics of the proposed structure were analyzed using two-dimensional (2-D) numerical simulations and compared with the characteristics of the conventional, fully depleted SOI MOSFET (C-SOI). Also, critical short-channel effects (SCEs) such as threshold voltage, drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL), subthreshold slope degradation, hot-carrier effect, GIDL, and leakage power consumption are improved. According to the results obtained, the proposed nano SOI MOSFET is a reliable device, especially for use in low-power and high-temperature applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Chaudhry and M. Jagadesh Kumar, IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 4, 1 (2004).
T.H. Ning, C.M. Osburn, and H.N. Yu, J. Appl. Phys. 48, 286 (1997).
H. Krautscheider, A. Kohlhase, and H. Terlezki, Microelectron. Reliab. 37, 19 (1997).
H.C. Poon, L.D. Yau, R.L. Johnston, and D. Beecham, IEDM Tech. Dig. 8.4, 156 (1974).
R.W. Cottrel, R.R. Troutman, and T.H. Ning, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 26, 520 (1979).
M.V. Fischetti, S.E. Laux, and D.J. DiMaria, Appl. Surf. Sci. 39, 578 (1989).
D.R. Walters and A.T.A. Zegers-van Duynhoven, Appl. Surf. Sci. 39, 565 (1989).
H. Wong and Y.C. Cheng, J. Appl. Phys. 67, 7132 (1990).
K. Venkataswamy and S. Kumar, Performance tradeoff of leakage reduction techniques in nanoscale CMOS circuits, Master’s Thesis, The University of Texas at San Antonio (2009).
M.K. Anvarifard and A.A. Orouji, Superlattices Microstruct. 60, 561 (2013).
Device simulator Atlas, Atlas User’s Manual (Santa Clara: Silvaco International Software, 2014).
H. Wong, Y. Fub, J.J. Liou, and Y. Yue, Microelectron. Reliab. Elsevier J. 49, 13 (2009).
Z. Ramezani and A.A. Orouji, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 61, 10 (2014).
M. Rahimian and A.A. Orouji, Superlattices Microstruct. 50, 667 (2011).
J. Chen, J. Luo, Q. Wu, Z. Chai, T. Yu, Y. Dong, and X. Wang, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 43, 1346 (2011).
B. Gu, H.Y. Liu, Y.W. Mai, X.Q. Feng, and S.W. Yu, Eng. Fracture Mech. 75, 4996 (2008).
B. Ghyselen, J.M. Hartmann, T. Ernst, C. Aulnette, B. Osternaud, Y. Bogumilowicz, A. Abbadie, P. Besson, O. Rayssac, A. Tiberj, N. Daval, I. Cayrefourq, F. Fournel, H. Moriceau, C. Di Nardo, F. Andrieu, V. Paillard, M. Cabi, L. Vincent, E. Snoeck, F. Cristiano, A. Rocher, A. Ponchet, A. Claverie, P. Boucaud, M.N. Semeria, D. Bensahel, N. Kernevez, and C. Mazure, Solid-State Electron. 48, 1285 (2004)
J. Du, W.H. Ko, and D.J. Young, Sens. Actuators A Phys. 112, 116 (2004).
A.H. Aminbeidokhti, Ali A. Orouji, S. Rahmaninezhad, and M. Ghasemian, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59, 5 (2012).
Z. Ramezani, A.A. Orouji, and P. Keshavarzi, Phys. E 59, 202 (2014).
D.K. ShRMRa and K.V. Ramanathan, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 4, 362 (1983).
S.M. Sze and K.K. Ng, Physics of Semiconductor Devices, 3rd ed. (New Jersey: Wiley, 2007).
B. Iniguez and T.A. Fjeldly, Solid-State Electron. 41, 87 (1997)
M. Tanizawa, M. Ikeda, N. Kotani, K. Tsukamoto, and K. Horie, IEEE Trans. CAD/ICAS 12, 1749 (1993).
T.C. Ong, P.K. Ko, and C. Hu, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 37, 7 (1990).
S. Tam, P.K. Ko, and C. Hu, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 31, 1116 (1984).
S. Tanaka, Solid-State Electron. 38, 683 (1995).
T. Wang, T.E. Chang, C.M. Huang, J.Y. Yang, K.M. Chang, and L.P. Chiang, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 16, 566 (1995).
K. Roy, S. Mukhopadhyay, and H. Mahmoodi-Meimand, Proc. IEEE 91, 305 (2003).
A. Bouhdada, S. Bakkali, and A. Touhami, Microelectron. Reliab. 37, 649 (1997).
J. Chen, T.Y. Chan, I.C. Chen, P.K. Ko, and C. Hu, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 8, 515 (1987).
O. Kane, J. Appl. Phys. 32, 83 (1961).
K. Ohyu, M. Ohkura, A. Hiraiwa, and K. Watanabe, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 42, 1404 (1995).
Y.P. Tsividis, Operation and Modeling of the MOS Transistor (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1987).
A. Godoy, J.A. Lopez- Villanueva, J.A. Jimemez-Tijada, A. Palma, and F. Gamiz, Solid-State Electron. 45, 391 (2001).
A.A. Orouji and M. Rahimian, Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 1366 (2012).
M. Rahimian and A.A. Orouji, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 1248 (2013).
A.A. Orouji and M. Rahimian, Phys. E 44, 333 (2011).
S.K. Kim, S.I. Kim, H. Lim, D.S. Jeong, B. Kwon, S.H. Baek, and J.S. Kim, Scientific report 5, No. 8023, Supported by the Korea Institute of Science and Technology, South Korea (2015).
C.G. Sodini, T.W. Ekstedtd, and J. Moll, Solid State Electron. 25, 833 (1982).
R.H. Dennard, F.H. Gaensslen, L. Kuhn, and H.N. Yu, IEDM Tech. Dig. 12, 168 (1972).
R.H. Dennard, F.H. Gaensslen, H.N. Yu, V.L. Rideout, E. Bassous, and A. Le Blanc, IEEE J. Solid-State Circ. 9, 256 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramezani, Z., Orouji, A.A. Amended Electric Field Distribution: A Reliable Technique for Electrical Performance Improvement in Nano scale SOI MOSFETs. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 2269–2281 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5222-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5222-x