Abstract
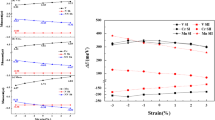
The effects of isotropic strains on the magnetic properties in ZnO and GaN induced by cation vacancies are comparatively investigated by density functional theory calculations. The magnetic moments and the couplings between vacancies in different charged states are calculated as a function of strains. The modulation of strain on the magnetic properties relies on the materials and the charge states of cation vacancies in them. As the occurrence of charge transfer in ZnO:V Zn under compression, the coupling between \(V_{\rm{Zn}}^{0} \) is antiferromagnetic (AFM) and it could be stabilized by strains. Tensions can strengthen the ferromagnetic (FM) coupling between \(V_{\rm{Zn}}^{0} \) but weaken that of \(V_{\rm{Ga}}^{ - } \). The neutral V Ga are always AFM coupling under strains from −6 to +6% and could be stabilized by compressions. The interactions between \(V_{\rm{Ga}}^{ - } \) are always FM with ignorable variations under strains; however, the FM couplings between \(V_{\rm{Ga}}^{2 - } \) could be strengthened by compressions. These varying trends of magnetic coupling under strains are interpreted by the band coupling models. Therefore, strain-engineering provides a route to manipulate and design high Curie temperature ferromagnetism derived and mediated by intrinsic defect for spintronic applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, and D. Ferrand, Science 287, 5455 (2000).
H. Pan, J.B. Yi, L. Shen, R.Q. Wu, J.H. Yang, J.Y. Lin, Y.P. Feng, J. Ding, L.H. Van, and J.H. Yin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 127201 (2007).
H.W. Peng, H.J. Xiang, S.-H. Wei, S.S. Li, J.B. Xia, and J.B. Li, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 017201 (2009).
P. Dev, Y. Xue, and P. Zhang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 117204 (2008).
O. Volnianska and P. Boguslawsk, Phys. Rev. B. 83, 205205 (2011).
L. Shen, R.Q. Wu, H. Pan, G.W. Peng, M. Yang, Z.D. Sha, and Y.P. Feng, Phys. Rev. B. 78, 073306 (2008).
H.F. Sluiter, Y. Kawazoe, P. Sharma, A. Inoue, A.R. Raju, C. Rout, and U.V. Waghmare, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 187204 (2005).
E. Kan, F. Wu, Y.M. Zhang, H.J. Xiang, R.F. Lu, C.Y. Xiao, K.M. Deng, and H.B. Su, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 072401 (2012).
T.M. Ritter, B.A. Weinstein, R.M. Park, and M.C. Tamargo, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 964 (1996).
V. Iota and B.A. Weinstein, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 4955 (1998).
X.P. Wang, M.W. Zhao, T. He, Z.H. Wang, and X.D. Liu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 062411 (2013).
H.H. Ren, J.K. Jian, C. Chen, D. Pan, A. Ablat, Y.F. Sun, J. Li, and R. Wu, Appl. Phys. A 116, 185C191 (2014).
H.T. Ren, G. Xiang, G.X. Gu, X. Zhang, W.J. Wang, P. Zhang, B.Y. Wang, and X.Z. Cao, J. Nanomater. 5, 295358 (2012).
Q. Wang, Q. Sun, G. Chen, Y. Kawazoe, and P. Jena, Phys. Rev. B 77, 205411 (2008).
M. Bououdina, A.A. Dakhel, M. El-Hilo, D.H. Anjum, M.B. Kanoun, and S. Goumri-Said, RSC Adv. 5, 33233 (2015).
Y.B. Lu, Y. Dai, W. Wei, Y.T. Zhu, and B.B. Huang, Chem. Phys. Chem. 14, 3916 (2013).
L. Bergqvist, B. Belhadji, S. Picozzi, and P.H. Dederichs, Phys. Rev. B. 77, 014418 (2008).
N.M. Souza-Neto, D. Haskel, Y.-C. Tseng, and G. Lapertot, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 057206 (2009).
I.N. Goncharenko and I. Mirebeau, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1082 (1998).
A. Mir, B. Bekkouche, A. Boukortt, S. Kacimi, M. Djermouni, and A. Zaoui, Model. Numer. Simul. Mater. Sci. 2, 37–42 (2012).
G.M. Dalpian, S.-H. Wei, X.G. Gong, A.J.R. Silva, and A. Fazzio, Solid State Commun. 138, 353 (2006).
J.Y. Zhu, F. Liu, G.B. Stringfellow, and S.-H. Wei, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 195503 (2010).
G. Kresse and J. Hafner, Phys. Rev. B 47, 558 (1993).
P.E. Blochl, Phys. Rev. B 50, 17953 (1994).
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
H. Monkhorst and J. Pack, Phys. Rev. B 13, 5188 (1976).
P. Dev and P.H. Zhang, Phys. Rev. B 81, 085207 (2010).
W.A. Adeagbo, G. Fischer, A. Ernst, and W. Hergert, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22, 436002 (2010).
H.W. Peng, J.B. Li, and S.-H. Wei, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 122409 (2013).
J. Kudrnovsky, I. Turek, V. Drchal, F. Mca, P. Weinger, and P. Bruno, Phys. Rev. B 69, 11 (2004).
F. Mca, J. Kudrnovsky, V. Drchal, and G. Bouzerar, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 18–20 (2008).
Acknowledgements
Dr. Yanqin Gai is grateful to Professor Zhenyu Li for helpful discussions. We acknowledge financial supports from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant No. 2010LKWL03, the Special Fund for Theoretical Physics under Grant No. 11047130, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11104345 and the Key Project of Chinese National Programs for Fundamental Research and Development(973 program) under Grant No. 2011CB302003. We are grateful to the Advanced Analysis and Computation Center of CUMT for the award of CPU hours to accomplish this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gai, Y., Jiang, J., Wu, Y. et al. Strain Manipulated Magnetic Properties in ZnO and GaN Induced by Cation Vacancy. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 3300–3306 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4482-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4482-9