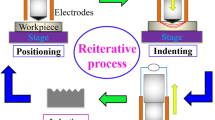
Impression creep testing of tin was performed in the temperature range of 343 K to 398 K and under a punching stress of 12 MPa to 55 MPa. During the impression test at constant load, a direct electric current in the range of 0 A to 6 A flowed through the punch into the sample, introducing an electromechanical interaction. Steady-state creep was observed under the simultaneous action of the electric current and mechanical stress. The steady-state impression velocity increased with increasing temperature, punching stress, and electric current. A hyperbolic sine relation was used to describe the stress dependence of the steady-state impression velocity for impression creep of tin. The apparent activation energy decreased with increasing electric current.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abtew and G. Selvaduray, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 27, 95 (2000).
S.N.G. Chu and J.C.M. Li, J. Mater. Sci. 12, 2200 (1977).
S.N.G. Chu and J.C.M. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. 39, 1 (1979).
C. Park, X. Long, S. Hoberman, S. Ma, and I. Dutta, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 5182 (2007).
F.Q. Yang and L.L. Peng, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 409, 87 (2005).
G. Le Meur, B. Bourouga, and J.P. Bardon, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 49, 387 (2006).
R.S. Timsit, IEEE Trans. Comp. Hybrids Manuf. Technol. 14, 285 (1991).
R. Chen and F.Q. Yang, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 065404 (2008).
R. Chen and F.Q. Yang, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 155406 (2008).
J. Nah, F. Ren, K. Paik, and K.N. Tu, J. Mater. Res. 21, 698 (2006).
F. Ren, J.W. Nah, K.N. Tu, B. Xiong, L. Xu, and J.H.L. Pang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 141914 (2006).
T.H. Hyde, K.A. Yehia, and A.A. Becker, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 35, 451 (1993).
F.Q. Yang, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 40, 87 (1998).
F.Q. Yang, J.C.M. Li, and C.W. Shih, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 201, 50 (1995).
F. Garofalo, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 227, 351 (1963).
R. Darveaus and K. Banerji, Proceedings of the IEEE Electronic Components Technology Conference ECTC’92 (San Diego, CA, 1992), pp. 538.
F.Q. Yang and J.C.M. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 201, 40 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, R., Yang, F. Effect of DC Current on the Creep Deformation of Tin. J. Electron. Mater. 39, 2611–2617 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-010-1355-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-010-1355-5