Abstract
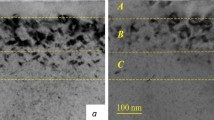
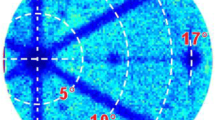
Application of the low-temperature halo-carbon epitaxial growth technique to produce heavily doped p-type epitaxial layers was investigated. While growth at 1300°C facilitated Al incorporation, possible degradation of crystalline quality had to be evaluated. A quantitative measure of the defects generated during epitaxial growth was obtained using molten potassium hydroxide (KOH) etching. The trend with increased doping was for an increase in threading dislocations and Al precipitates. The degradation initially involved an increase in generation of threading dislocations, which was followed at higher doping by generation of defects giving rise to smaller KOH etch pits. The properties of the small-etch-pit defects were reminiscent of Al precipitates. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used to establish that the small-etch-pit defects were localized at various depths inside the epilayers. Energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) indicated that these small-etch-pit defects contained a higher concentration of aluminum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Hamada, Mater. Sci. Forum 600–603, 889 (2009).
J.W. Palmour, Mater. Sci. Forum 527–529, 1129 (2006).
M.K. Linnarsson, M.S. Janson, U. Zimmermann, B.G. Svensson, P. Persson, L. Hultman, J. Wong-Leung, S. Karlsson, A. Schoner, H. Bleichner, and E. Olsson, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 2016 (2001).
Y.A. Vodakov, E.N. Mokhov, M.G. Ramm, and A.D. Roenkov, Amorphous and Crystalline Silicon Carbide III, Springer Proc. Phys., Vol. 56 (1992), p. 329.
H. Jacobson, J. Birch, C. Hallin, A. Henry, R. Yakimova, T. Tuomi, E. Janzén, and U. Lindefelt, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3689 (2003).
J.Q. Liu, H.J. Chung, T. Kuhr, Q. Li, and M. Skowronski, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 2111 (2002).
R.S. Okojie, M. Zhang, and P. Pirouz, Mater. Sci. Forum 457–460, 529 (2004).
Y. Koshka, H.D. Lin, G. Melnychuk, and C. Wood, J. Cryst. Growth 294, 260 (2006).
B. Krishnan, H. Das, H.-D. Lin, and Y. Koshka, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 262103 (2006).
B. Krishnan, S.P. Kotamraju, G. Melnychuk, H. Das, J.N. Merrett, and Y. Koshka, J. Electron. Mater. (2009). doi:10.1007/s11664-009-0953-6.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Science Foundation Grant No. IIP-0839748.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, H., Krishnan, B., Kotamraju, S.P. et al. Generation of Defects in Heavily Al-Doped 4H-SiC Epitaxial Layers Grown by the Low-Temperature Halo-Carbon Method. J. Electron. Mater. 39, 534–539 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-010-1099-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-010-1099-2