Abstract
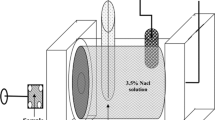
The effect of the anode and cathode on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of lead-free Sn-Ag-Cu and Sn-Ag-Cu-Bi solder joints in deionized water was investigated. Corrosion studies indicate that SnO crystals were generated on the surfaces of all lead-free solder joints. The constituents of the lead-free solder alloys, such as Ag, Cu, and Bi, did not affect the corrosion reaction significantly. In contrast to lead-free solders, PbO x was formed on the surface of the traditional 63Sn-37Pb solder joint in deionized water. A cathode, such as Au or Cu, was necessary for the electrochemical corrosion reaction of solders to occur. The corrosion reaction rate decreased with reduction of the cathode area. The formation mechanism of SnO crystals was essentially a galvanic cell reaction. The anodic reaction of Sn in the lead-free solder joints occurred through solvation by water molecules to form hydrated cations. In the cathodic reaction, oxygen dissolved in the deionized water captures electrons and is deoxidized to hydroxyl at the Au or Cu cathode. By diffusion, the anodic reaction product Sn2+ and the cathodic reaction product OH− meet to form Sn(OH)2, some of which can dehydrate to form more stable SnO·xH2O crystals on the surface of the solder joints. In addition, thermodynamic analysis confirms that the Sn corrosion reaction could occur spontaneously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
US Environmental Protection Agency, Strategy for Reducing Lead Exposure, 21 February, 1991
US Environmental Protection Agency, Advanced Notice of Rulemaking, 13 May, 1991
US Environmental Protection Agency, Comprehensive Review of Lead in the Environmental under TSCA, 56 FR 22096-98, 13 May, 1991
B.P. Richards, C.L. Levoguer, C.P. Hunt, K. Nimmo, S. Peters, and P. Cusack, An analysis of the current status of␣lead-free soldering, available at: http://www.npl.co.uk/ei/documents/pbfreereport.pdf
IPC, Lead free solder selection, available at: http://leadfree.ipc.org/RoHS_3-2-1.asp
H. Oulfajrite, A. Sabbar, T.W. Eagar, and A. Matsunawa, Mater. Lett. 27, 4368 (2003).
T. Takemoto and R.M. Latanision, Corros. Sci. 8, 1415 (1997).
K.L. Lin and T.P. Liu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 56, 171 (1998).
S.H. Bonilla and J. Rodriguez, Corros. Sci. 47, 835 (2005).
C. Santato and C.M. Lopez, Electrochem. Commun. 9, 1519 (2007).
I. Saadeddin and B. Pecquenard, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 5240 (2007).
P.E. Alvarez and C.A. Gervasi, Corros. Sci. 46, 91 (2004).
K.L. Lin and T.P. Liu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 56, 171 (1998).
K.L. Lin, F.C. Chung, and T.P. Liu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 53, 55 (1998).
H. Oulfajrite, A. Sabbar, M. Boulghallat, A. Jouaiti, R. Lbibb, and A. Zrineh, Mater. Lett. 57, 4368 (2003).
U.S. Mohanty and K.L. Lin, Corros. Sci. 48, 662 (2006).
D.Q. Yu, W. Jillek, and E. Schmitt, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 17, 219 (2006).
B.Y. Wu, Y.C. Chan, M.O. Alam, and W. Jillek, J. Mater. Res. 21, 62 (2006).
W.J. Chou, G.P. Yu, and J.H. Huang, Surf. Coat. Technol. 167, 59 (2003).
G. Quartarone, T. Bellomi, and A. Zingales, Corros. Sci. 45, 715 (2003).
J.J. Park and S.I. Pyun, Corros. Sci. 45, 995 (2003).
Y. Zuo, P.H. Zhao, and J.M. Zhao, Surf. Coat. Technol. 166, 237 (2003).
V.S. Sastri, Corrosion Inhibitors—Principles and Applications (Winchester, UK: Wiley, 1998).
M. Mori, K. Miura, T. Sasaki, and T. Ohtsuka, Corros. Sci. 44, 887 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, H., Chen, H., Li, M. et al. Generation of Tin(II) Oxide Crystals on Lead-Free Solder Joints in Deionized Water. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 2170–2178 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0868-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0868-2