Abstract
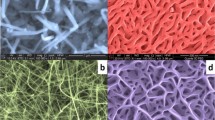
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was applied to study GaN nanowires grown on carbon nanotube surfaces by chemical reaction between Ga2O and NH3 gas in a conventional furnace. These wires grew in two crystallographic directions, 〈2\(\underline {11} \)0〉 and 〈01\(\underset{\raise0.3em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle-}$}}{1} \)0〉 (fast growth directions of GaN), in the form of whiskers covered by small elongated GaN platelets. The morphology of these platelets is similar to that observed during the growth of single crystals from a Ga melt at high temperatures under high nitrogen pressure. It is thought that growth of nanowires in two different crystallographic directions and the arrangement of the platelets to the central whisker may be influenced by the presence of Ga2O3 (based on the observation of the energy dispersive x-ray spectra), the interplanar spacings in the wire, and the presence of defects on the interface between the central part of the nanowire and the platelets surrounding it.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Iijima, Nature (London) 354, 56 (1991).
S. Nakamura, N. Iwasa, M. Senoh, and T. Mukui, Jpn. J. Appl. Phs. 31, 1258 (1992).
S. Nakamura (Paper Plenary 1 presented at the 24th Int. Symp. on Compound Semiconductors, San Diego, CA, September 8–11, 1997).
H. Amano, M. Kito, K. Hiramatsu, and I. Akasaki, Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 106, 725 (1998).
U.K. Mishra, Y.F. Wu, B.P. Keller, S. Keller, and S.P. Denbars, IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 46, 756 (1998).
W. Han, S. Fan, Q. Li, and Y. Hu, Science 277, 1287 (1997).
G.S. Cheng, L.D. Zhang, Y. Zhu, G.T. Fei, L. Li, C.M. Mo, and Y.Q. Mao, Appl. Phs. Lett. 75, 2455 (1998).
W. Han, P. Redlich, F. Ernst, and M. Ruhle, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 652 (1999).
J. Zhu and S. Fan, J. Mater. Res. 14, 1175 (1999).
I. Grzegory, J. Jun, M. Bockowski, S. Krukowski, M. Wroblewski, B. Lucznik, and S. Porowski, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 56, 639 (1995).
Z. Liliental-Weber, M. Benamara, J. Washburn, I. Grzegory, and S. Porowski, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 572, 363 (1999).
M. He, I. Minus, P. Zhou, S.N. Mohammed, J.B. Halpern, R. Jakobs, W.L. Sarney, L. Salamanca-Riba, and R.D. Vispute, Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 3731 (2000).
G.A. Bootsma and H.J. Gassen, J. Cryst. Growth 10, 223 (1971).
S. Otoishi and Y. Tange, J. Crst. Growth 200, 467 (2000).
T. Kaneko, J. Cryst. Growth 63, 239 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liliental-Weber, Z., Gao, Y.H. & Bando, Y. Transmission electron microscopy characterization of GaN nanowires. J. Electron. Mater. 31, 391–394 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-002-0089-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-002-0089-4