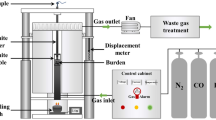
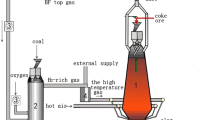
Abstract
The distribution of iron-bearing granular materials in the throat of a blast furnace (BF) plays a crucial role in influencing their performance at high temperatures. Therefore, it is essential to establish a quantitative relationship between the charging operation of the iron-bearing materials at ambient temperatures and their subsequent softening and melting behaviors at elevated temperatures. In this study, the discrete element method (DEM) is employed to quantify the instantaneous mass segregation of quaternary iron-bearing materials throughout the continuous charging process, starting from the feeding conveyor belt and continuing up to the throat. Subsequently, employing quaternary basicity (R4) as a pivotal bridge, softening and melting experiments (the temperature above 900 °C and in an atmosphere with a mole fraction of 30 pct CO to 70 pct N2) are conducted to assess the influence of physical segregation on chemical performances under simulated BF conditions. The results reveal that the sequence of loading quaternary iron-bearing materials onto the feeding belt causes fluctuations in R4, ranging from 1.08 to 1.75. Moreover, these fluctuations are propagated throughout the charging process, resulting in notable fluctuations in the mass fractions of iron-bearing materials and the R4 at the hopper outlet and the end of the chute. Therefore, the primary factor influencing the flowing characteristics of the granular materials is their distribution within the hopper. Then, the segregation in the throat is further characterized by the presence of two distinct R4 ranges (1.2 to 1.29, and 1.3 to 1.39) observed across a total of 48 equal-area blocks, and the significant difference between these two categories is determined by sinters. Besides, the influence of the R4 on softening and melting temperatures is quantitatively evaluated, resulting in a ‘w’-shaped temperature distribution from the center to the edge of the BF. Our findings provide evidence of the inadequacy of evaluating the softening and melting behaviors of iron-bearing materials solely based on their initial proportions in the structure of iron-bearing materials. Instead, a quantitative examination of the granular segregation in the throat, arising from the BF charging operation, is deemed essential to provide substantial support for well-designed elevated-temperature experiments. This approach enables a more comprehensive understanding of the intricate journey of iron-bearing materials in the BF.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Proctor, K. Fehling, E. Shay, J. Wittenborn, J. Green, C. Avent, R. Bigham, M. Connolly, B. Lee, T. Shepker, and M. Zak: Environ. Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 34, pp. 1576–82.
Z. Liu, J. Zhang, H. Zuo, and T. Yang: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 1713–23.
S. Kuang, Z. Li, and A. Yu: Steel Res. Int., 2018, vol. 89, p. 1700071.
G. Wang, Z. Liao, Z. Hu, D. Wang, H. Bai, Z. Zou, and J. Xu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2022, vol. 53B, pp. 931–37.
H. Mio, Y. Narita, S. Matsuzaki, K. Nishioka, and S. Nomura: Powder Technol., 2019, vol. 344, pp. 797–803.
Y. Yu and H. Saxén: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2010, vol. 65, pp. 5237–50.
C. Ho, S. Wu, H. Zhu, A. Yu, and S. Tsai: Miner. Eng., 2009, vol. 22, pp. 986–94.
Y. Yu and H. Saxén: Steel Res. Int., 2013, vol. 10, pp. 1018–33.
V. Radhakrishnan and K. Ram: J. Process. Control., 2001, vol. 11, pp. 565–86.
L. Shi, G. Zhao, M. Li, and X. Ma: Appl. Math. Model., 2016, vol. 40, pp. 10254–73.
H. Zhao, M. Zhu, P. Du, S. Taguchi, and H. Wei: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 2177–85.
K. Zhou, Z. Jiang, D. Pan, W. Gui, and J. Huang: Steel Res. Int., 2022, vol. 93, p. 2100332.
Y. Xu, J. Xu, Z. Liao, Y. Pei, L. Gao, C. Sun, M. Kou, and L. Wen, Powder Technol., 2019, vol. 343, pp. 422–35.
H. Mio, M. Kadowaki, S. Matsuzaki, and K. Kunitomo: Miner. Eng., 2012, vol. 33, pp. 27–33.
W. Xu, S. Cheng, and C. Li: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2022, vol. 49, pp. 208–16.
W. Xu, S. Cheng, Q. Niu, and G. Zhao: ISIJ Int., 2017, vol. 57, pp. 1173–80.
Z. Liao, J. Xu, C. Sun, Y. Yang, Y. Pei, M. Kou, Z. Hu, L. Meng, and L. Wen: Adv. Powder Technol., 2020, vol. 31, pp. 670–77.
S. Wu, M. Kou, J. Xu, X. Guo, K. Du, W. Shen, and J. Sun: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2013, vol. 99, pp. 314–23.
X. Huang, Q. Zheng, A. Yu, and W. Yan: Powder Technol., 2020, vol. 361, pp. 179–89.
X. Huang, Q. Zheng, D. Liu, A. Yu, and W. Yan: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2022, vol. 253, p. 117579.
J. Chen, H. Zuo, Y. Wang, Q. Xue, and J. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2022, vol. 53B, pp. 3793–3804.
Z. Hong, H. Zhou, J. Wu, L. Zhan, Y. Fan, Z. Zhang, S. Wu, H. Xu, L. Wang, and M. Kou: Steel Res. Int., 2021, vol. 92, p. 2000262.
J. Chen, H. Zuo, H. Zhao, Q. Xue, and J. Wang: Powder Technol., 2022, vol. 409, p. 117845.
J. Xu, S. Wu, M. Kou, L. Zhang, and X. Yu: Appl. Math. Model., 2011, vol. 35, pp. 1439–55.
M. Kou, J. Xu, S. Wu, H. Zhou, K. Gu, S. Yao, and B. Wen: Particuology, 2019, vol. 44, pp. 194–206.
B. Dai, J. Yang, F. Liu, X. Gu, and K. Lin: Powder Technol., 2020, vol. 363, pp. 611–20.
S. Kumar, S. Khatoon, S. Parashar, P. Dubey, J. Yogi, and A. Anand: Powder Technol., 2023, vol. 427, p. 118682.
Z. Deng, Y. Fan, J. Theuerkauf, K. Jacob, P. Umbanhowar, and R. Lueptow: Powder Technol., 2020, vol. 374, pp. 389–98.
T. Zhang, J. Gan, A. Yu, D. Pinson, and Z. Zhou: Powder Technol., 2020, vol. 361, pp. 435–45.
Y. Yang, C. Sun, Z. Liao, C. Leng, Z. You, and J. Xu: Powder Technol., 2022, vol. 411, p. 117954.
C. Li, K. Dong, S. Liu, G. Chandratilleke, Z. Zhou, and Y. Shen: Powder Technol., 2022, vol. 407, p. 117660.
W. Xu, S. Cheng, Q. Niu, and G. Zhao: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2017, vol. 46, pp. 105–12.
L. Jiao, S. Kuang, A. Yu, Y. Li, X. Mao, and H. Xu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B, pp. 258–75.
X. Dong, A. Yu, S. Chew, and P. Zulli: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, vol. 41B, pp. 330–49.
L. Jiao, S. Kuang, Y. Li, X. Mao, H. Xu, and A. Yu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2023, vol. 54B, pp. 734–55.
X. An, J. Wang, R. Lan, Y. Han, and Q. Xue: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2013, vol. 20, pp. 11–16.
P. Nogueira and R. Fruehan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 829–38.
P. Nogueira and R. Fruehan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2005, vol. 36B, pp. 583–90.
P. Nogueira and R. Fruehan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, vol. 37B, pp. 551–58.
B. Lyu, G. Wang, F. Yang, H. Zuo, Q. Xue, and J. Wang: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2023, vol. 30, pp. 2366–77.
P. Tan, J. Zhang, J. Huang, Y. Wang, Z. Liu, and F. Han: Chin. J. Eng., 2023, vol. 45, pp. 890–98.
T. Li, C. Sun, X. Liu, S. Song, and Q. Wang: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2018, vol. 45, pp. 755–63.
F. Silva, L. Lemos, P. DeFreitasNogueira, and M. Bressan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2021, vol. 52B, pp. 69–76.
C. Loo, L. Matthews, and D. O’dea: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 930–38.
B. Lyu, G. Wang, L. Zhao, H. Zuo, Q. Xue, and J. Wang: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2023, vol. 30, pp. 227–35.
S. Wu, L. Wang, Y. Lu, and K. Gu: Steel Res. Int., 2018, vol. 89, p. 1800041.
X. She, J. Wang, J. Liu, X. Zhang, and Q. Xue: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 2728–36.
S. Wu, H. Han, H. Xu, H. Wang, and X. Liu: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 686–94.
G. Park, Y. Kang, and J. Park: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 1375–82.
P. Ma, K. Ma, J. Deng, Q. Wu, and J. Xu: ISIJ Int., 2023, vol. 63, pp. 1957–64.
J. Deng, K. Ma, L. Hu, M. Kou, L. Wen, and J. Xu: Ceram. Int., 2020, vol. 46, pp. 11854–60.
K. Ma, J. Xu, J. Deng, M. Kou, and L. Wen: Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2019, vol. 44, pp. 19555–62.
K. Ma, J. Xu, J. Deng, D. Wang, Y. Xu, Z. Liao, C. Sun, S. Zhang, and L. Wen: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 2308–21.
P. Cundall and O.L. Strack: Géotechnique, 1980, vol. 30, pp. 331–36.
J. Xu, Z. Hu, Y. Xu, D. Wang, L. Wen, and C. Bai: Powder Technol., 2017, vol. 308, pp. 273–89.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding through projects from the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant Nos. cstc2019jcyj-msxmX0089, cstc2021ycjh-bgzxm0165, cstb2023nscq-msx0514), and Galen scholarship.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, Z., Wang, K., Yang, Y. et al. Local Influences of Transient Basicity Segregation in Iron-Bearing Materials on Softening and Melting in Blast Furnaces at High Temperatures. Metall Mater Trans B (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03121-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03121-2