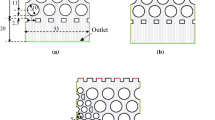
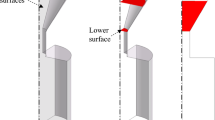
Abstract
In the lower part of the blast furnace (BF), with gas introduced through tuyeres and slag flowing downward from cohesive zone to the hearth, strong cross-flow of gas relative to the slag occurs in front of the raceway, while in the upper parts, counter-current flow of gas and slag exists. The interaction between gas and slag is closely associated with the special flow phenomena such as loading, flooding, or channeling. These phenomena link to furnace irregularities, affecting smooth operation and limiting production. Therefore, understanding the gas–slag interaction and its influencing factors is critical for process control and stable BF operation. In the current study, counter-current gas–slag flow in the packed bed is numerically investigated using the Volume of Fluid technique. Different superficial gas velocities, slag properties, packing structures, and gas inlets are considered in the study. The gas–slag flow behavior at a mesoscopic level was visualized. In particular, localized slag flooding and gas channeling caused by the strong interaction between gas and slag were uniquely identified. Gas channeling, which is a critical phenomenon in a packed bed with counter-current gas–slag flow, can be enhanced by more wetting and higher viscosity slag, and poor permeability regions. It can be speculated that significant gas channeling in the BF can inevitably occur prior to operational limits being reached. In the BF process, the formation of permanent gas channeling and large slag rivulets should be avoided to maintain the proper contact between phases and furnace permeability.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a t :
-
Surface area per packing volume, m2 m−3; for the packing with spherical particle \(A = 6\varepsilon_{{\text{s}}} /d_{{\text{s}}}\)
- A :
-
Area, m2
- F :
-
Surface tension force, kg m−2 s−2
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration, m s−2
- p :
-
Pressure, Pa
- t :
-
Time, s
- \(u\) :
-
Velocity, m s−1
- \(U\) :
-
Superficial velocity, m s−1
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Volume fraction, –
- \(\eta_{{\text{l}}}\) :
-
Liquid viscosity in centipoise, ×10−3 kg m−1 s−1
- \(\kappa_{{\text{i}}}\) :
-
Curvature of the interface, m−1
- \(\theta\) :
-
Contact angle, °
- μ :
-
Viscosity, kg m−1 s−1
- ρ :
-
Density, kg m−3
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Surface tension, kg s−2
- \(\tau\) :
-
Stress tensor, Pa
- g :
-
Gas
- i :
-
Phase i
- j :
-
Phase j
- l :
-
Liquid
- s :
-
Solid
References
Y. Omori: Blast Furnace Phenomena and Modelling, Elsevier Applied Science, London, 1987.
L. Baussaron, C. Julcour-Lebigue, A.M. Wilhelm, H. Delmas, and C. Boyer: AIChE J., 2007, vol. 53, pp. 1850–60.
A.K. Biswas: Principles of Blast Furnace Ironmaking, Cootha Publishing House, Brisbane, 1981.
A.E. Scheidegger: The Physics of Flow Through Porous Media, Oxford University Press, Great Britain, 1963.
M. Leva: Tower Packings and Packed Tower Design, United States Stoneware Company, Akron, 1953.
G.C. Gardner: Chem. Eng. Sci., 1956, vol. 5, pp. 101–14.
T. Fukutake and V. Rajakumar: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1982, vol. 22, pp. 355–64.
X.F. Dong, T. Pham, A.B. Yu, and P. Zulli: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, pp. 189–94.
G.S. Gupta, J.D. Litster, V.R. Rudolph, E.T. White, and A. Domanti: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp. 32–39.
D.Y. Liu, G.X. Wang, and J.D. Litster: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 10–17.
G.X. Wang, S.J. Chew, A.B. Yu, and P. Zulli: ISIJ Int., 1997, vol. 37, pp. 573–82.
J.C. Elgin and F.B. Weiss: Ind. Eng. Chem., 1939, vol. 31, pp. 435–45.
T.K. Sherwood: Absorption and Extraction, 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1952.
T. Sugiyama and M. Sugata, Nippon Steel Technical Report, 1987, pp. 32–42.
J. Szekely and Y. Kajiwara: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1979, vol. 19, pp. 76–84.
Y. Ohno and M. Schneider: Tetsu to Hagane, 1988, vol. 74, pp. 1923–30.
J. Wang, R. Takahashi, and J. Yagi: Tetsu to Hagane, 1991, vol. 77, pp. 1585–92.
G.X. Wang, S.J. Chew, A.B. Yu, and P. Zulli: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28B, pp. 333–43.
S.J. Chew, P. Zulli, and A. Yu: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 1112–21.
C.G. Sun, F.H. Yin, A. Afacan, K. Nandakumar, and K.T. Chuang: Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2000, vol. 78, pp. 378–88.
P. Spicka, M.M. Dias, and J.C.B. Lopes: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2001, vol. 56, pp. 6367–83.
I. Iliuta, B.P.A. Grandjean, S. Piche, and F. Larachi: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2003, vol. 58, pp. 1373–80.
C.W. Hirt and B.D. Nichols: J. Comput. Phys., 1981, vol. 39, pp. 201–25.
X.F. Dong, A. Jayasekara, D. Sert, R. Ferreira, P. Gardin, B.J. Monaghan, S.J. Chew, D. Pinson, and P. Zulli: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2021, vol. 52B, pp. 255–66.
X.F. Dong, A. Jayasekara, D. Sert, R. Ferreira, P. Gardin, B.J. Monaghan, S.J. Chew, D. Pinson, and P. Zulli: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2021, vol. 52B, pp. 2926–38.
X.F. Dong, A. Jayasekara, D. Sert, R. Ferreira, P. Gardin, S.J. Chew, D. Pinson, B.J. Monaghan, and P. Zulli: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2023, vol. 54, pp. 56–69.
J.U. Brackbill, D.B. Kothe, and C. Zemach: J. Comput. Phys., 1992, vol. 100, pp. 335–54.
S. Yuan, R. Dabirian, O. Shoham, and R.S. Mohan: J. Energy Resour. Technol. Trans. ASME, 2020, vol. 142, pp. 102101–111.
H.L. George, R.J. Longbottom, S.J. Chew, and B.J. Monaghan: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 820–26.
T.W. Kang, S. Gupta, N. Saha-Chaudhury, and V. Sahajwalla: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 1526–35.
H.L. George, B.J. Monaghan, R.J. Longbottom, S.J. Chew, and P.R. Austin: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 1172–79.
J.S. Oh and J. Lee: J. Mater. Sci., 2016, vol. 51, pp. 1813–19.
D.D. Geleta, M.I.H. Siddiqui, and J. Lee: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B, pp. 102–13.
S. Ergun: Chem. Eng. Prog., 1952, vol. 48, pp. 89–94.
J.F. Elliott, R.A. Buchanan, and J.B. Wagstaff: J. Met., 1952, vol. 194, pp. 709–17.
J. Szekely and J. Mendrykowski: Chem. Eng. Sci., 1972, vol. 27, pp. 959–63.
H.L. Shulman, C.F. Ullrich, and N. Wells: AIChE J., 1955, vol. 1, pp. 247–53.
H.L. George, R.J. Longbottom, S.J. Chew, D.J. Pinson, and B.J. Monaghan: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 1790–96.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the funding from the Australian Research Council (ARC) through the Industrial Transformation Research Hubs Scheme under Project Number: IH200100004. The funding support and permissions from ArcelorMittal and BlueScope Ltd to publish are gratefully acknowledged. This research was undertaken with the assistance of resources and services from the National Computational Infrastructure (NCI), which is supported by the Australian Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, X.F., Jayasekara, A., Sert, D. et al. Numerical Investigation of Gas and Slag Flow in the Packed Bed. Metall Mater Trans B (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03026-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03026-0