Abstract
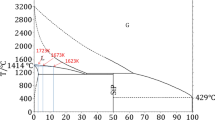
In this paper, the thermodynamic behavior of phosphorus removal from Si-Fe alloys was investigated using a computational approach based on a molecular interaction model combined with the Miedema model and the Tanaka equation. In the Si-P system, the variation of the infinitely dilute activity coefficient of phosphorus with temperature is given as: \({\text{ln}}{\gamma }_{p in si}^{o}=-0.02573-2286.07/T\). In the Si-Fe-P system, the variation of the Fe-P interaction parameter as a function of temperature is represented by the expression: \({\varepsilon }_{P}^{Fe}=0.5095+548.69/T\). Based on the above theoretical analysis, the separation efficiency of phosphorus removal from the Si-Fe-P system was calculated, and the reliability of the model was evaluated using results from dephosphorization experiments conducted with electromagnetically levitated Si-Fe alloy droplets. It is found that a removal efficiency of 94.42 pct can be achieved with a refining time of 55 min at 2023 K in a 50 pct Ar-50 pct H2 gas atmosphere.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \({G}_{m}^{E}\) :
-
Molar excess Gibbs free energy
- \({\overline{G} }_{i}^{E}\) :
-
Partial molar excess Gibbs free energy of component i
- \(R\) :
-
Gas constant
- \(T\) :
-
System temperature
- \({x}_{i}\) :
-
Molar fraction of component i
- \({w}_{i}\) :
-
Mass fraction of component \(i\)
- \({V}_{m}\) :
-
Molar volume
- \({Z}_{i} ,{Z}_{j}\) :
-
Central molecular coordination number of component \(i\) and \(j\)
- \({B}_{ij} , {B}_{ji}\) :
-
Pair-potential energy interaction parameters of the \(i-j\) binary system
- \({k}_{B}\) :
-
Boltzma constant
- \({k}_{B}\) :
-
Activity coefficient of component i
- \(\text{N}{\gamma }_{i}^{0}\) :
-
Infinite dilute activity coefficient of component \(i\)
- \(\text{N}{\varepsilon }_{ii}^{\prime} ,{\varepsilon }_{jj}^{\prime} ,{\varepsilon }_{ij}^{\prime} ,{\varepsilon }_{ji}^{\prime}\) :
-
Pair-potential energies
- \(\text{N}{\rho }_{m}\) :
-
Molecular number density
- \(\text{N}{r}_{o} ,{r}_{m}\) :
-
The beginning and first peak values of radial distance in a radial distribution function near the melting point
- \(\text{N}\Delta {H}_{m}\) :
-
Enthalpy of fusion
- \(\text{N}{T}_{m}\) :
-
Melting temperature
- \(N{d}_{cov}\) :
-
Atomic covalent diameter
- \(\text{N}{\Delta \overline{H} }_{m}^{0}\) :
-
Partial molar enthalpy at infinite dilution
- \(\text{N}{\overline{S} }_{m}^{E}\) :
-
Partial molar excess entropy at infinite dilution
- \(\text{N}{NZ}_{c}\) :
-
Close packed coordination number
- \(\text{N}\phi\) :
-
Electronegativity
- \(\text{N}{n}_{ws}\) :
-
Electron density
- \(\text{N}u, p, r,\sigma\) :
-
Empirical constants
- \(\text{N}{\varepsilon }_{i}^{i} , {\varepsilon }_{j}^{i}\) :
-
Interaction coefficient
- \({t}_{0}, {t}_{t}\) :
-
Levitation refining time in the beginning and end
- \({a}_{i}\) :
-
Activity of component \(i\)
- \(\beta\) :
-
Separation coefficient
- \({P}_{i}^{*}\) :
-
Saturated vapor pressure of component \(i\)
- \({P}_{i}\) :
-
Partial pressure of solute \(i\) in gas phase
- \(\eta\) :
-
Removal efficiency
- \(M\) :
-
Molar mass
- \({\rho }_{i}\) :
-
Mass density of component \(i\)
- \({c}_{i}\) :
-
Concentration of component i at \({t}_{0}\) or \({t}_{t}\)
- \({Ng}_{i}\) :
-
Weight of sample at \({t}_{0}\) or \({t}_{t}\)
- \(A\) :
-
Surface area of levitated sample
- \(V\) :
-
Volume of levitated sample
References
K. Morita and T. Miki: Intermetallics, 2003, vol. 11, pp. 1111–17.
K. Le, Y.D. Yang, M. Barati, A. Mclean: Proceedings of the 3rd Pan American Materials Congress, Springer, Cham, 2017, pp. 125–33.
M.D. Johnston and M. Barati: J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2011, vol. 357, pp. 970–75.
N. Yuge, M. Abe, K. Hanazawa, H. Baba, N. Nakamura, Y. Kato, Y. Sakaguchi, S. Hiwasa, and F. Aratani: Prog. Photovoltaics, 2001, vol. 9, pp. 203–09.
Q. Wang, W. Dong, Y. Tan, D.C. Jiang, C. Zhang, and X. Peng: Rare Met., 2011, vol. 30, pp. 274–77.
B.G. Gribov and K.V. Zinov’ev: Inorg. Mater., 2003, vol. 39, pp. 653–62.
P.S. Ravishankar, L.P. Hunt, and R.W. Francis: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1984, vol. 131, p. 872.
D.C. Jiang, S.Q. Ren, S. Shi, W. Dong, J.S. Qiu, Y. Tan, and J.Y. Li: J. Electron. Mater., 2014, vol. 43, pp. 314–19.
P. Wu, Y.D. Yang, M. Barati, and A. McLean: High Temp. Mater. Process., 2014, vol. 33, pp. 477–83.
W. Yan, Y.D. Yang, W.Q. Chen, M. Barati, and A. McLean: Vacuum, 2017, vol. 135, pp. 101–08.
Z.M. You, H. Zhang, S.L. Cui, Z.H. Jiang, and I.H. Jung: Materials, 2023, vol. 16, p. 4099.
H.K. Hardy: Acta Metall., 1953, vol. 1, pp. 611–12.
G.M. Wilson: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1964, vol. 86, pp. 127–30.
H. Renon and J.M. Prausnitz: AIChE J., 1968, vol. 14, pp. 135–44.
D.S. Abrams, F. Seneci, P.L. Chueh, and J.M. Chueh: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1975, vol. 14, pp. 52–54.
A.R. Miedema, P.F. Chatel, and F.R. Boer: Physical B+C, 1980, vol. 100, pp. 1–28.
K.C. Chou and S.K. Wei: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28B, pp. 439–45.
D.P. Tao: Thermochim. Acta., 2000, vol. 363, pp. 105–13.
D.P. Tao: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2002, vol. 33B, pp. 502–06.
T. Tanaka, N.A. Gokcen, and Z.I. Morita: Int. J. Mater. Res., 1990, vol. 81, pp. 349–53.
Q. Yu, J.J. Wu, W.H. Ma, and K. Liu: Silicon, 2017, vol. 9, pp. 355–62.
D.P. Tao: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2014, vol. 45B, pp. 2232–46.
D.P. Tao: J. Alloys Compd., 2008, vol. 457, pp. 124–30.
K. Liu, J.J. Wu, K.X. Wei, W.H. Ma, K.Q. Xie, S.Y. Li, et al.: Vacuum, 2015, vol. 114, pp. 6–12.
S.Y. Li, K. Liu, F. Wang, F.S. Xi, J.J. Wu, W.H. Ma, Y. Lei, Y.J. Wang, and X.N. Zhang: J. Min. Metall. Sect. B, 2020, vol. 56, pp. 69–76.
D.P. Tao: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 3495–97.
T. Iida and R.I.L. Guthrie: The Physical Properties of Liquid Metals, Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1988, pp. 19–46.
R.C. Evans: J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. (Scientific ed.), 1941, vol. 30, p. 121.
N.A. Gokcen: Statistical Thermodynamics of Alloys, Plenum Press, New York, 1986.
F.R. de Boer, R. Boom, W.C.M. Mattens, A.R. Miedema, and A.K. Niessen: Cohesion in Metals, North-Holland, Netherlands, 1988.
Y. Sun, D.P. Tao, J.J. Wu, X. Huang, and W.H. Ma: Vacuum, 2016, vol. 128, pp. 106–11.
G.W. Xu, B. Wang, H. Suzuki, S.Q. Gao, X.X. Ma, N. Nakagawa, et al.: J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 1999, vol. 32, pp. 82–90.
Predel and Landolt-Börnstein: Group IV: Physical Chemistry, Springer, Berlin, 2006.
C. Wagner: Thermodynamics of Alloys, Addison-Wesley, Massachusetts, 1952, p. 51.
X.G. Huang: Ferrous Metallurgy Principle, 3nd ed., Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, CHN, 2008, pp. 104-105 (In Chinese).
Q. Yu, J.J. Wu, W.H. Ma, Kai, Liu: Silicon, 2017, vol. 9, pp. 355–62.
Y.B. Zheng, Z.Q. Chen, F. Chen, L. Qiao, and L.L. Mao: Metall. Eng., 2015, vol. 2(3), pp. 158–67.
J.X. Chen: Handbook of Common Diagrams, Tables and Data for Steelmaking, 2nd ed., Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, CHN, 2013, pp. 704-730 (In Chinese).
H. Dalaker: Comput. Methods Mater. Sci., 2013, vol. 13, pp. 407–11.
J. Safarian and M. Tangstad: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 1427–45.
I.H. Jung and Y.M. Zhang: JOM, 2012, vol. 64, pp. 973–81.
T. Miki, K. Morita, and N. Sano: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 1996, vol. 27B, pp. 937–41.
Y.N. Dai, B. Yang: Vacuum Metallurgy for Nonferrous Metals and Materials, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, CHN, 2000, pp. 38-47 (In Chinese).
S. Shi, P.T. Li, J.X. Meng, D.C. Jiang, Y. Tan, and H.M. Asghar: Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017, vol. 19, pp. 28424–33.
L. Feng and W.Y. Shi: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2016, vol. 101, pp. 629–36.
H.L. Yan, C.W. Dong, H. Xiong, B. Yang, X.M. Chen, Y. Deng, et al.: Chin. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., 2015, vol. 35, pp. 1338–341. (In Chinese).
Y.H. Yun and C.Z. Zhang: J. Vac. Sci. Technol., 2015, vol. 35, pp. 386–90. (In Chinese).
Acknowledgments
We greatly acknowledge the support of the Yunnan Provincial Department of Education Scientific Research Fund Project (Grant: 2023J0130), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant: 52074140) and Hunan Zhongke Electric Co. Ltd.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, P., Zhang, G., Yi, B. et al. Thermodynamic Assessment of Phosphorus Removal From Si-Fe Levitated Droplets. Metall Mater Trans B 54, 3377–3389 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-023-02915-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-023-02915-0