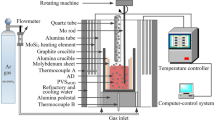
Abstract
Spent V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst (SVWTC) is considered hazardous waste and a valuable resource of Ti, W, and V. Herein, Ti, W, and V were recovered from waste via silicothermic reduction to prepare W- and V-containing Si-Ti alloys with potential applications. An optimal reduction slag system (CaO-SiO2-TiO2-20 wt pct MgO) and reduction temperature (1773K) were determined to ensure completion of the Si reduction of spent V2O5-WO3/TiO2. The effects of the reduction time (holding time) and basicity (CaO/SiO2 mass ratio) of the initial slag on the separation of the alloy and reduction of Ti, W, and V oxides were investigated. Extending the holding time and basicity of the initial slag improved the separation of the alloy from the residual slag and increased the extraction ratios of Ti, W, and V. The equilibrium time was determined as 6 hours, and the maximum extraction ratios of Ti, W, and V were 96.9, 95.5, and 93.6 pct, respectively. The corrosion of the refractory material during Si reduction was investigated and was controlled at 2.65 pct with high recovery of the oxides. No waste liquid was discharged, and the residual slag could be recycled. This study introduces a green and efficient method for recycling Ti, W, and V from SVWTC and provides a new method for preparing W- and V-containing Si-Ti alloys.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.J. Yuan: Resour. Conserv. Recy., 2018, vol. 129, pp. 290–92.
M.A. Dmitrienko, G.S. Nyashina, and P.A. Strizhak: J. Clean. Prod., 2018, vol. 177, pp. 284–301.
L. Chen, H.J. Li, and H.M. Ge: J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, vol. 113(50), pp. 21177–84.
S.X. Li, D.C. Liu, X. Li, Y. Peng, and H.J. Li: Catal. Commun, 2017, vol. 100, pp. 112–16.
A. Marberger, M. Elsener, D. Ferri, and O. Kröcher: Catalysts, 2015, vol. 5(4), pp. 1704–20.
L.J. Alemany, F. Berti, G. Busca, G. Ramis, D. Robba, G.P. Toledo, and M. Trombetta: Appl. Catal. B, 1996, vol. 10(4), pp. 299–311.
B.M. Reddy, I. Ganesh, and E.P. Reddy: J. Phys. Chem. B, 1997, vol. 101(10), pp. 1769-1774.
S. Cimino, L. Lisi, and M. Tortorelli: Chem. Eng. J., 2016, vol. 283, pp. 223–30.
C.P. Cho, Y.D. Pyo, J.Y. Jang, G.C. Kim, and Y.J. Shin: Appl. Therm. Eng., 2017, vol. 110, pp. 18–24.
X. Li, J. Li, Y. Peng, H. Chang, T. Zhang, S. Zhao, W. Si, and J. Hao: Appl. Catal. B, 2016, vol. 184, pp. 246–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.11.042.
J. Yang, Q. Yang, J. Sun, Q. Liu, D. Zhao, W. Gao, and L. Liu: Catal. Commun., 2015, vol. 59, pp. 78–82.
C.U.I. Odenbrand: Appl. Catal. B, 2018, vol. 234, pp. 365–77.
M.L. Cao, Q. Wang, W. Zhang, F.Z. Qiu, and J. Yang: J. Equip. Environ. Eng., 2018, vol. 2, pp. 55–61 (in Chinese).
C.P. Qi, W.J. Bao, L.G. Wang, H.Q. Li, and W.F. Wu: Catalysts, 2017, vol. 7(4), art. no. 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7040110.
G. Moon, J.H. Kim, Y.C. Cho, I.H. Choi, H.N. Kang, T.H. Lee, J.Y. Lee, and J. Kang: Rare Met. Technol., 2019, vol. 2019, pp. 119–29.
Y. Cao, J. Yuan, H. Du, D. Dreisinger, and M. Li: Miner. Eng., 2021, vol. 165, p. 106857.
Q.C. Li, Z.Y. Liu, and Q.Y. Liu: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, vol. 53(8), pp. 2956–62.
W. Wu, C. Wang, W. Bao, and H. Li: Hydrometallurgy, 2018, vol. 179, pp. 52–59.
Q. Su, J. Miao, H. Li, Y. Chen, J. Chen, and J. Wang: Hydrometallurgy, 2018, vol. 181, pp. 230–39.
J.W. Kim, W.G. Lee, I.S. Hwang, J.Y. Lee, and C. Han: J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2015, vol. 28, pp. 73–77.
G. Moon, J.H. Kim, J.Y. Lee, and J. Kang: Hydrometallurgy, 2019, vol. 189, p. 105132.
Q.J. Zhang, Y.F. Wu, and T.Y. Zuo: ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2018, vol. 6(3), pp. 3091–3101.
Z.C. Li, Y. Lei, W.H. Ma, Y.K. Zhang, S.D. Wang, Y.S. Ren, and G.Q. Lv: Green Chem., 2022, vol. 24(8), pp. 3344–57.
W.X. Wang, Z.L. Xue, S.Q. Song, P. Li, and Z.C. Chen: ADV Mater. Res., 2012, vol. 476, pp. 164–69.
Y.V. Bendre, V.F. Goryushkin, R.E. Kryukov, N.A. Kozyrev, and L.P. Bashchenko: Steel Transl., 2018, vol. 48, pp. 163–67.
Z.C. Li, Y. Lei, W.H. Ma, Y.K. Zhang, and C. Wang: Sep. Purif. Technol., 2021, vol. 265, p. 118473.
B. Xiang, Q.X. Wang, Z. Wang, X.Z. Zhang, L.Q. Liu, J. Xu, and D.P. Yu: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2005, vol. 86(24), p. 243103.
Y.C. Zhang, M.Y. Chen, Z.Y. Chen, Y. Wang, S. Li, P.X. Duan, Y.J. Zhong, Z.G. Wu, X.D. Guo, Z.J. Yan, and X.L. Wang: J. Alloy Compd., 2021, vol. 876, p. 160125.
H.Y. Wang, W.P. Si, S. Li, N. Zhang, and Q.C. Jiang: J. Mater. Res., 2010, vol. 25(12), pp. 2317–24.
H.Y. Yang, P.J. Ji, C.H. Zhan, Y.X. Jin, and S.L. Shu: Int. J. Mod. Phys. B, 2019, vol. 33, p. 1940051.
G.X. Qiu, D.J. Miao, X.L. Wei, C. Bai, and X.M. Li: J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2022, vol. 585, p. 121545.
H. Xu, H. Wang, D. Tang, and Y. Li: Mod. Mach., 2011, vol. 4, pp. 67–69 (in Chinese).
Y.K. Zhang, L.E. Sun, Y. Lei, W.H. Ma, and Z.C. Li: Ceram. Int., 2021, vol. 47(13), pp. 18044–18052.
I.B. Rumpf: Vet. Immunol. Immunop., 1997, vol. 4(55), pp. 359–60.
Z.Y. Chen, Y.Q. Li, Y. Tan, and K. Morita: Mater. Trans., 2015, vol. 56, pp. 1919–22.
S.H. Tabaian, M. Maeda, T. Ikeda, and Y. Ogasawara: High Temp. Mater. PR-ISR, 2000, vol. 19(3–4), pp. 257–64.
H.Z. Gu, J. Cao, J.J. Wu, M. Xu, and W.H. Ma: J. Clean Prod., 2022, vol. 359, p. 132080.
I.H. Jung, S.A. Decterov, and A.D. Pelton: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2005, vol. 25(4), pp. 313–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2004.02.012.
H. Okamoto, M.E. Schlesinger, and E.M. Mueller: Alloy Phase Diagrams, ASM Handbook, vol. 3, ASM International, 2016, p. 89. https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v03.a0006247.
C. Vahlas, P.Y. Chevalier, and E. Blanquet: Calphad, 1989, vol. 13(3), pp. 273–92.
Q. Zeng, J.L. Li, Y. Yu, and H.Y. Zhu: High Temp Mater., 2020, vol. 39(1), pp. 74–80.
S. Lyu, X.D. Ma, M. Chen, Z.Z. Huang, Z. Yao, G. Wang, and B.J. Zhao: Calphad, 2020, vol. 68, 101721.
Q.J. Zhang, Y.F. Wu, L.L. Li, and T.Y. Zuo: ACS Sustain Chem. Eng., 2018, vol. 6(9), pp. 12502–10.
I.H. Choi, G. Moon, J.Y. Lee, and R.K. Jyothi: J. Clean. Prod., 2018, vol. 197, pp. 163–69.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFC1907500) and the Yunnan Major Scientific and Technological Projects (No. 202202AG050007).
Author contributions
ZL: writing—original draft, data curation, investigation, validation. YL: supervision, project administration, resources, writing—review and editing, conceptualization. WM: supervision, resources. YZ: investigation, validation. SW: investigation, validation.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Lei, Y., Ma, W. et al. Green Recovery of Ti, W, and V From Spent V2O5-WO3/TiO2 Catalyst to Prepare W- and V-Containing Si-Ti Alloy. Metall Mater Trans B 54, 2614–2628 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-023-02862-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-023-02862-w