Abstract
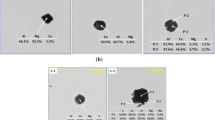
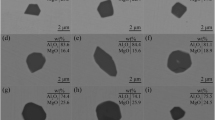
In order to explore the reaction between the molten steel and the slag containing rare earth oxides, the effect of the La2O3 in slag on inclusions in the molten steel was carried out through laboratory experiments and thermodynamic calculations. In the case of steel–slag ratio of 5:1, the chemical reaction between La2O3 in slag and the molten steel occurred so that the element La was transferred to the molten steel and reacted with the existing inclusions in the steel generating a large amount of inclusions containing La2O3. As the La2O3 content in the slag increased to 5 pct, the total La content in the steel and the La2O3 content in inclusions gradually increased to 1.9 ppm and 4.63 pct, respectively. Both of them changed slightly when the La2O3 in slag further increased to 10 pct. The number density of >5 μm inclusions decreased from 4.76 to 0.44 #/mm2 when the La2O3 content in the slag increased from 0 to 10 pct. Moreover, it was found that the La2O3 in the slag was beneficial to remove Al2O3-MgO inclusions from the molten steel. An activity model of slag was established based on the ion and molecule coexistence theory, and it was proved that the activity of Al2O3 in the slag increased with the increase of La2O3 in the slag. In addition, the dissolved aluminum in the molten steel would promote the reduction of La2O3 in the slag, which was verified by both the experimental data and the thermodynamic calculation. The formation mechanism of inclusions during the steel–slag equilibrium reaction was discussed.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhang: Non-metallic Inclusions in Steels: Fundamentals, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2019. (in Chinese).
L. Zhang: Non-metallic Inclusions in Steels: Industrial Practice, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2020. (in Chinese).
J. Wang, L. Zhang, W. Chen, S. Wang, Y. Zhang, and Y. Ren: Chin. J. Eng., 2021, vol. 43, pp. 786–96.
X. Yang, L. Hu, G. Cheng, C. Wu, and B. Wu: J. Rare Earths., 2011, vol. 29, pp. 1079–84.
P. Rocabois, J.-N. Pontoire, V. Delville, and I. Marolleau: ISSTech2003 Conference Proceedings, 2003, pp. 995–1006.
M. Burty, P. Dunand, J.P. Ritt, H. Soulard, A. Blanchard, F. Penet, G. Jeanne, R. Pluquet, and I. Poissonnet: Ironmak. Conf. Proc., 1997, vol. 56, pp. 711–17.
M. Byrne, T.W. Fenicle, and A.W. Cramb: Steelmaking Conference Proceedings., 1985, vol. 68, pp. 451–61.
T. Komai: Tetsu-to-Hagane., 1981, vol. 67, pp. 1152–61.
H. Zeder and L. Pocze: Berg Huttenmann. Monatsh., 1980, vol. 125, pp. 1–5.
G. Benko, S. Simon, and G. Szarka: Neue Hutte., 1972, vol. 17, pp. 40–44.
J.M. Middleton and B. Cauwood: Brit Foundryman, 1967, vol. 60, pp. 320–30.
X. Zhang and K. Cai: Project Report: Investigation of Inclusion Behavior of 16MnR Steel at WISCO, Wuhan, 1996.
Y. Hong, X. Ye, Z. Guo, W. Zhang, and G. Li: Iron Steel., 1980, vol. 15, pp. 29–36.
C. Wang and Y. Zhang: J. Chin. Soc. Rare Earths., 2012, vol. 30, pp. 530–37.
C. Wang and Y. Zou: Acta Metall. Sin., 1980, vol. 16, pp. 190–94.
L. Yu: Study on the Yield of Active Element and Precipitates During Electroslag Remelting Process, University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2012.
Q. Ren and L. Zhang: Metall. Trans. B., 2020, vol. 51, pp. 589–600.
C. Liu, Z. Jiang, J. Zhao, X. Cheng, Z. Liua, D. Zhang, and X. Li: Corros. Sci., 2020, vol. 166, p. 463.
C. Yang, Y. Luan, D. Li, and Y. Li: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 35, pp. 1298–1308.
L. Wang, Y. Liu, Q. Wang, and K. Chou: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 970–75.
S. Ueda, K. Morita, and N. Sano: ISIJ Int., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 1292–96.
R. Kitano, M. Ishii, M. Uo, and K. Morita: ISIJ Int., 2016, pp. 723-30.
Z. Zhao, X. Chen, B. Glaser, and B. Yan: Metall. Trans. B., 2019, vol. 50, pp. 395–407.
D. Wang, M. Jiang, C. Liu, P. Shi, Y. Yao, and H. Wang: J. Rare Earths, 2005, vol. 23, pp. 68–73.
S.J. Jeong, T.S. Kim, and J.H. Park: Met. Mater. Int., 2020, vol. 26, pp. 1872–80.
S.J. Jeong, T.S. Kim, and J.H. Park: Metall. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48, pp. 545–54.
F. Schamber (Ed.): Introduction to Automated Particle Analysis by Focused Electron Beam, Corporation, 2009.
V. Singh, S.N. Lekakh, and K.D. Peaslee: SFSA Technical and Operating Conference, Steel Founders’ Society of America, 2008.
Y. Luo, L. Zhang, W. Yang, Y. Ren, and A.N. Conejo: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2019, vol. 46, pp. 359–67.
V. D. Eisenhuttenleute: Germany: Verlag Stahleisen Gmbh, 1995.
J. Chen: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2010.
C. Wang, S. Ye, D. Yu, and W. Guo: Acta Metall. Sin., 1984, vol. 20, pp. 357–64.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for support from the National Science Foundation China (Grant No. 52004025, No. U1860206, No. 51725402), and S&T Program of Hebei (Grant No. 20311005D), the High Steel Center (HSC) at Yanshan University, Hebei Innovation Center of the Development and Application of High Quality Steel Materials, Hebei International Research Center of Advanced and Intelligent Manufacturing of High Quality Steel Materials.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Y., Wu, M., Yang, W. et al. Effect of the La2O3 Content in Slag on Inclusions in Al-Killed Steels. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 2088–2103 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02510-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02510-9