Abstract
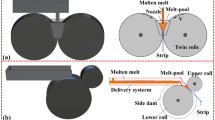
The solid-liquid-solid twin-roll casting (SLS-TRC) is a process of continuously pouring melt between two solid clad trips in the cast roll gap to produce a sandwich composite plate. In the process, the cast roll sleeve material considerably influences the temperature field. The numerical simulation of SLS-TRC is performed to analyze the effects of cast roll sleeve material on molten pool temperature field, roll surface temperature, and clad strip temperature at different casting speeds. The sandwich composite plate was manufactured on the vertical twin-roll casting mill on the basis of the simulation results, and the composite plate was analyzed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Finally, the thermal resistance model of the heat transfer from the molten pool to the cast roll in SLS-TRC was proposed. When the cast roll sleeve material changed from steel to copper, the KISS point, which is the dividing point between the casting stage and the rolling stage, increases by 5 to 10 mm, and the outlet temperature decreases by 134 °C. If the KISS point maintains the same height, the casting speed can increase by 0.3 to 0.6 m/min. The increase of casting speed results in the increase of copper roll surface temperature that is considerably less than that of steel roll surface temperature. This scenario helps improve the thermal fatigue service conditions of the cast roll. SEM analysis indicates that when the cast roll sleeve material is copper, the core grain size increases with the increase of casting speed. However, it decreases when the sleeve is steel. The thermal resistance model shows that when the sleeve material changes from steel to copper, the heat transfer thermal resistance is reduced, thereby increasing the melt solidification rate. This scenario helps increase the casting speed, thereby improving the manufacturing efficiency.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Chen, J. Li, and G. Xu: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2017, vol. 246, pp. 1–12.
M. Xu, M. Zhu, and G. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2015, vol. 46B(3), pp. 1510–19.
M. Xu and M. Zhu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2016, vol. 47B(1), pp. 740–48.
P. Chen, H. Huang, C. Ji, X. Zhang, and Z. Sun: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China., 2018, vol. 28, pp. 2460–69.
D.W. Kim, D.H. Lee, J.S. Kim, S.S. Sohn, H.S. Kim, and S. Lee: Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7(1), pp. 1–11.
C. Ji, H. Huang, X. Zhang, and X. Zhao: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2020, vol. 51(4), pp. 1617–31.
A. Hadadzadeh, M.A. Wells, and V. Jayakrishnan: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2014, vol. 73, pp. 449–63.
J. Park, H. Song, J.S. Kim, S.S. Sohn, and S. Lee: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2017, vol. 48A(1), pp. 57–62.
J.H. Bae, A.K. Prasada Rao, K.H. Kim, and N.J. Kim: Scr. Mater., 2011, vol. 64, pp. 836–39.
R. Nakamura, T. Haga, H. Tsuge, S. Kumai, and H. Watari: Adv. Mater. Res., 2011, vol. 189–193, pp. 4037–40.
R. Nakamura, T. Haga, S. Kumai, and H. Watari: Adv. Mater. Res., 2010, vol. 97–101, pp. 1053–56.
J.J. Park: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2016, vol. 93, pp. 491–99.
O. Grydin, G. Gerstein, F. Nürnberger, M. Schaper, and V. Danchenko: J. Manuf. Process., 2013, vol. 15(4), pp. 501–07.
D. Münster and G. Hirt: Metals., 2019, vol. 9(11), p. 1156.
M. Stolbchenko, O. Grydin, and M. Schaper: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2019, vol. 21(4), p. 1800454.
C. Ji, H. Huang, J. Zhang, and R. Zhao: Appl. Therm. Eng., 2019, vol. 158, p. 113818.
S. Sahoo, A. Kumar, B.K. Dhindaw, and S. Ghosh: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 915–24.
J.J. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2018, vol. 941A, pp. 1354–59.
M. Stolbchenko, O. Grydin, A. Samsonenko, V. Khvist, and M. Schaper: Forsch. Ingenieurwes., 2014, vol. 78, pp. 121–30.
J.J. Park: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2016, vol. 100, pp. 590–98.
J. Zhang, H. Huang, R. Zhao, M. Feng, and K. Meng: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China., 2021, vol. 31(3), pp. 626–35.
P.K. Penumakala, A.K. Nallathambi, E. Specht, U. Urlau, D. Hamilton, and C. Dykes: Appl. Therm. Eng., 2018, vol. 134, pp. 275–86.
S. Li, C. He, J. Fu, J. Xu, G. Xu, and Z. Wang: Mater. Charact., 2020, vol. 161, p. 145.
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2018YFA0707303), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51974278), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province Distinguished Young Fund Project (E2018203446), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province Young Fund Project (E2020203118), and the Hebei Province High Level Talent Fund Project (B2020003013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, R., Huang, H., Yan, M. et al. Effect of Cast Roll Sleeve Material on Temperature Field of Sandwich Composite Plate Solid-Liquid-Solid Twin-Roll Casting Process. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 2051–2065 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02503-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02503-8