Abstract
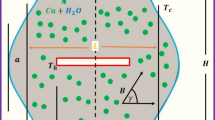
Slurry electrolysis (SE) is a one-step green electrochemical technology used for the treatment of complex ores and solid waste. To explore the solid–liquid suspension characteristics of an SE stirred tank for antimony ores, a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model was adopted using a Eulerian-Eulerian model. The kinetic theory of granular flow model was utilized to consider the particle–particle and particle–wall interactions. The solids holdup distribution predicted by the CFD model was consistent with water model experiments. According to the velocity vector distribution, the stirred tank was divided into five regions. The solids concentration was higher in the weak circulation region around the tank wall, and it was lower in the convection region and the upper part of the fluid falling region. Moreover, the variation curves of the liquid velocity and solids concentration demonstrated that the flow was centrally symmetric and that the presence of membranes and anodes contributed to the ordering of fluid flow. The mixing times in the strong circulation and weak circulation regions were both close to 20 seconds. The fluid flow between the anodic baffles, 94 seconds, was the limiting factor for mixing time.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.F. Qiu: Min. Metall., 1998, vol. 7(4), pp. 40–5 (in Chinese).
C.Y. Wang, D.F. Qiu, F. Yin, H.Y. Wang, and Y.Q. Chen: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China., 2010, vol. 20(S1), pp. 60–64.
Q. Wang, Y. Zhu, Q.Y. Wu, E. Gratz, and Y. Wang: RSC Adv., 2015, vol. 5(8), pp. 5501–07.
Q. Wang and Y. Wang: ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2016, vol. 8(16), pp. 10334–42.
Q. Wang, M.C. Shang, Y. Zhang, Y. Yang, and Y. Wang: ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2018, vol. 10(8), pp. 7162–70.
Y.L. Zhang, C.Y. Wang, Y.Q. Chen, Y.Q. Yang, W.F. Wang, and X. Xie: Nonferrous Met. (Extract Metall)., 2014, vol. (11), pp. 16–20 (in Chinese).
Y.Q. Chen, Y. Liu, C.Y. Wang, Y.Q. Yang, and Y.L. Zhang: Nonferrous Met. (Extract Metall)., 2015, vol. (12), pp. 5–7 (in Chinese).
Y.L. Zhang, C.Y. Wang, B.Z. Ma, X.W. Jie, and P. Xing: Hydrometallurgy., 2019, vol. 186, pp. 284–91.
X.W. Yang, Y.J. Zhang, L.H. Deng, and D.F. Qiu: Eng. Sci., 2000, vol. 2(6), pp. 49–51 (in Chinese).
C.Y. Wang, D.F. Qiu, Y.S. Zhang, and P.H. Jiang: Nonferrous Met., 1995, vol. 47(2), pp. 54–59 (in Chinese).
Y.L. Zhang, C.Y. Wang, X.W. Jie, W. Gao, S.F. Ruan: Nonferrous Met. (Extract Metall)., 2020, vol. (7), pp. 1–4 (in Chinese).
W. Jin and Y. Zhang: ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2020, vol. 8(12), pp. 4693–4707.
Y.D. Xue and Y.T. Wang: Green Chem., 2020, vol. 22(19), pp. 6288–6309.
Y.G. Zhang, M.J. Chen, Q.X. Tan, B. Wang, and S. Chen: Hydrometallurgy., 2018, vol. 175, pp. 150–54.
S. Hosseini, D. Patel, F. Ein-Mozaffari, and M. Mehrvar: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2010, vol. 49(9), pp. 4426–35.
S. Hosseini, D. Patel, F. Ein-Mozaffari, and M. Mehrvar: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2010, vol. 65(4), pp. 1374–84.
Z. Chen, P. Zhou, P. Li, G.M. Xiao, H.J. Yan, and W.W. Wei: Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 2012, vol. 22(6), 1835–41.
A. Tamburini, A. Cipollina, G. Micale, A. Brucato, and M. Ciofalo: Chem. Eng. J., 2012, vol. 193, pp. 234–55.
A. Tamburini, A. Cipollina, G. Micale, A. Brucato, and M. Ciofalo: Chem. Eng. J., 2013, vol. 223, pp. 875–90.
A. Kazemzadeh, F. Ein-Mozaffari, and A. Lohi: Powder Technol., 2020, vol. 360, pp. 635–48.
H.L. Lu, Y.R. He, and D. Gidaspow: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2003, vol. 58(7), pp. 1197–1205.
D. Wadnerkar, M.O. Tade, V.K. Pareek, and R.P. Utikar: Particuology, 2016, vol. 29, pp. 16–33.
L. Yang, J.T. Padding, and J.A.M. Kuipers: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2016, vol. 152, pp. 783–94.
L. Xie, J.D. Zhu, J. Hu, and C.W. Jiang: Miner. Eng., 2020, vol. 149, p. 10628.
S.Y. Wang, X.X. Jiang, R.C. Wang, X. Wang, and S.W. Yang: Adv. Powder Technol., 2017, vol. 28(6), pp. 1611–24.
L. Xie and Z.H. Luo: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2018, vol. 176, pp. 439–53.
H.J. Duan, L.F. Zhang, B.G. and Thomas, and A.N. Conejo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49(5). pp. 2722–43.
P. Mishra and F. Ein-Mozaffari: Int. J. Multiph. Flow., 2017, vol. 91, pp. 194–207.
T. Wang, G.Z. Yu, Y.M. Yong, C. Yang, and Z.S. Mao: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2010, vol. 49(3), pp. 1001–09.
H.L. Zhao, Z.M. Zhang, T.A. Zhang, Y. Liu, and S.Q. Gu: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China., 2014, vol. 24(8), pp. 2650–59.
A.W. Patwardhan and J.B. Joshi: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1999, vol. 38, pp. 3131–43.
G.J. Zhang, J. Min, Z.M. Gao, and L.T. Shi: J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ., 2005, vol. 19(2), pp. 169–74.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51974018).
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, T., Shen, H., Na, G. et al. CFD Simulation of Suspension Characteristics in a Stirred Tank for Slurry Electrolysis. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 1747–1758 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02484-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02484-8