Abstract
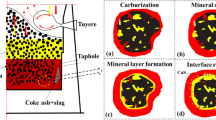
A blast furnace operates under a countercurrent flow process, and a wide variety of physical and chemical reactions take place, especially in the hearth at the highest temperature. Therefore, the working status and erosion of the carbon brick have a critical influence on the longevity of the blast furnace. Although the phenomena in the hearth cannot be directly observed through the black box, hearth dissection provides an alternative way to access and subsequently evaluate the internal conditions. In this paper, a 4000 m3 blast furnace hearth was dissected, and 12 residual iron samples were collected and subjected to composition, morphology, and thermal conductivity analyses. The results show that in the center of the hearth, the residual iron had thicker metallic iron strips. This is because the residual iron in the center of the dissected hearth was fully mixed with carbon or coke, and this mixing apparently enhanced the heat conductivity in the center of the hearth to as great as 80.5 W/(m K). However, such a mixing state was gradually relieved in the regions either close to the wall or settling on the bottom. Thus, the residual iron near the wall formed a needle-like surface with a layer-by-layer structure in the form of alternatively thinner strip-shaped carbon and metallic iron, and the thermal conductivities of the residual iron near the wall were above 40.0 W/(m K) regardless of the relative height. Moreover, the erosion mechanisms of the blast furnace hearth wall are proposed, and the erosion thickness is accordingly evaluated based on the heat transfer model, in which the measured thermal conductivities of the residual iron are taken into consideration. According to the erosion mechanism, the thickness of residual iron is thinner, the erosion is more serious.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.L. Jiao, S.B. Kuang, L.L. Liu, A.B. Yu, Y.T. Li, X.M. Mao, and H. Xu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2021, vol. 52B(1), pp. 138–55.
S.B. Kuang, Z.Y. Li, and A.B. Yu: Steel Res. Int., 2018, vol. 89(1), p. 1700071.
X.B. Yu and Y.S. Shen: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B(5), pp. 2079–94.
L. Zhang, J.L. Zhang, K.X. Jiao, and C. Wang: ISIJ Int., 2020, vol. 60(8), pp. 1655–61.
F.M. Zhang: J. Iron Steel Res. (Int.), 2013, vol. 20(9), pp. 53–60.
J.F. Ma, H.B. Zhao, and S.S. Chen: J. Iron Steel Res. (Int.), 2009, vol. 16(5), pp. 859–63.
T.J. Park, K.H. Ko, J.H. Lee, S. Gupta, V. Sahajwalla, and B.C. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B(3), pp. 1282–88.
L. Zhang, J.L. Zhang, K.X. Jiao, X.K. Zhang, S.J. Duan, X. Wu, and J.C. Wang: Metall. Res. Technol., 2021, vol. 118(4), p. 410.
M. Naito, K. Takeda, and Y. Matsui: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55(1), pp. 7–35.
A. Preuer, J. Winter, and H. Hiebler: Steel Res., 1992, vol. 63(4), pp. 139–46.
H. B. Zhao, S. S. Chen, J. F. Zhu, H. W. Pan, Z. J. Wang, and J. S. Sun: 5th International Congress on the Science and Technology of Ironmaking, ICSTI 2009, 2009, pp. 897–901.
L. Zhang, J.L. Zhang, K.X. Jiao, G. Jia, J.T. Gong, X.T. Yang, M.X. Zhao, and W.B. Duan: Metall. Res. Technol., 2021, vol. 118(1), p. 106.
P.C. Lai, S.W. Du, S.H. Liu, and W.T. Cheng: Thermal Sci. Eng. Prog., 2021, vol. 23, p. 100908.
A. Shinotake, H. Nakamura, N. Yadoumaru, Y. Morizane, and M. Meguro: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43(3), pp. 321–30.
L. Shao and H. Saxén: Steel Res. Int., 2012, vol. 83(9), pp. 878–85.
M.F. Barbés, R. Marinas, E. Brandaleze, R. Parra, and R. Colás: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48(2), p. 134.
C.E. Huang, S.W. Du, and W.T. Cheng: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48(2008), pp. 1182–87.
X.F. Dong and P. Zulli: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2020, vol. 47(3), pp. 307–15.
X.F. Dong, P. Zulli, and M. Biasutti: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2019, vol. 47(5), pp. 1–6.
X.F. Wang and Q.J. Zhai: J. Iron Steel Res. (Int.)., 2017, vol. 24(10), pp. 1016–22.
Q. Niu, S.S. Cheng, W.X. Xu, and W.J. Niu: ISIJ Int., 2019, vol. 59(10), pp. 1776–85.
S.N. Silva, F. Vernilli, S.M. Justus, O.R. Marques, A. Mazine, J.B. Baldo, E. Longo, and J.A. Varela: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2013, vol. 32(6), pp. 459–67.
K.X. Jiao, C. Wang, J.L. Zhang, S. Ren, and E. Dian-Yu: JOM, 2020, vol. 72(5), pp. 1935–42.
M.S. Song and Z.J. Yu: Res. Iron Steel, 2009, vol. 37(2), pp. 1–6.
M.S. Song, Z.Q. Zou, and Z.J. Yu: China Metall., 2005, vol. 15(11), pp. 6–10.
L. Zhang, J.L. Zhang, K.X. Jiao, Z.P. Zou, and Y.J. Zhao: ISIJ Int., 2019, vol. 59(11), pp. 1991–96.
K. Nishioka, T. Maeda, and M. Shimizu: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45(5), pp. 669–76.
K.X. Jiao, J.L. Zhang, Z.J. Liu, Z.Z. Liu, Y. Deng, and X.Y. Fan: Metall. Res. Technol., 2018, vol. 115(1), p. 109.
H.B. Zhao, S.F. Huo, and S.S. Cheng: Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2013, vol. 20(4), pp. 345–53.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding through projects from the Venture & Innovation Support Program for Chongqing Overseas Returnees (cx2019138), the Young Top-notch Talent Program of Chongqing, China (cstc2021ycjh-bgzxm0165).
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Liao, Z., Hu, Z. et al. Influence of the Residual Iron on the Erosion of Carbon Bricks in a 4000 m3 Blast Furnace Hearth: From the Measured Properties to the Proposed Mechanisms. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 931–937 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02438-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02438-0