Abstract
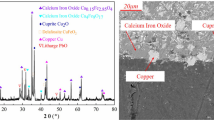
The vanadium slag processing residue (VSPR) is a hazardous waste produced during the vanadium extraction process based on steelmaking process, which contains various toxic and valuable metal elements including chromium, vanadium, and iron. To remediate the VSPR and recover the valuable elements, we propose a novel approach for VSPR self-digestion via the hot metal pre-treatment (an essential procedure before converter steelmaking). The carbothermic reduction roasting of VSPR was performed to decompose the stable spinel phase containing iron, chromium, and vanadium at 1100 °C, yielding pre-reduced VSPR (PR-VSPR). Consequently, the 85.1 pct of iron oxide in VSPR could be reduced into "joined crystal", while the chromium and vanadium mainly existed in the residual spinel with porous structure. The 30 pct CaO addition to adjust VSPR or PR-VSPR composition could significantly improve its smelting performance. After the interaction of the flux (VSPR & CaO) and the flux (PR-VSPR & CaO) with hot metal, the desulfurization rates of the hot metal reached 94.3 and 97.1 pct, respectively, meeting the desulfurization requirement for steelmaking. Correspondingly, the iron oxides in VSPR and PR-VSPR were reduced into hot metal with the recovery yield of 78.1 and 93.7 pct, respectively. A majority of chromium (66.0 pct) and vanadium (73.9 pct) from the flux (VSPR & CaO) remained in the spinel phase of residual slag, whereas a large proportion of vanadium (91.1 pct) and chromium (88.0 pct) from the flux (PR-VSPR & CaO) was recovered into the hot metal. Finally, we designed two process routes employing (VSPR & CaO) and (PR-VSPR & CaO), respectively, and the latter has advantages in the recovery of valuable elements and the harmlessness treatment.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.F. Zhang, F.G. Liu, X.X. Xue, and T. Jiang: J. Alloys. Compd., 2016, vol. 686, pp. 356–65.
B. Zhang, P.Y. Shi, and M.F. Jiang: Miner., 2016, vol. 6, pp. 7–18.
J. Diao, W. Zhou, Z.Q. Ke, Y. Qiao, T. Zhang, X. Liu, and B. Xie: J. Clean. Prod., 2016, vol. 125, pp. 1159–67.
J. Diao, Y.Y. Qiu, J. Lei, Q. Zhang, W.F. Tan, H.Y. Li, and B. Xie: JOM., 2021, vol. 73, pp. 999–1003.
J. Diao, L. Liu, J. Lei, W.F. Tan, H.Y. Li, and B. Xie: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2021, vol. 52, pp. 494–501.
X. Zhang, B. Xie, J. Diao, and X.J. Li: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2012, vol. 39, pp. 147–54.
Y. Guo, H.Y. Li, Y.H. Yuan, J. Huang, J. Diao, G. Li, and B. Xie: Int. J. Miner Metall. Mater., 2021, vol. 28, pp. 974–80.
G. Wang, M.M. Lin, J. Diao, H.Y. Li, B. Xie, and G. Li: ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2019, vol. 7, pp. 18133–41.
H.Y. Li, C.J. Wang, Y.H. Yuan, Y. Guo, and J. Diao: J. Clean. Prod., 2020, vol. 260, p. 121091.
Z.H. Wang, S.L. Zheng, S.N. Wang, B. Liu, D.W. Wang, H. Du, and Y. Zhang: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China., 2014, vol. 24, pp. 1273–88.
Y. Guo, H.Y. Li, J. Cheng, S. Shen, J. Diao, and B. Xie: Sep. Purif. Technol., 2021, vol. 263, p. 118396.
G.Q. Zhang, D.M. Luo, C.H. Deng, L. Lv, B. Liang, and C. Li: J. Alloys Compd., 2018, vol. 742, pp. 504–11.
T. Jiang, J. Wen, M. Zhou, and X.X. Xue: J. Alloys. Compd., 2018, vol. 742, pp. 402–12.
G. Wang, J. Diao, L. Liu, M. Li, H.Y. Li, and G. Li: J. Clean. Prod., 2019, vol. 237.
H. Liu, H. Du, D.W. Wang, S.N. Wang, S.L. Zheng, and Y. Zhang: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China., 2013, vol. 23, pp. 1489–1500.
B. Liu, H. Du, S.N. Wang, Y. Zhang, S.L. Zheng, L.J. Li, and D.H. Chen: AIChE J., 2013, vol. 59, pp. 541–52.
Y. Guo, H.Y. Li, S. Shen, J. Cheng, J. Diao, and B. Xie: J. Hazard. Mater., 2021, vol. 405, p. 124669.
S. Sampath, S. Sali, and N.C. Jayadevan: Thermochim. Acta., 1990, vol. 159, pp. 327–35.
S.C. Jagupilla, W. Mahmoud, and H.M. Deok: Chemo-sphere., 2015, vol. 136, pp. 95–101.
S. Dey and A.K. Paul: Chemosphere., 2016, vol. 156, pp. 69–75.
B. Zhang, C.J. Liu, Z.Z. Liu, Z.Q. Li, and M.F. Jiang: Process Saf. Environ. Prot., 2019, vol. 128, pp. 362–71.
J. Ma, G.Q. Fu, W. Li, and M.Y. Zhu: Int. J. Miner Metall. Mater., 2020, vol. 27, pp. 28–36.
Z.Y. Cai, B. Song, L.F. Li, Z. Zhen, and X.K. Cui: Met., 2019, vol. 9, pp. 1–9.
W.Q. Wang, Y.G. Zhu, S.Q. Zhang, J. Deng, Y. Huang, and W. Yan: Miner., 2017, vol. 7, p. 134.
C. Yin, S. Zhang, X. Yang, W.N. Yuan, W.Z. Yu, L.Y. Wen, T. Li, and C.G. Bai: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2021, vol. 52, pp. 4096–4108.
S. Saleem and G.G. Roy: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2020, vol. 51, pp. 2735–55.
Z. Dong, J. Zhang, and B. Yan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2021, vol. 52, pp. 3961–69.
Acknowledgments
Financial support to this project is provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52174383; 51774087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Wang, R., Liu, C. et al. Self-digestion of Cr-Bearing Vanadium Slag Processing Residue via Hot Metal Pre-treatment in Steelmaking Process. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 1183–1195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02430-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02430-8