Abstract
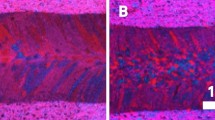
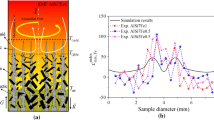
A phase-field model is utilized to associate the solidification behavior of dendrites to the microscopic characteristics of the weld and to characterize the microstructure evolution in dissimilar pulsed laser welded Hastelloy X to 347 stainless steel alloy. The simulations reveal that the morphology of the dendrites during rapid solidification of the molten zone is affected by a melt flow and dilution level. The effect of melt flow as a result of Marangoni convection is modeled by Boussinesq approximation to adjust the concentration field around a developing dendrite, modifying its growth morphologies. The enhancement of hot cracking resistance is studied by adjusting the microstructure morphology through the possibility of the backfilling of the melt for the most efficient dendrite spacing, which was evaluated by correlation of the heat conduction problem and the phase-field model. Besides, the laser offset was estimated by finding the optimal chemical composition of the weld zone in the ternary Fe-Nieq-Creq system that affects the microstructure predicted by the phase-field model. The segregation of nanoparticle compounds analyzed by TEM in interdendritic regions is possible for primary dendrite spacing higher than 3 μm and consequently the solidification cracking susceptibility is increased.
Graphic Abstract






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.R.N. Esfahani, J. Coupland, and S. Marimuthu: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, vol. 224, pp. 135–42.
K. Hao, M. Gao, R. Wu, and X. Zeng: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2020, vol. 275, p. 116330.
W. Kurz, C. Bezençon, and M. Gäumann: Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2001, vol. 2, pp. 185–91.
X.H. Zhan, Z.B. Dong, Y.H. Wei, and R. Ma: J. Cryst. Growth, 2009, vol. 311, pp. 4778–83.
A. Farzadi, M. Do-Quang, S. Serajzadeh, A.H. Kokabi, and G. Amberg: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2008, vol. 16, p. 065005.
D. Montiel, L. Liu, L. Xiao, Y. Zhou, and N. Provatas: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 5925–32.
V. Fallah, M. Amoorezaei, N. Provatas, S.F. Corbin, and A. Khajepour: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 1633–46.
W.J. Zheng, Z.B. Dong, Y.H. Wei, K.J. Song, J.L. Guo, and Y. Wang: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2014, vol. 82, pp. 525–30.
N.S. Bailey, K.-M. Hong, and Y.C. Shin: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2020, vol. 172, p. 109291.
F. Yu, Y. Wei, Y. Ji, and L.-Q. Chen: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2018, vol. 255, pp. 285–93.
M. Gaoyang, X. Lingda, W. Chunming, J. Ping, and Z. Guoli: Mater. Des., 2019, vol. 181, p. 107980.
S. Geng, P. Jiang, X. Shao, G. Mi, H. Wu, Y. Ai, C. Wang, C. Han, R. Chen, and W. Liu: Scr. Mater., 2018, vol. 150, pp. 120–4.
P. Nie, O.A. Ojo, and Z. Li: Acta Mater., 2014, vol. 77, pp. 85–95.
J.A. Dantzig and L.S. Chao: in 10th U.S. Natl. Cong. Appl. Mech., J.P. Lamb, ed., ASME, 1986, pp. 249–55.
J.-H. Jeong, N. Goldenfeld, and J.A. Dantzig: Phys. Rev. E, 2001, vol. 64, p. 041602.
A. Zhang, S. Meng, Z. Guo, J. Du, Q. Wang, and S. Xiong: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, 50:1514-26. Doi:10.1007/s11663-019-01549-5.
Y. Zhao, B. Zhang, H. Hou, W. Chen, and M. Wang: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 35, pp. 1044–52.
T. Suzuki, M. Ode, S.G. Kim, and W.T. Kim: J. Cryst. Growth, 2002, vol. 237–239, pp. 125–31.
H. Kobayashi, M. Ode, S. G Kim, W. T Kim, and T. Suzuki: Scr. Mater., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 689–94.
S.G. Kim: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 4391–9.
J. Kundin, L. Mushongera, and H. Emmerich: Acta Mater., 2015, vol. 95, pp. 343–56.
T. Azimzadegan and S.A.A.A. Mousavi: J. Manuf. Process., 2019, 44:226-40. Doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.06.005.
R. Siquieri, J. Rezende, J. Kundin, and H. Emmerich: Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top., 2009, vol. 177, pp. 193–205.
L. Wang, Y. Wei, F. Yu, Q. Zhang, and Q. Peng: Cryst. Res. Technol., 2016, vol. 51, pp. 602–9.
J.N. Dupont, S.W. Banovic, and A.R. Marder: Weld. J. 2002; 7:374-83.
A. Badillo and C. Beckermann: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 2015–26.
M.C. Tsai and S. Kou: Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids, 1989; 9:1503-16. doi:10.1002/fld.1650091206.
D.L. Olson and G.R. Edwards: Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 1998; 356:927-40. doi:10.1098/rsta.1998.0197.
A. Kumar and P. Dutta: J. Mater. Sci., 2009, vol. 44, pp. 3952–61.
S. Chen, X.-X. Ye, D.K.L. Tsang, L. Jiang, K. Yu, C. Li, and Z. Li: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 35, pp. 29–35.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the University of Tehran for providing facilities and equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted October 13, 2020; accepted March 29, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azimzadegan, T., Mousavi, S.A.A.A. Microstructure and Solidification Cracking Analysis of Dissimilar Pulsed Laser Welded Hastelloy X to 347 Stainless Steel Using Phase-Field Models. Metall Mater Trans B 52, 2307–2326 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02168-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02168-9