Abstract
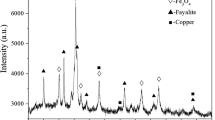
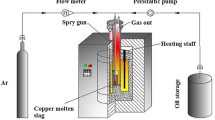
In view of the non-renewable reductant resources and carbon neutralization in the process of copper slag cleaning in an electric furnace, this study proposed to use waste cooking oil as reductant to replace fossil energy. Combined with the phase equilibrium theory and experimental results, the harm of excessive magnetite in the copper smelting slag to the cleaning process was clarified. The reduction thermodynamics of magnetite by using WCO is analyzed. A series of copper slag cleaning experiments with different WCO dosages along with various temperatures and settling durations was systematically carried out in a laboratory-scale electric furnace. The distribution of matte particles in each slag layer after cleaning was investigated in detail, which indicates that the copper content in the upper slag layer can be reduced to 0.56 wt pct via WCO reduction, realizing the green cleaning of copper slag.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Sridhar, J.M. Toguri and S. Simeonov: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 1997, vol. 28, pp. 191-200.
S. Demetrio, S.A.J. Ahumada, M.Á. Durán, E. Mast, U. Rojas, J. Sanhueza, P. Reyes and E. Morales: JOM, 2000, vol. 52, pp. 20-25.
A. Warczok, G. Riveros, P. Echeverríã, C.M. Díaz, H. Schwarze and G. Sãnchez: Can. Metall. Q., 2013, vol. 41, pp. 465-73.
N. Karimi, R. Vaghar and M.R.T. Mohammadi: J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D., 2013, vol. 94, pp. 43-50.
A. Sarrafi, B. Rahmati, H.R. Hassani and H.H.A. Shirazi: Miner. Eng., 2004, vol. 17, pp. 457-59.
U. Kumar, S. Maroufi, R. Rajarao, M. Mayyas, I. Mansuri, R.K. Joshi and V. Sahajwalla: J. Clean. Prod., 2017, vol. 158, pp. 218-24.
S. Zhou, Y. Wei, B. Li and H. Wang: J. Clean. Prod., 2019, vol. 217, pp. 423-31.
Z. Zuo, Q. Yu, M. Wei, H. Xie, W. Duan, K. Wang and Q. Qin: J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 2016, vol. 126, pp. 481-91.
S. Chen and L. Xu: China Food Drug Adm. Mag., 2018, vol. 4, pp. 50-53. (In Chinese)
C.D. Mandolesi de Araújo, C.C. de Andrade, E. de Souza e Silva and F.A. Dupas: Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2013, vol. 27, pp. 445–52.
M.J.A. Romero, A. Pizzi, G. Toscano, G. Busca, B. Bosio and E. Arato: Waste Manage., 2016, vol. 47, pp. 62-68.
S. Zhou, Y. Wei, S. Zhang, B. Li, H. Wang, Y. Yang and M. Barati: J. Clean. Prod., 2019, vol. 236, 117668.
S. Zhou, Y. Wei, B. Li and H. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2018, vol. 49, pp. 3086-96.
J. Oh and D. Noh: Fuel, 2017, vol. 196, pp. 144-53.
H. Zhang, X. Shi, Z. Bo and H. Xin: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2014, vol. 45, pp. 582-89.
J.H. Heo, B.S. Kim and J.H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2013, vol. 44, pp. 1352-63.
W.K. Jozwiak, E. Kaczmarek, T.P. Maniecki, W. Ignaczak and W. Maniukiewicz: Appl. Catal. A, 2007, vol. 326, pp. 17-27.
X. Huang: Principles of iron and steel metallurgy, 3rd ed., Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2002, pp. 418–19 (In Chinese)
H.J. Grabke: Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 2972-75.
R. Sridhar, J.M. Toguri and S. Simeonov: JOM, 1997, vol. 49, pp. 48-52.
P.K. Iwamasa and R.J. Fruehan: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp. 1319-27.
P. Coursol, N. CardonaValencia, P. Mackey, S. Bell and B. Davis: JOM, 2013, vol. 64, pp. 1305-13.
J.M. Toguri and N.H. Santander: Can. Metall. Q., 1969, vol. 8, pp. 167-71.
P.J. Mackey: Can. Metall. Q., 1982, vol. 21, pp. 221-60.
M. Nagamori: Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 531-38.
C. Liu: Physical chemistry of copper metallurgy, Science and technology of China press, Beijing, 1990, pp. 600-02 (In Chinese)
N. Eustathopoulos, M.G. Nicholas, and B. Drevet: Wettability at High Temperatures, Pergamon, Oxford, 1999.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51664039 and U1602272); China Scholarship Council (the International Clean Energy Talent Program, 2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted May 20, 2020; accepted September 22, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Zhang, T., Li, B. et al. Copper Smelting Slag Cleaning in an Electric Furnace by Using Waste Cooking Oil. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 2756–2768 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01986-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01986-7