Abstract
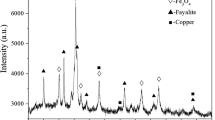
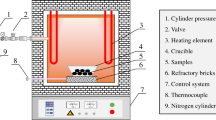
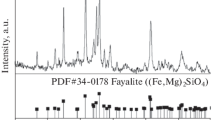
Through the reduction reaction of Fe3O4 and graphite rod, the viscosity of slag was reduced and the settlement of matte in slag was promoted. The reduction of Fe3O4 in copper slag by a graphite rod was studied and the kinetics of the reduction process analyzed. The results show that the content of Fe3O4 decreased with increase in reduction temperature and reduction time. The slag samples after reduction were examined and found to consist of three layers: a slag foam layer, a fayalite layer, and a matte layer. A substantial number of large-sized matte particles were found in the slag foam layer. Also, a layer of Fe3O4 was attached to the upper surface of the matte layer. The reduction of Fe3O4 was concluded to be a second-order reaction, the apparent activation energy was 610 kJ/mol, and the limiting step was the Boudouard reaction.
Graphical Abstract

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
[1] Z.H. Yang, Q. Lin, S.C. Lu, Y. He, G.D. Liao, and Y. Ke: Ceram Int, 2014, vol. 40, pp. 7297-305.
[2] J. Zhang, Y.H. Qi, D.L. Yan, X.L. Cheng, and P. He: J Iron Steel Res Int., 2015, vol. 2, pp. 121-27.
J Zhang, YH Qi, DL Yan, and HC Xu (2015) J Iron Steel Res Int., vol. 5, pp. 396-401.
[4] L. Miganei, E. Gock, M. Achimovicová, L. Koch, H. Zobel, and J. Kähler: J Clean Prod., 2017, vol. 164, pp. 534-42.
[5] Y. Shi, Y.G. Wei, S.W. Zhou, B. Li, Y.D. Yang, and H. Wang: J Alloy Compd., 2020, vol. 822, pp. 153478-84.
[6] S.W. Zhou, Y.G. Wei, B. Li, and H. Wang: Metall Mater Trans B., 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 3086-96.
[7] R.G. Reddy, V.L. Prabhu, and D. Mantha: High Temp Mat Pr-isr., 2003, vol. 22, pp. 25-33.
[8] S. Jahanshahi, and S. Wright: Metall Mater Trans B. 2017, vol. 48B, pp. 2057-66.
B Li, YG Wei, H Wang, YD Yang (2018) ISIJ Int. vol. 58, pp. 1168-74.
[10] S.W. Zhou, Y.G. Wei, Y. Shi, B. Li, and H. Wang: Metall Mater Trans B. 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 2458-68.
[11] J. Martinsson, B. Glaser, and S. Du: Metall Mater Trans B. 2016, vol. 47, pp. 1-4.
[12] A. Davydenko, A. Karasev, G. Lindstrand, and P. Jonsson: Steel Res Int., 2015, vol. 86, pp. 146-53.
[13] S.W. Li, J. Pan, D.Q. Zhu, Z.Q. Guo, J.W. Xu, and J.L. Chou: Powder Technol, 2019, vol. 347, pp. 159-69.
[14] E.D. Wilde, I. Bellemans, L. Zheng, M. Campforts, M. Guo, B. Blanpain, N. Moelans, and K. Verbeken: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2016, vol. 32, pp. 1911–24.
[15] G.R. Qu, Y.G. Wei, B. Li, H. Wang, Y.D. Yang, and A. McLean: J Alloy Compd., 2020, vol. 824, pp. 15910-18.
[16] C.B. Wu, J.B. Zhang, Q.J. Wu, and L. Yue: Journal of Chongqing University, 2015, vol. 38, pp. 11-16.
[17] S.N. Lekakh, and B. Hrebec: Int J Metalcast., 2016, vol. 10, pp. 1-12.
[18] D.Y. Kim, I.H. Jeong, and S.M. Jung: Ironmak Steelmak., 2015, vol. 43, pp. 526-32.
[19] X.L. Huang: Iron and Steel Metallurgy (Ironmaking Part), Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2000, pp. 413-38.
[20] Y.G. Guo, R. Zhu, Z.Z. Fei, M.S. Ma, Y. Wang, and J. Liu: China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2017, vol. 5, pp. 75-80.
[21] G. Wang, Q.G. Xue, Y.F. Shen, and J.S. Wang: Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016, vol. 5, pp. 623-29.
[22] Z. Z. Huang, X.G. Xiao, and Z.Q. Xiao: The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 1994, vol. 4, pp. 283-88.
[23] H. M. Long, J. X. Li, P. Wang and S. Q. Shi: Ironmak Steelmak, 2012, vol. 39, pp. 585-92.
[24] J.L. Zhang, Z.Y. Wang, X.D. Xing, Z.J. Liu and X.L. Liu: J Cent South Univ (Science and Technology), 2015, vol. 46, pp. 41-48.
[25] S.M. Jung, and S.H. Yi: Ironmak Steelmak, 2014, vol. 41, pp. 38-46.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this study was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U1602272, 51664039, and 51764035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted May 3, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Li, B., Wei, Y. et al. Reduction of Magnetite from Copper Smelting Slag in the Presence of a Graphite Rod. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 2663–2672 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01963-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01963-0