Abstract
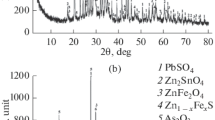
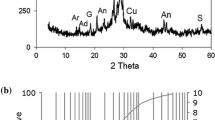
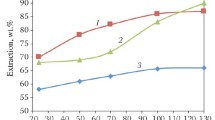
The smelting technology and flue dust treatment have an influence on the physical and chemical characteristics of flue dusts collected in copper smelting. We characterized flue dusts from a Bottom-Blowing Bath Smelting (BBS) process and from a Flash Smelting (FS) process by determining their comprehensive physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics. Annual flue dust generation data showed that the rate of the BBS process (2 to 3 pct) was clearly lower than that of FS process (5 to 6 pct). The results revealed that copper smelting flue dusts from the FS exhibited a larger entrainment of solids and a smaller particle size than the BBS. The crystallographic and chemical compositions of the samples indicated that the FS flue dusts have a higher degree of crystallinity than those of the BBS. Fe3O4, CuSO4 and PbSO4, Fe3O4, CuFe5O8 were the predominant crystalline phases in the FS and BBS flue dusts, respectively. In the FS and BBS flue dusts, amorphous multicomponent Cu-Zn-FeOx and Cu-Zn-S phases were formed, respectively. Mineralogical examinations and a stepwise chemical extraction confirmed that the majority of arsenic existed in amorphous form and mostly as pentavalent As5+ arsenate or As2O5 except that in BBS-ESPD.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlesinger M. E., King M. J., Sole K. C., & Davenport W. G. Extractive Metallurgy of Copper, Elsevier, Amsterdam 2011, p. 2.
Guo X., Wang Q., Liao L., Tian Q., & Zhang Y.: Nonferr. Metals Science Engineering, 2014, Vol. 5, pp. 28-34.
Guo X., Song Y., & Wang Y.: Res. Conserv. Recycling, 2008, Vol. 52, pp. 871-882.
Li M., Tong C., Huang J., & Wang J.: Chinese J. Process Engin., 2016, Vol. 16, pp. 1028-1037.
S. Zhou: Nonferr. Met., 2009, pp. 11–15, 20 (in Chinese).
Liu J., Gui W., Xie Y., & Yang C.: Appl. Mathem. Modell., 2014, Vol. 38, pp. 2206-2213.
Y. He: World Non-ferr. Met., 2018, pp. 7–10 (in Chinese).
Coursol P., Mackey P., Kapusta J., Kapusta, N., & Cardona V.: JOM, 2015, Vol. 67, pp. 1066-1074.
Liu L., Yan H., Zhou J., Gao Q., Zhang Z., Liu F., & Cui Z.: Chinese J. Nonferr. Metals, 2012, Vol. 22, pp. 2116-2124.
Yu Y., Wen Z., Liu X., Su F., Lan H., & Hao X.: Appl. Mechan. Mater., 2014, Vol. 602-605, pp. 546-553.
Sohn H., Fukunaka Y., Oishi T., Asaki Z., & Song H.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, Vol. 35, pp. 651-661.
Chen C., Zhang L., & Jahanshahi S.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, Vol. 41, pp. 1175-1185.
Wang Q., Guo X., Tian Q., & Jiang T.: Metals, 2017, Vol. 7, pp. 1-11.
Wang Q., Guo X., Tian Q., Chen M., & Zhao B.: Metals, 2017, Vol. 7, pp. 1-12.
Chen H., Mei Z., Xie K., Li X., Zhou J., Wang X., & Ge Z.: Trans. Nonferr. Metals Soc. China, 2004, Vol. 14, pp. 631-636.
Itagaki K., & Yazawa A.: Mater. Trans. JIM, 2007, Vol.23, pp. 759-767.
Mendoza D., Hino M., & Itagaki K.: Mater. Trans. B, 2001, Vol. 42, pp. 2427-2433.
Swinbourne D., & Kho T.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, Vol. 43, pp. 823-829.
Z. Chen: China Nonferr. Metall., 2009, pp. 16–22 (in Chinese).
R. Kaur, C. Nexship, M. Wilson, and D. George-Kennedy: in: Proc. Copper 2010. DGBM, Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany, 2010, pp. 2415–32.
Balladares E., Kelm U., Helle S., Parra R., & Araneda E.: Dyna, 2014, Vol. 81, pp. 11-18.
Montenegro V., Sano H., & Fujisawa T.: Mater. Trans., 2008, Vol. 49, pp. 2112-2118.
Montenegro V., Sano H., & Fujisawa T.: Miner. Engin., 2013, Vol. 49, pp. 184-189.
Samuelsson C., & Carlsson G.: CIM Bulletin, 2005, Vol. 94, pp. 111-115.
Jarošíková A., Ettler V., Mihaljevič M., Drahota P., Culka A., & Racek M.: J. Environm. Managem., 2018, Vol. 209, pp. 71-80.
Zhong D., Li L., & Tan C.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, Vol. 48, pp. 1308-1314.
Tae K.-H., Bok H.-K., Kye S.-P., & Debasish M.: Separ. Purif. Techn., 2015, Vol. 142, pp. 116-122.
Wu J., Chang F., Wang H., Tsai M., Ko C.-H., & Chen C.-C.: Environm. Technol., 2015, Vol. 36, pp. 2952-2958.
Csavina J., Taylor M., Omar F., Rine K., Sáez A., & Betterton E.: Sci. Total Environm., 2014, Vol. 493, pp. 750-756.
Morales A., Cruells M., Roca A., & Bergó R.: Hydrometallurgy, 2010, Vol. 105, pp. 148-154.
Z. Li and B. Xu: Metallurgy Technology of Copper, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2012, p. 7.
H. Ren: Non-ferrous Metal Bath Smelting, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2001, pp. 2–6.
Zhu Z., & He J.: Modern copper smelting, Science Press, Beijing, 2003, pp. 23-45.
J. Talja, S. Chen, H. Mansikkaviita, and C. Berg: in: Proc. Copper 2013, vol. III (Book 1), Santiago, Chile. Ch IMM, 2013, pp. 67–77.
FEI MLA software, Thermo Fischer Scientific, USA; accessed in October 2019 at: https://www.fei.com/materials-science/minerals-mining/.
Toby B. H.: J. Appl. Cryst., 2005, Vol. 38, pp. 1040-1041.
Redwan M., Rammlmair D., & Meima J.: Sci. Total Environ., 2012, Vol. 414, pp. 480.
Stathopoulos V., Papandreou A., Kanellopoulou D., & Stournaras C.: J. Haz. Mater., 2013, Vol. 262, pp. 91-99.
Samuelsson C., & Björkman B.: Thermodynamic studies. Scand. J. of Metall., 1998, Vol. 27, pp. 64-72.
Stefanova V., Shentov D., Mihailova I., & Iliev P.: Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Metals, 2012, Vol. 53, pp. 26-32.
CA Martinson, & Reddy K.: J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2009, Vol. 336, pp. 406-11.
Nasef M., Saidi H., Nor H., & Yarmo M.: J. Appl. Polymer Sci., 2000, Vol. 76, pp. 336-349.
H. Zhang: Chemical Phase Analysis of Ores and Industrial Products: Nonferrous Metals Industry Analysis Series, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 1992, pp. 50–53 (in Chinese).
Yang W., Tian S., Wu J., Chai L., & Liao Q.: JOM, 2017, Vol. 69, pp. 1077-1083.
Safarzadeh M., Miller J., & Huang H.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, Vol. 45, pp. 568-581.
Cheng R., Zhang H., & Ni H.: Processes, 2019, Vol. 7, pp. 754.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC0210405), the key project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (51634010), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51722407) and the “Double First Class” Funding Project of Central South University (31801-160170002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted December 13, 2019.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhao, Z., Taskinen, P. et al. Characterization of Copper Smelting Flue Dusts from a Bottom-Blowing Bath Smelting Furnace and a Flash Smelting Furnace. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 2596–2608 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01907-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01907-8