Abstract
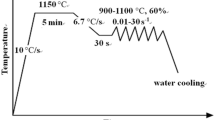
According to the calculation results of a 3D thermomechanical-coupled finite-element (FE) model of GCr15 bearing steel bloom during a heavy reduction (HR) process, the variation ranges in the strain rate and strain under HR were described. In addition, the hot deformation behavior of the GCr15 bearing steel was studied over the temperature range from 1023 K to 1573 K (750 °C to 1300 °C) with strain rates of 0.001, 0.01, and 0.1 s−1 in single-pass thermosimulation compression experiments. To ensure the accuracy of the constitutive model, the temperature range was divided into two temperature intervals according to the fully austenitic temperature of GCr15 steel [1173 K (900 °C)]. Two sets of material parameters for the constitutive model were derived based on the true stress–strain curves of the two temperature intervals. A flow stress constitutive model was established using a revised Arrhenius-type constitutive equation, which considers the relationships among the material parameters and true strain. This equation describes dynamic softening during hot compression processes. Considering the effect of glide and climb on the deformation mechanism, the Arrhenius-type constitutive equation was modified by a physically based approach. This model is the most accurate over the temperatures ranging from 1173 K to 1573 K (900 °C to 1300 °C) under HR deformation conditions (ignoring the range from 1273 K to 1573 K (1000 °C to 1300 °C) with a strain rate of 0.1 s−1). To ensure the convergence of the FE calculation, an approximated method was used to estimate the flow stress at temperatures greater than 1573 K (1300 °C).















Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. M. Sellars, W. J. Mc Tegart: Acta Metall., 1966, vol. 14, pp. 1136-38.
L. Anand: ASME J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 1982, vol. 104, pp. 12-17.
S. B. Brown, K. H. Kim,L. Anand: Int. J. Plasticity, 1989, vol. 5, pp. 95-130.
G.R. Johnson and W.H. Cook: Proc. 7th Int. Symp., Ballistics. 1983, pp. 541–47.
F. J. Zerilli, R. W. Armstrong: J. Appl. Phys., 1987, vol. 61, pp. 1816-25.
D.S. Fields and W.A. Bachofen: ASTM. In Proc. Am. Soc. Test Mater., 1957, vol. 57, pp. 1259–72.
H. Mirzadeh: Mech Mater, 2015, Vol. 85, pp. 66-79.
R. Baktash, H. Mirzadeh: J. Eng. Mater. Technol, 2016, vol. 138, 021004.
T. Mirzaie, H. Mirzadeh, J. M. Cabrera: Mech Mater, 2016, Vol. 94, pp. 38-45.
P. F. Kozlowski, B. G. Thomas, J. A. Azzi, H. Wang: Metall. Trans. A, 1992. Vol. 23, pp. 903-918.
P. J. Wray: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13, pp. 125-34.
T. Suzuki, K. H. Tacke, K. Wunnenberg, K. Schwerdtfeger: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1988, vol. 15, pp. 90-100.
H. N. Han, Y Lee, K H Oh, D. N. Lee: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, vol. 206, pp. 81-89.
F. Garofalo: Trans. Metall. Sot. AIME, 1963, vol. 227, pp. 351-56.
M. Uehara, I. V. Samarasekera, J. K. Brimacombe: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1986, vol. 13, pp. 138-53.
D. J. Seol, Y. M. Won, T. Yeo, K. H. Oh, J. K. Park, C. H. Yim: ISIJ Int., 1999, vol. 39, pp. 91-98.
Y. M. Won, T. Yeo, D. J. Seol, K. H. Oh: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31B, pp. 779-94.
J. K. Park, B. G. Thomas, I. V. Samarasekera: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2002, vol. 29, pp. 359-75.
J. Fu, J. Li, H. Zhang: Acta Metall. Sin., 2010, vol. 46, pp. 91-96.
S. Koric B. G. Thomas: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, vol. 197, pp. 408-18.
Z. Cai, M. Zhu: Acta Metall. Sin., 2011, vol. 47, pp. 671-77.
C. Ji, C. Wu, M. Zhu: JOM, 2016, vol. 68, pp. 3107-15.
F. Yin, L. Hua, H. Mao, X. Han: Mater. Des., 2013, vol. 43, pp. 393-401.
M. Militzer, E. B. Hawbolt, and T. R. Meadowcroft: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31, pp. 1247-59.
H. Yu, X. Liu, X. Li, A. Godbole: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 1001-1009.
X. Shen, S. Tang, J. Chen, Z. Liu and G. Wang: ISIJ International, 2015, vol. 55, pp. 2657-2660.
M. E. Mehtedi, F. Gabrielli, S. Spigarelli: Mater. Des., 2014, vol. 53, pp. 398-404.
C. Yue, L. Zhang, S. Liao, H. Gao: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2009, vol. 45, pp. 462-66.
M. Buchholz, V. Uhlenwinkel, A. Freyberg, K. Bauckhage: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. 326, pp. 165-75.
H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 57, pp. 268-435.
C. M. Sellars, W M. Tegart: Int. Metall. Rev., 1972, vol. 17, pp. 1-24.
Z. J. Pu, K. H. Wu, J. Shi, D. Zou: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1995, vol. 192/193, pp. 780-87.
D. Samantaray, S. Mandal, A. K. Bhaduri: Mater. Des. 2010, vol. 31, pp. 981-84.
S. Mandal, V. Rakesh, P. V. Sivaprasad, S. Venugopal, K. V. Kasiviswanathan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 500, pp. 114-21.
C. Zener, J. H. Hollomon: J. Appl. Phys., 1944, vol. 15, pp. 22-32.
K. Duraisamy, J. D. Baeder: SIAM J. Sci.Comput., 2007, vol. 29, pp. 2607-20.
S. B. Hosseini, T. Beno, U. Klement, J. Kaminski, K. Ryttbergc: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2014, vol. 214, pp. 1293–1300.
X. Xiao, G. Q. Liu, B. F. Hua, X. Zheng, L. N. Wang, S. J. Chen, A. Ullah: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 62, pp. 227-34.
G. Ji, F. Li, Q. Li, H. Li, Z. Li: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 4774-82.
H. Mirzadeh, J. M. Cabrera, A. Najafizadeh, Acta Mater, 2011, vol. 59 pp. 6441–48.
J. M. Cabrera, J. J. Jonas, J. M. Prado. Mater Sci Technol, 1996, vol. 12, pp. 579-85.
H. J. Frost, M. F. Ashby. Deformation-mechanism maps: the plasticity and creep of metals and ceramics. Oxford: Pergamon Press; 1982.
Deformation-mechanism maps: the plasticity and creep of metals and ceramics. http://engineering.dartmouth.edu/defmech.
Acknowledgments
The current study is financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFB0300105); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51474058, U1560208 and U1708259); the Program for Liaoning Excellent Talents in University (LJQ2015036) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (N150205002). Special thanks are due to our cooperating company for help during industrial trials and application.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 27, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, C., Wang, Z., Wu, C. et al. Constitutive Modeling of the Flow Stress of GCr15 Continuous Casting Bloom in the Heavy Reduction Process. Metall Mater Trans B 49, 767–782 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1188-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1188-9