Abstract
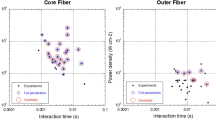
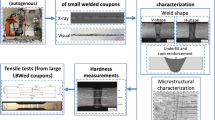
The weldability of 1.2 mm thick Haynes 188 alloy sheets by a disk Yb:YAG laser welding was examined. Butt joints were made, and the influence of parameters such as power, size, and shape of the spot, welding speed, and gas flow has been investigated. Based on an iconographic correlation approach, optimum process parameters were determined. Depending on the distribution of the power density (circular or annular), acceptable welds were obtained. Powers greater than 1700 W, welding speeds higher than 3.8 m mm−1, and spot sizes between 160 and 320 μm were needed in the circular (small fiber) configuration. By comparison, the annular (large fiber) configuration required a power as high as 2500 W, and a welding speed less than 3.8 m min−1. The mechanical properties of the welds depended on their shape and microstructure, which in turn depended on the welding conditions. The content of carbides, the proportion of areas consisting of cellular and dendritic substructures, and the size of these substructures were used to explain the welded joint mechanical properties.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.W. Duley, Laser welding, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998.
W.M. Steen and J. Mazumder: Laser Material Processing, Springer Verlag, London, 2010, pp. 199-249.
X. Gao, L. Zhang, J. Liu and J. Zhang: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, vol. 559, pp. 14-21.
A.J. Kemp, G.J. Valentine and D. Burns: Prog. Quantum Electron., 2004, vol. 28, pp. 305-344.
N.P. Barnes: IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2007, vol. 13-3, pp. 435-447.
A. Geisen and J. Speiser: IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2007, vol. 13-3, pp. 598-609.
S. Ruppik, F. Becker, F. Grundmann, W. Rath, and U. Hefter: Proc. SPIE8235 Solid State Lasers XXI—Technology and Devices, 2012, vol. 8235, pp. 1–15.
T. Scheller, A. Bastick, and M. Griebel: Proc. SPIE 8239, High Power Laser Materials Processing: Lasers, Beam Delivery, Diagnostics, and Applications, 82390B, San Francisco, 2012, vol. 8239, pp. 1–10.
O.A. Idowu, O.A. Ojo, and M.C. Chaturvedi: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, vol. 454–455, pp. 389–97.
M. Pang, G. Yu, H.-H. Wang and C.-Y. Zheng: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, vol. 207, pp. 271–275.
R.G. Thompson, J.J. Cassimus, D.E. Mayo and J.R. Dobbs: Weld. J., 1985, vol. 64, no. 4, pp. S91-S96.
J.J. Pepe, and W.F. Savage: Weld. J. Res. Suppl., 1967, vol. 46(9), pp. 411–422.
M. Zhong, H. Sun, W. Liu, and X. Zhuand: J. He: Scr. Mater., 2005, vol. 53 (2), pp. 159–164.
A. Odabası, N. Ünlü, G. Göller, E. Kayalı and M. Eruslu: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, vol.559, pp. 731-741.
B.S. Yilbas, and S. Akthar: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2011, vol. 56(1), pp. 115–124.
F. Caiazzo, V. Alfieri, V. Sergi, A. Schipani and S. Cinque: Int J Adv Manuf Technol., 2013, vol. 68(5), pp. 1809-1820.
Y. Makino, K. Honda and S. Kimura: Welding international, 1999, vol. 13, pp. 612-620.
J. Graneix, J.-D. Beguin, F. Pardheillan, J. Alexis and T. Masri: MATEC Web of Conferences, 2014, vol. 14, 13006, pp. 1-6.
M. Lesty: La revue de Modulad, 1999, vol. 22, pp. 41-77.
S. Postma. Weld Pool Control in Nd:YAG Laser Welding, thesis, Enschede, the Netherlands. Printed by Océ, 2003.
J. Brooks. Weld solidification and microstructural development trends in welding research. Proceeding of the 4th International Conference, 2003. pp. 123–133, Gatlinburg, Tennessee.
A.F. Giamei, E.H. Kraft, and F.D. Lemkey. New trends in Materials Processing: papers presented at a seminar of the American Society for Metals, October 19 and 20, 1974, Metal Parks, Ohio, 1976.
A.-M. El-Batahgy: Mater. Lett., 1997, vol. 32, pp. 155-163.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to EXAMECA for their financial support, in particular for providing the Haynes 188 alloy. They furthermore thank Cédric Bellot, Director of ACRDM, for giving them access to the synchrotron facilities at ESRF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 13, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graneix, J., Beguin, JD., Alexis, J. et al. Influence of Yb:YAG Laser Beam Parameters on Haynes 188 Weld Fusion Zone Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 2007–2016 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-0989-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-0989-6