Abstract
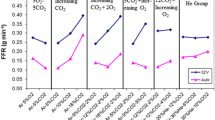
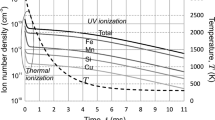
In this study, a semi-empirical model of fume formation rate (FFR) from a shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) process has been developed. The model was developed for a DC electrode positive (DCEP) operation and involves the calculations of droplet temperature, surface area of the droplet, and partial vapor pressures of the constituents of the droplet to predict the FFR. The model was further extended for predicting FFR from nano-coated electrodes. The model estimates the FFR for Fe and Mn assuming constant proportion of other elements in the electrode. Fe FFR was overestimated, while Mn FFR was underestimated. The contribution of spatters and other mechanism in the arc responsible for fume formation were neglected. A good positive correlation was obtained between the predicted and experimental FFR values which highlighted the usefulness of the model.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A d :
-
Drop surface area (m2)
- A w :
-
Wire cross-sectional area (m2)
- (C p) e :
-
Specific heat capacity of the electrode (J/kg/K)
- (C p) i :
-
Specific heat capacity of the ith component of the flux (J/kg/K)
- e :
-
Charge of an electron (C)
- E i :
-
Evaporation rate per unit area for ith element (kg/s/m2)
- G :
-
Universal gas constant (J/mol/K)
- H fe :
-
Latent heat of fusion of the electrode (J/kg)
- (H f) i :
-
Latent heat of fusion of the ith component of flux
- (M f) i :
-
Mass fraction of the ith component of flux
- H L :
-
Heat content at the tip of the core welding wire (J/m3)
- I :
-
Current intensity (A)
- j w :
-
Wire current density (A/m2)
- k :
-
Boltzman’s constant (J/mol/K)
- L e :
-
Electrode length under consideration (m)
- M i :
-
Molecular weight of ith element (kg/mol)
- ρ d :
-
Drop density (kg/m3)
- ρ w :
-
Wire density (kg/m3)
- P i :
-
Pure vapor pressure of ith element (N/m2)
- R d :
-
Droplet radius (m)
- t :
-
Time taken for the formation of a droplet (s)
- T a :
-
Ambient temperature (K)
- T d :
-
Droplet temperature (K)
- T p :
-
Plasma (arc) temperature (K)
- f r :
-
Electrode feed rate (m/s)
- f :
-
Flow rate of the fume chamber extraction unit (l/min)
- v d :
-
Droplet volume (m3)
- V a :
-
Anode potential (V)
- V c :
-
Condensation potential of electrons (V)
- V wf :
-
Droplet material work function potential (V)
- x i :
-
Mass fraction of ith element in the electrode
- X i :
-
Mole fraction of ith element in the electrode
References
1. R. Komanduri and Z.B. Hou: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31B, pp. 1353-70.
2. W.H. Kim, H.G. Fan, and S.J. Na: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28, pp. 679-86.
3. G. Wang, P.G. Huang, and Y.M. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35, pp. 857-66.
4. G. Fan and R. Kovacevic: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30, pp. 791-801.
5. P.J. Hewitt and A.A. Hirst: Ann. Occup. Hyg., 1991, vol. 35, pp. 223–32.
6. R.T. Deam, S.W. Simpson, and J. Haidar: Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2000, vol. 33, pp. 1393-1402.
7. J.H. Dennis, P.J. Hewitt, C.A.J. Redding, and A.D. Workman: Ann. Occup. Hyg., 2001, vol. 45, pp. 105–113.
C.A.J. Redding: Weld. Res., 2002, pp. 95–103.
9. T. Shinichi and T. Manabu: Trans. JWRI, 2011, vol. 40, pp. 21-27.
10. W. Chan, K.L. Gunter and J.W. Sutherland: Trans. NAMRI/SME., 2002, vol. 30, pp. 581–588.
11. S. Mohan, S.P. Sivapirakasam, M.C. Santhosh Kumar, and M. Surianarayanan: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, vol. 219, pp. 237–47.
12. S.P. Sivapirakasam, M. Sreejith, M.C. Santhosh Kumar, and M. Surianarayanan: J. Cleaner Prod., 2015, vol. 108, pp. 131-44.
13. E. Gmelin and S. M. Sarge: Thermochim. Acta; 2000, vol. 347, pp. 9-13.
14. R. G. Reddy, T. Wang, and D. Mantha: Thermochim. Acta; 2012, vol. 531, pp. 6-11.
15. R. I. Olivares and W. Edwards: Thermochim. Acta; 2013, vol. 560, pp. 34-42.
16. S. M. Sarge, W. Hemminger, E. Gmelin, G. W. H. Hohne, H. K. Cammenga, and W. Eysel: J Therm. Anal.; 1997, Vol. 49, pp.1125-1134.
17. J. Chun, D.A. Pierce, R. Pokorny, and P. Hrma: Thermochim. Acta, 2013, vol. 559, pp.32–39.
18. S. Omrana, P. Heggsa, and Y. Ding: Energy Procedia, 2014, vol. 46, pp. 317-323.
19. H.S. Kim, S.I. Hong, and S.J. Kim: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2001, vol. 112, pp.109–113.
E. Halmøy: Proceedings of International Conference, The Welding Institute, Abington, 1979, pp. 49–57.
21. T.P. Quinn, R.B. Madigan, and T.A. Siewert: Weld. J., 1994, vol. 73, pp. 241–247.
22. J.C. Metcalfe and M.B.C. Quigley: Weld. J., 1975, vol. 54, pp. 99–103.
23. T. Zacharia, S.A. David, and J.M. Vitek: Metall. Trans. B, 1991, vol. 22, pp. 233–241.
24. J. Haidar and J.J. Lowke: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 1996, vol. 29, pp. 2951–60.
M. Sreejith, S.P. Sivapirakasam, M.C. Santhosh Kumar, and M. Surianarayanan: Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L, 2016, vol. 230, pp. 574–85.
26. S.Y. Chung, W.P. Nam, and H.M. Jeong: Ann. Occup. Hyg., 2003, vol. 47, pp. 671-680.
27. X. He, T. Deb Roy, and P. W. Fuerschbach: J. Appl. Phys., 2004, vol. 96, pp. 4547-4555
28. S.P. Sivapirakasam, M. Jose, and M. Surianarayanan: Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2012, vol. 36, pp. 1493–1503.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Director, National Institute of Technology (NIT), Tiruchirappalli for his continual encouragement and support to this work. The authors profusely thank Technical Education Quality Improvement Programme (TEQIP), NIT Trichy for its support to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 4, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivapirakasam, S.P., Mohan, S., Santhosh Kumar, M.C. et al. Modeling of Fume Formation from Shielded Metal Arc Welding Process. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 1268–1278 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0904-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0904-6