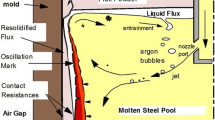
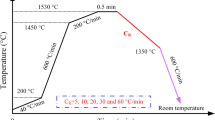
Abstract
The in situ crystallization behavior of highly volatile commercial mold fluxes for medium carbon steels was investigated using the confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) equipped with an optimized isolated observation system. The highly volatile compounds of the mold flux were suppressed during heating allowing direct observation in the CLSM. Cooling rates of 25, 50, 100, 400, and 800 K/min were incorporated and continuous cooling transformation (CCT) diagrams of 4 different commercial mold fluxes for medium carbon steels were developed. Identification of the crystalline phase was conducted with XRD and SEM–EDS analysis. A cuspidine crystalline was observed in all samples at various cooling rates. With higher basicity, CaF2, and NaF, the crystallization of the fluxes was enhanced according to the CCT diagram. As the slag structure becomes depolymerized, the diffusion rate of the cathodic ions seems to increase.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. C. Mills and A. B. Fox: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 1479-86.
W. Wang, K. Gu, L. Zhou, F. Ma, I. Sohn, D. J. Min, H. Matsuura, and F. Tsukihashi: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 1838-45.
H. G. Ryu, Z.T. Zhang, J.W.Cho, G.H. Wen, and S. Sridhar: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 1142-50.
H. Nakada, M. Suza, Y. Seko, M. Hayashi and K. Nagata: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 446-53.
M. Susa, R. Endo and Y. Kobayashi: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, pp. 1722-29.
J. W. Cho, T. Emi, H. Shibata and M. Suzuki: ISIJ Int., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 268-75.
K. Tsutsumi, T. Nagasaka and M. Hino: ISIJ Int., 1999, vol. 39, pp. 1150-59.
E.-Y. Ko, C. Joo, J.-Y. Park, I. Sohn: Met. Mater. Int., 2014, vol. 20, pp. 141-51.
J. W. Cho, K. Blazek, M. Frazee, H. Yin, J. H. Park, and S.-W. Moon: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 62-70.
H. Nakada and K. Nagata: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, pp. 441-49.
S. Likitvanichkul, W.C. Lacourse: J. Mater. Sci., 1995, vol. 30, pp. 6151-55.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, D. Huang, J. Wei, and J. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 925-36.
Y. Kashiwaya, C. E. Cicutti, A. W. Cramb and K. Ishii: ISIJ Int., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 348-56.
S.S. Jung, and I. Sohn: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2013, vol. 96, pp. 1309-16.
A. Semykina, J. Nakano, S. Sridhar, V. Shatokha, and S. Seetharaman: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42B, pp. 471-76.
S. S. Jung, and I. Sohn: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 1530-39.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, F. Ma, J. Li, J. Wei, H. Matsuura, and F. Tsukihashi: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 354-62.
M. Hanao: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 648-54.
B. Lu, W. Wang, J. Li, H. Zhao and D. Huang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 365-77.
T. Watanabe, H. Hashimoto, M. Hayashi and K. Nagata: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 925-33.
J. Wei, W. Wang, L. Zhou, D. Haung, H, Zhao, and F. Ma: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45B, pp. 643–52.
H. Kim and I. Sohn: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 1-8.
H. S. Park, H. Kim, and I. Sohn: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42B, pp. 324-30.
M. Hanao, M. Kawamoto, and T. Wantabe: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 44, pp. 827–35.
Y. Lu, G. Zhang, X. Yu: Adv. Mater. Res., 2013, vol. 455–456, pp. 134-38.
This study has been supported by BK21 plus (Brain Korea 21 plus) Project in the Division of the Humantronics Information Materials. This work was also partially supported by POSCO Project No. 2013-11-0032.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 31, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JY., Ryu, J.W. & Sohn, I. In-situ Crystallization of Highly Volatile Commercial Mold Flux Using an Isolated Observation System in the Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope. Metall Mater Trans B 45, 1186–1191 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-014-0087-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-014-0087-y