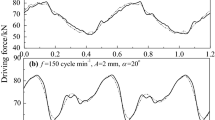
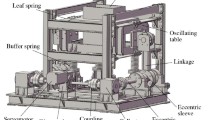
Abstract
The interaction of the strand shell surface and mold copper plates has significant effects on the slab surface quality and casting productivity. This article focuses on developing a reliable approach to measure the transient friction force between the slab and the mold for the purpose of the investigation of lubrication and friction behavior inside a mold. This method is presented to monitor transient mold frictions for the slab continuous caster equipped with hydraulic oscillators. A mathematical model is also developed to calculate the empty working force of the no casting state, and a new algorithm, based on the particle swarm optimization, is proposed to predict the dynamic characteristic parameters of mold oscillation. The results have shown that the method has a sufficient sensitivity to variation, especially to the periodical variation of the mold friction, and it has been identified that the transient mold friction can be used as an effective index with regard to detecting mold oscillation and optimizing the casting parameters for process control. It may lay the practical foundation for the online detection of powder lubrication and the visualization of the continuous-casting mold process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.H. Emling: Ironmaker Steelmaker, 1994, vol. 21, no. 7, pp. 47-8.
B.G. Thomas, M.S. Jenkins, and R.B. Mahapatra: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2004, vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 485-94.
M. Suzuki, H. Mizukami, T. Kitagawa, K. Kawakami, S. Uchida, and Y. Komatsu: ISIJ Int., 1991, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 254-61.
S. Chandra, I.V. Samarasekera, J.K. Brimacombe, I.A. Bakshi, and B.N. Walker: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1996, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 512-21.
M. Yao and D.C. Fang: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1996, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 522-7.
J.L. Brendzy, I.A. Bakshi, I.V. Samarasekera, and J.K. Brimacombe: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1993, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 63-74.
I.A. Bakshi, J.L. Brendzy, and N. Walker: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1993, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 54-62.
G.T. Alvarez, J. Ciriza, and J.J. Laraudogoitia: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2003, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 353-9.
P.P. Sahoo and S. Basu: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 219-25.
P. Valentin, C. Bruch, and A.C. Horn: Steel Res. Int., 2004, vol. 75, no. 10, pp. 666-71.
X.D. Wang, M. Yao, and X.F. Chen: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, no. 7, pp. 1047-53.
J. Watzinger, A. Pesek, N. Huebner, M. Pillwax, and O. Lang: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2005, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 208-12.
J. Kennedy and R. Eberhart: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, IEEE Service Center, Piscataway, NJ, 1995, pp. 1942–45.
K.H. Lee, S.W. Baek, and K.W. Kim: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2008, vol. 51, nos. 11,12, pp. 2772–83.
H. Qi, H.M. Ruan, H.C. Zhang, Y.M. Wang, and H.P. Tan: Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2007, vol. 46, no. 7, pp. 649-61.
X.Y. Zang, X.D. Wang, Y. Ma, M. Yao, and L. Zhang: Steel Res. Int., 2008, vol. 79, no. 7, pp. 564-8.
Y. Ma, X.D. Wang, X.Y. Zang, M. Yao, L. Zhang, and S.H. Ye: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2008, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 164-8.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51004012). This project was granted financial support from China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2012M520621/2013T60511). Also, the support of the High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2009AA04Z134) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 27, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, Z. & Yao, M. Online Measurement for Transient Mold Friction Based on the Hydraulic Oscillators of Continuous-Casting Mold. Metall Mater Trans B 44, 1499–1508 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9919-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9919-4