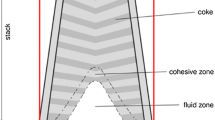
Abstract
A hydromechanics experiment on the countercurrent flow of gas and liquid simulating the flow conditions in the lower blast furnace was carried out. A cold model of a packed bed with various packing materials and liquids was used to study the holdup of liquid. Correlations for static holdup, dynamic holdup, and total holdup were obtained. A good agreement was found between the calculated and experimental data. A mathematical model simulating the flow fields was applied to study the effect of liquid holdup in blast furnace. The results of the model calculation show that static holdup is the determinant of the total holdup of molten materials when the blast furnace works in stable condition. The slag phase generally reaches flooding holdup ahead of the hot metal. The radial distribution of gas flow is almost not influenced by the holdup of molten materials, but it has a greater influence on the pressure drop. The size of coke has far greater influence on static holdup than liquid properties does. The study is useful for acquiring a deeper understanding of the complex phenomena in the blast furnace and for determining appropriate operational actions under different production conditions.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- d :
-
diameter (m)
- F r :
-
Froude number
- g:
-
acceleration of gravity (9.81 m s−2)
- h d :
-
dynamic holdup (pct)
- h s :
-
static holdup (pct)
- h t :
-
total holdup (pct)
- u :
-
superficial velocity (m s−1)
- ρ :
-
density (kg m−3)
- μ :
-
viscosity (Pa s)
- σ :
-
surface tension (N m−1)
- a :
-
specific surface area (m−1)
- ε :
-
porosity
- φ :
-
shape factor
- F:
-
flooding point
- g:
-
gas
- l:
-
liquid
- p:
-
packing
- S:
-
loading point
- w:
-
water
References
A.K. Biswas: Principles of Blast Furnace Ironmaking: Theory and Practice, Cootha Publishing House, Brisbane, Australia, 1981.
Y. Omori: Blast Furnace Phenomena and Modeling, Elsevier Applied Science, London, UK, 1987.
J. Yagi: ISIJ Int., 1993, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 619–39.
P.R. Austin, H. Nogami, and J. Yagi: ISIJ Int., 1997, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 458–67.
G.X. Wang, S.J. Chew, A.B. Yu, and P. Zulli: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28B, no. 2, pp. 333–43.
S. Pintowantoro, H. Nogami, and J. Yagi: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 304–09.
B.H. Xu, A.B. Yu, S.J. Chew, and P. Zulli: Powder Technol., 2000, vol. 109, no. 3, pp. 13–26.
H. Nogami, H. Yamaoka, and K. Takatani: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol, 44, no. 12, pp. 2150–58.
M.S. Chu, H. Nogami, and J. Yagi: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 510–17.
J.A. Castro, A.J. Silva, Y. Sasakl, and J.Yagi: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 748–58.
X.F. Dong, A.B. Yu, J. Yagi, and P. Zulli: ISIJ Int., 2007, vol. 47, 11, pp. 1553–70.
P.R. Austin, H. Nogami, and J. Yagi: ISIJ Int., 1998, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 246–55.
S.J. Chew, P. Zulli, and A.B. Yu: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 1112–21.
G.S. Gupta, J.D. Litster, V.R. Rudolph, E.T. White, and A. Domanti: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 32–39.
S.J. Chew, G.X. Wang, A.B. Yu, and P. Zulli: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1997, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 392–400.
H. Kawabata, Z.G. Liu, F. Fujita, and T. Usui: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, no. 10, pp. 1466–73.
D.Y. Liu, S. Wijeratne, and J.D. Litster: Scand. J. Metall., 1997, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 79–84.
M. Li, Y. Bando, R. Tanigawara, T. Tsuge, K. Yasuda, and M. Nakamura: J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 2001, vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 948–55.
Y. Bando, S. Hayashi, A. Matsubara, and M. Nakamura: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, no. 10, pp. 1461–65.
W.M. Husslage, M.A. Reuter, R.H. Heerema, T. Bakker, and A.G.S. Steeghs: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2005, vol. 36B, pp. 765–76.
T. Fukutake and V. Rajakumar: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1980, vol. 66, no. 13, pp. 1937–46.
M. Amatatsu: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1984, vol. 70, no. 12, p. S773.
Y. Sassa: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1987, vol. 73, no. 12, p. S842.
T. Sugiyama, T. Nakagawa, H. Sibaike, and Y. Oda: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1987, vol. 73, no. 15, pp. 2044–51.
Y. Eto, K. Takeda, S. Miyagawa, S. Taguchi, and H. Itaya: ISIJ Int., 1993, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 681–86.
T. Usui, K. Masamori, H. Kawabata, and Z. Morita: ISIJ Int., 1993, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 687–96.
M. Niu, T. Akiyama, R. Takahashi, and J. Yagi: AIChE J., 1996, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 1181–86.
W.M. Husslage, A.G.S. Steeghs, and R.H. Heerema: 60th Ironmaking Conf. Proc., 2001, pp. 323–35.
Y. Niwa, T. Sumigama, A. Maki, S. Nagano, A. Sakai, and M. Sakurai: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1990, vol. 76, no. 3, pp. 337–44.
R.H. Perry: Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook., McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, NY, 1997.
J.F. Davidson: Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng., 1959, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 131–36.
D.M. Mohunta and G.S. Laddha: Chem. Eng. Sci., 1965, vol. 20, no. 12, pp. 1069–72.
J.E. Buchanan: Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam., 1967, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 400–07.
R. Billet and M. Schultes: IChemE. Symp. Ser., 1992, vol. 128, pp. B129–36.
R. Billet: Packed Column Analysis and Design, Ruhr University Press, Bochum, Germany, 1989.
X.G. Bi, J. Qiu, W. Wang, Y. Bi, S. Lu, J. Cheng, Y. Xia, and X. Gu: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2001, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 27–32.
M. Ichida: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1987, vol. 73, no. 12, p. S748.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge financial support from Grant 50901054 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 25, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, W., Bi, XG., Wang, GQ. et al. Calculation and Analysis of Liquid Holdup in Lower Blast Furnace by Model Experiments. Metall Mater Trans B 43, 562–570 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-011-9628-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-011-9628-9